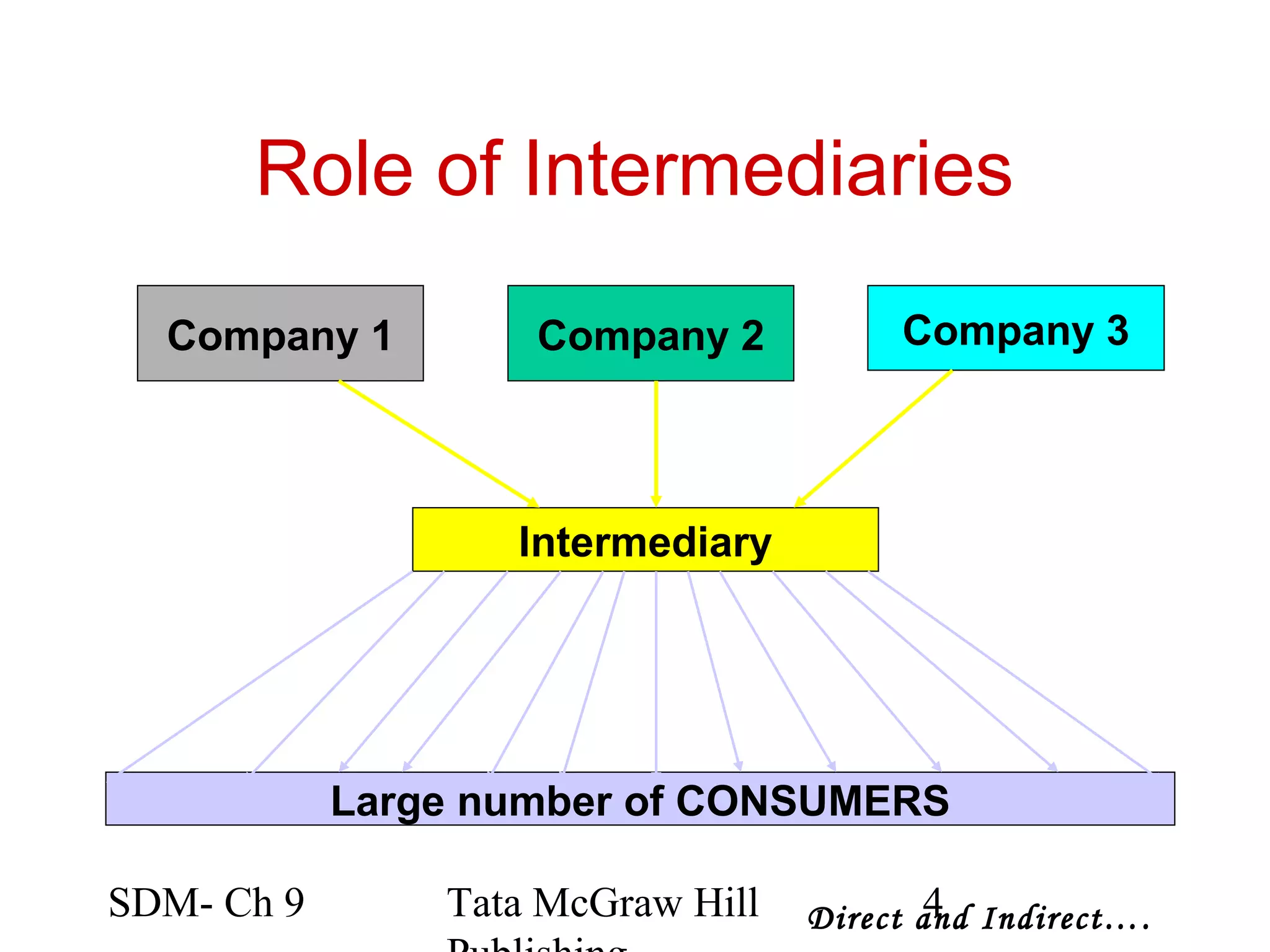
