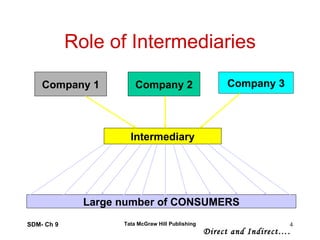
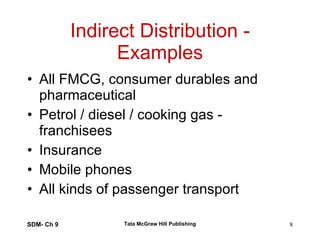
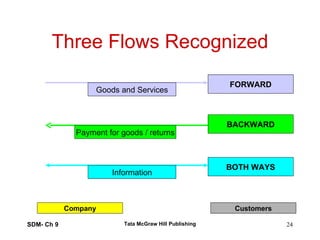
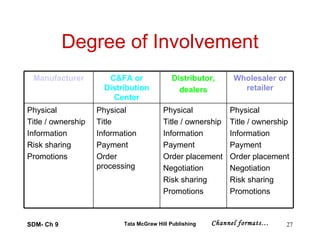
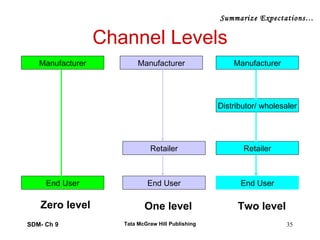
The document discusses marketing channels and distribution systems. It describes the key functions of marketing channels as gathering information, motivating consumers, managing risk, and providing after-sales support. Channel systems can be direct from company to consumer, or indirect using intermediaries. They help address discrepancies in space, time, quantity, product assortment, and financing. Channel structures include vertical, horizontal and multi-channel systems. The document outlines different channel formats, levels, and flows of physical goods, ownership, information, payments, and promotions through the channel.