1) A PivotTable is a tool in Excel that allows users to analyze and summarize data by automatically calculating comparisons in the data.
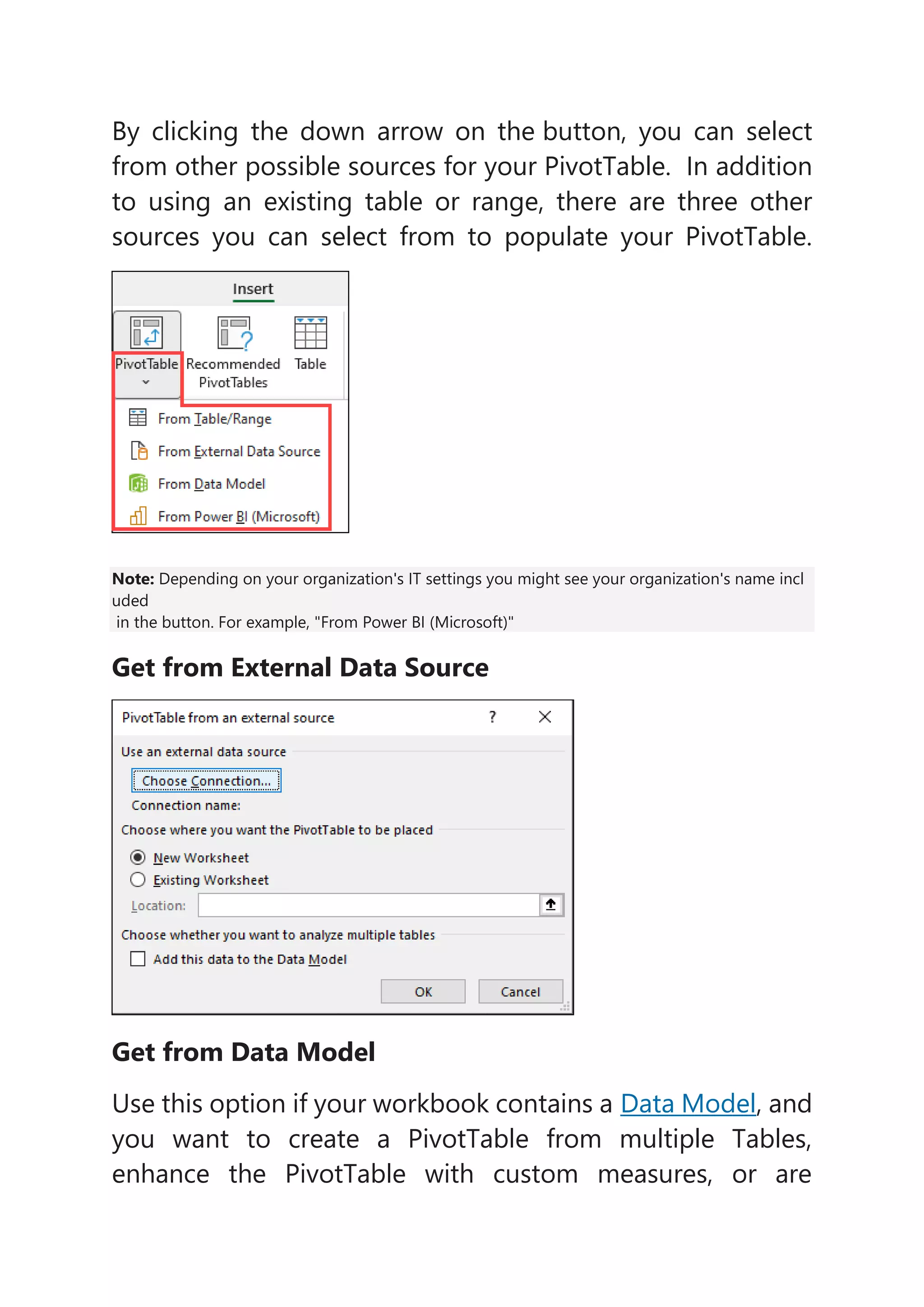