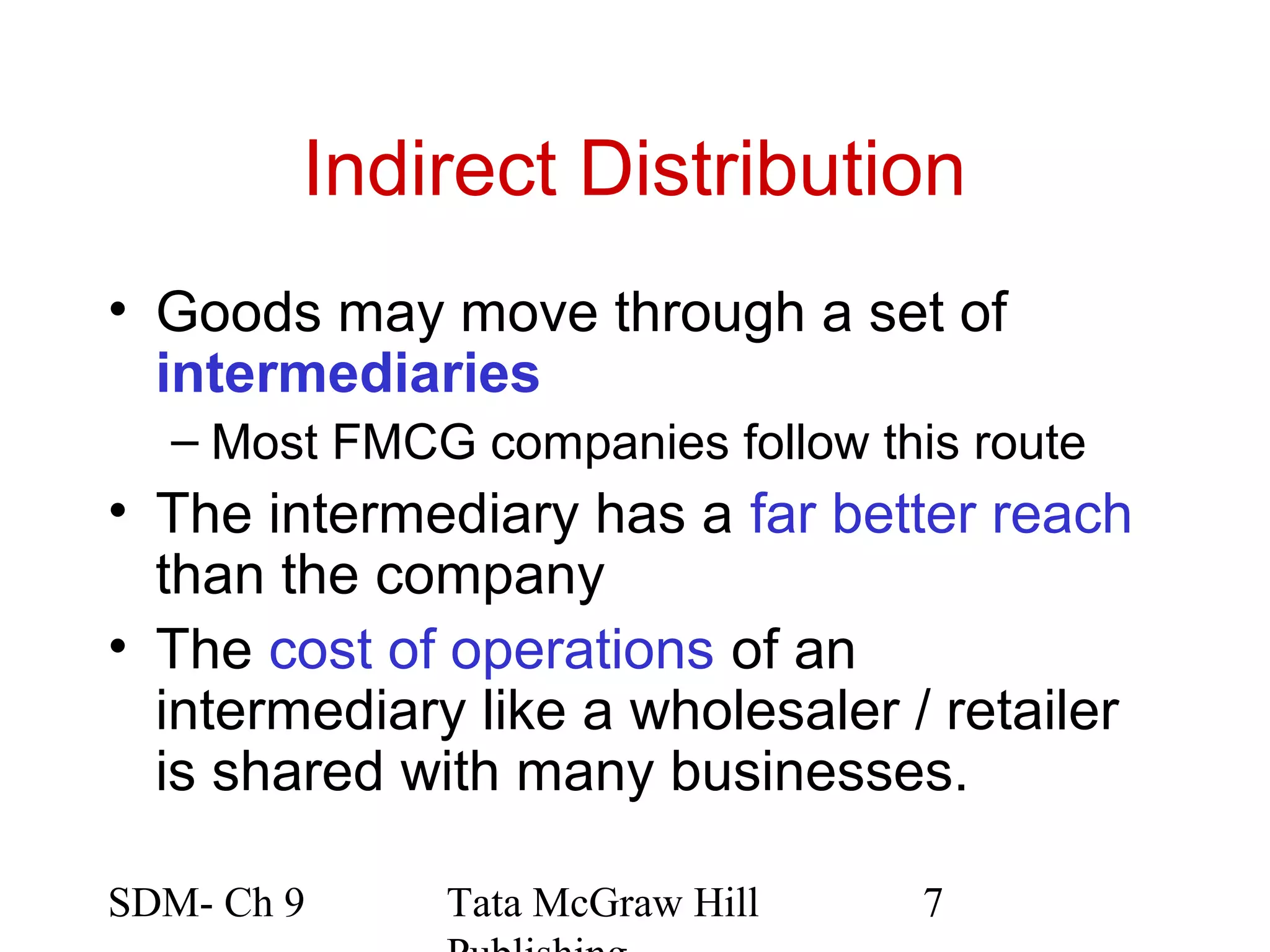