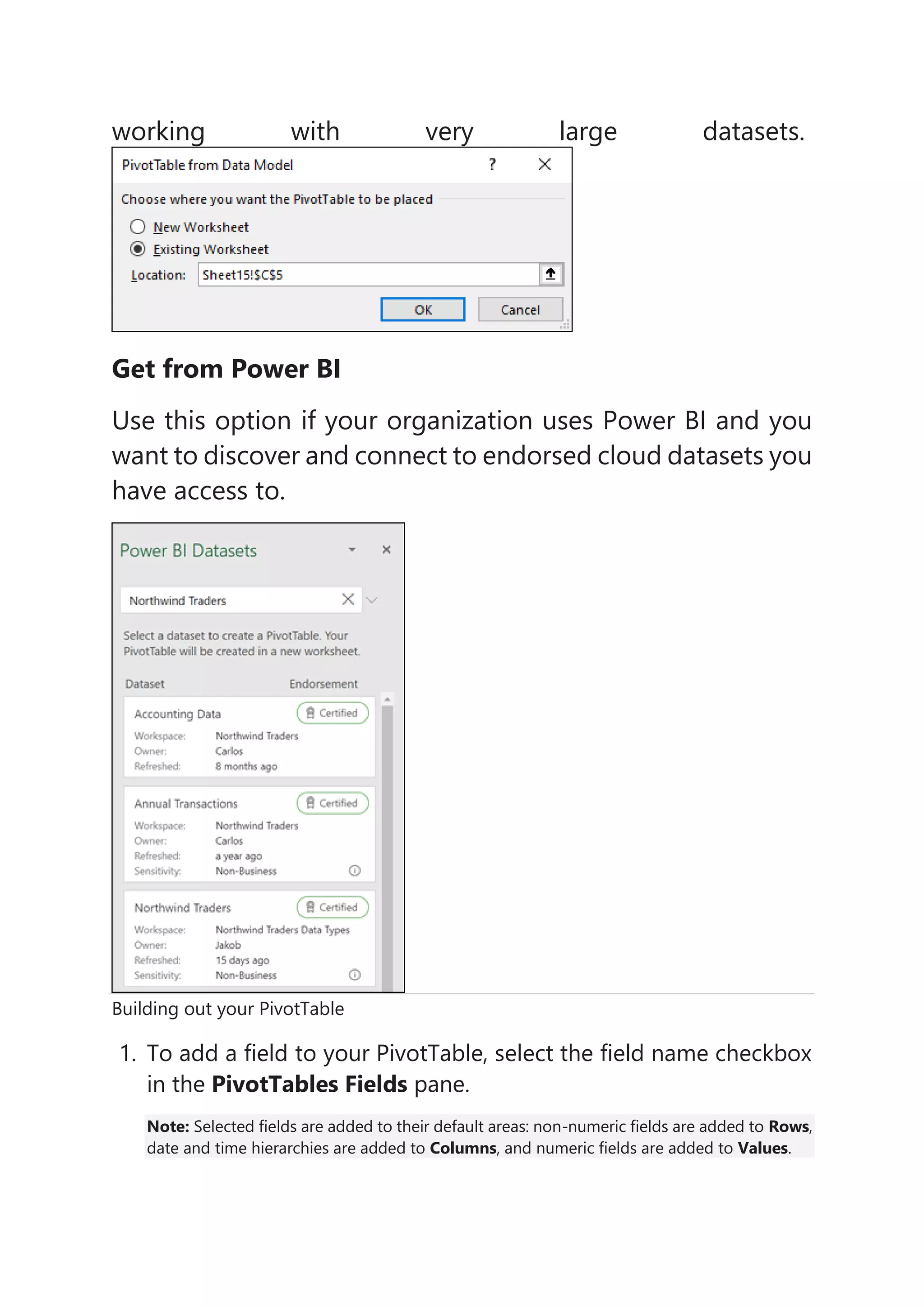
2) PivotTables can retrieve data from an existing table or range, an external data source, a data model, or Power BI depending on the options selected by the user.