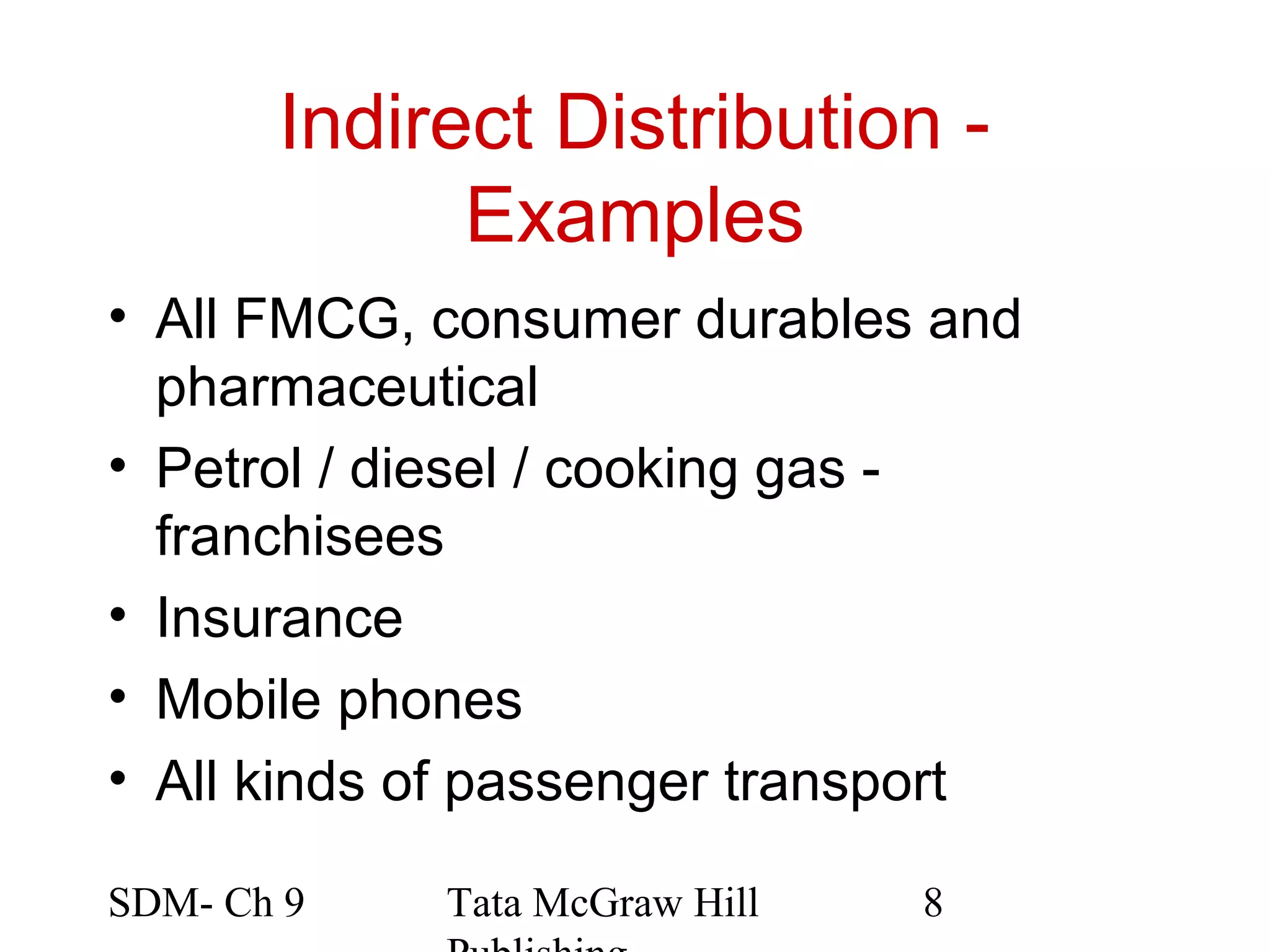