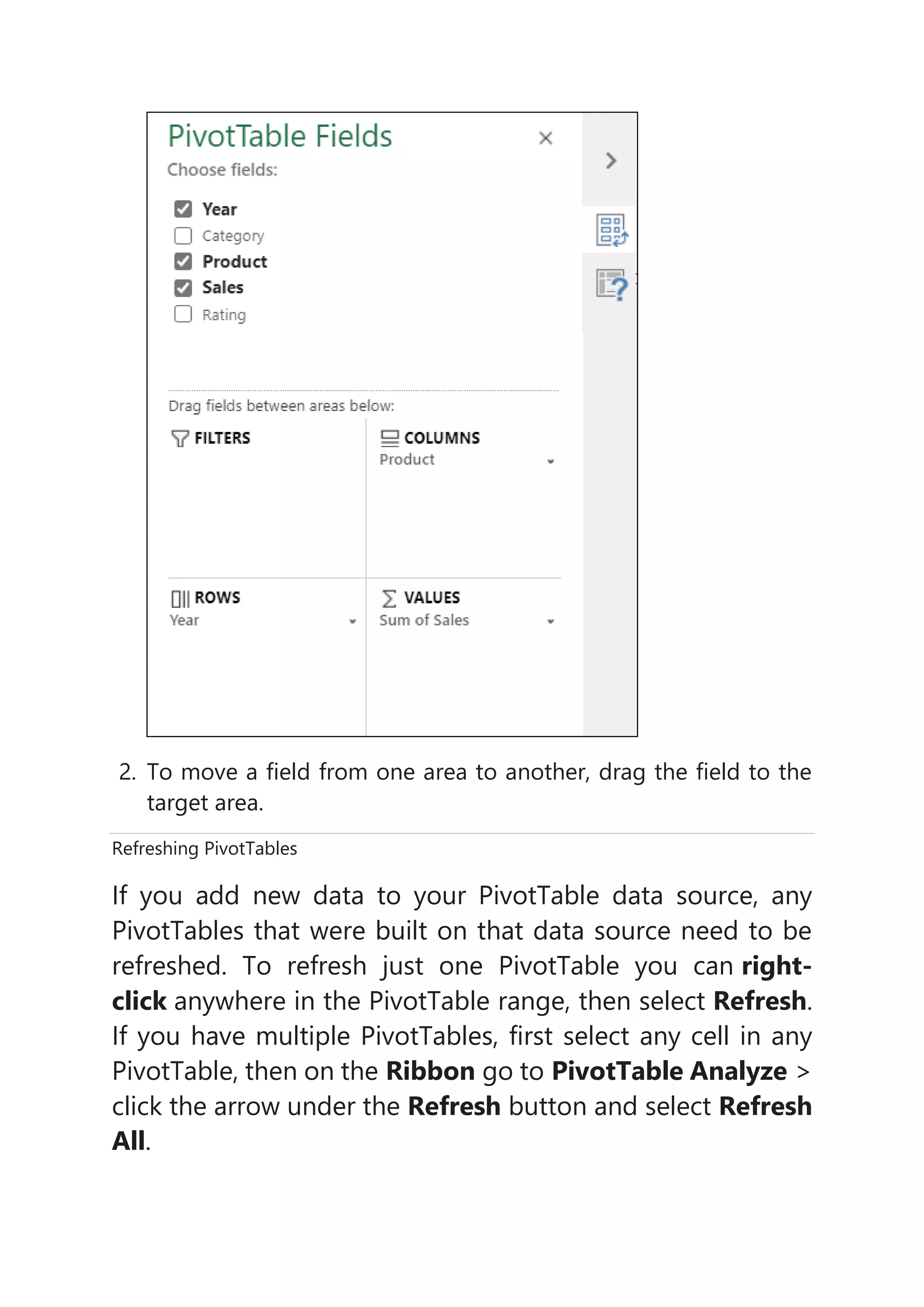
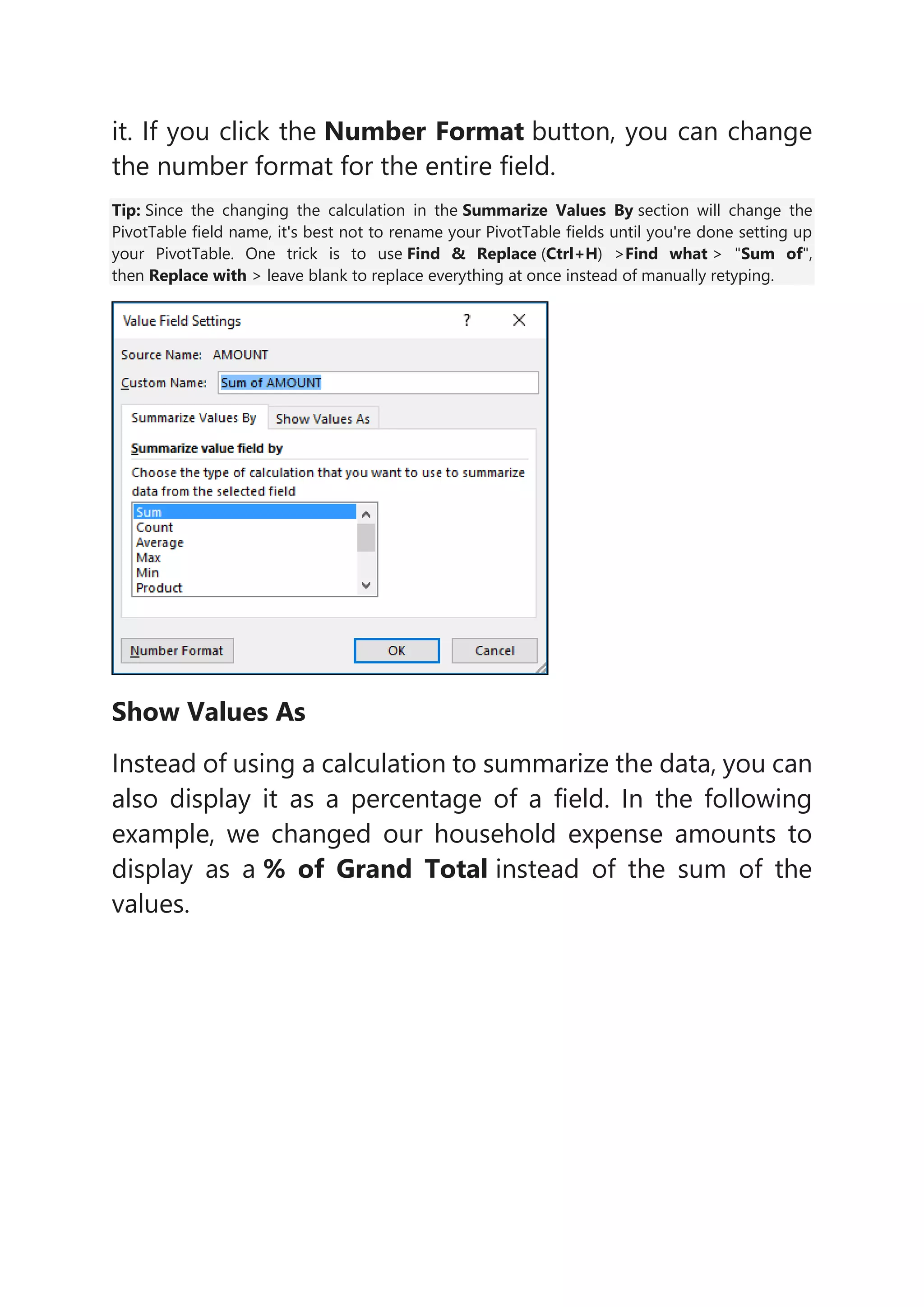
3) Users can build out a PivotTable by adding fields to the rows, columns, and values areas and then refresh the PivotTable if the underlying data is updated.