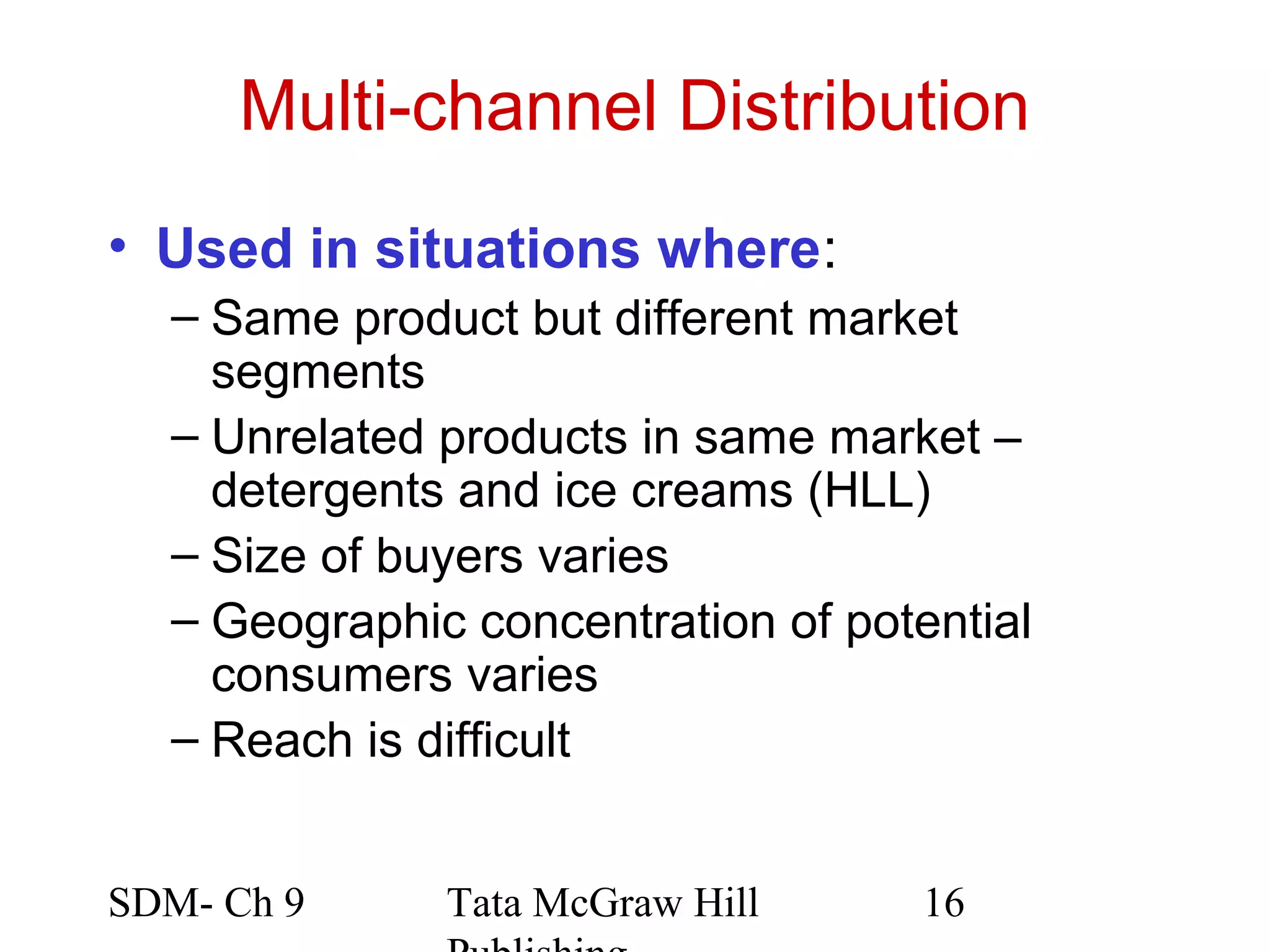
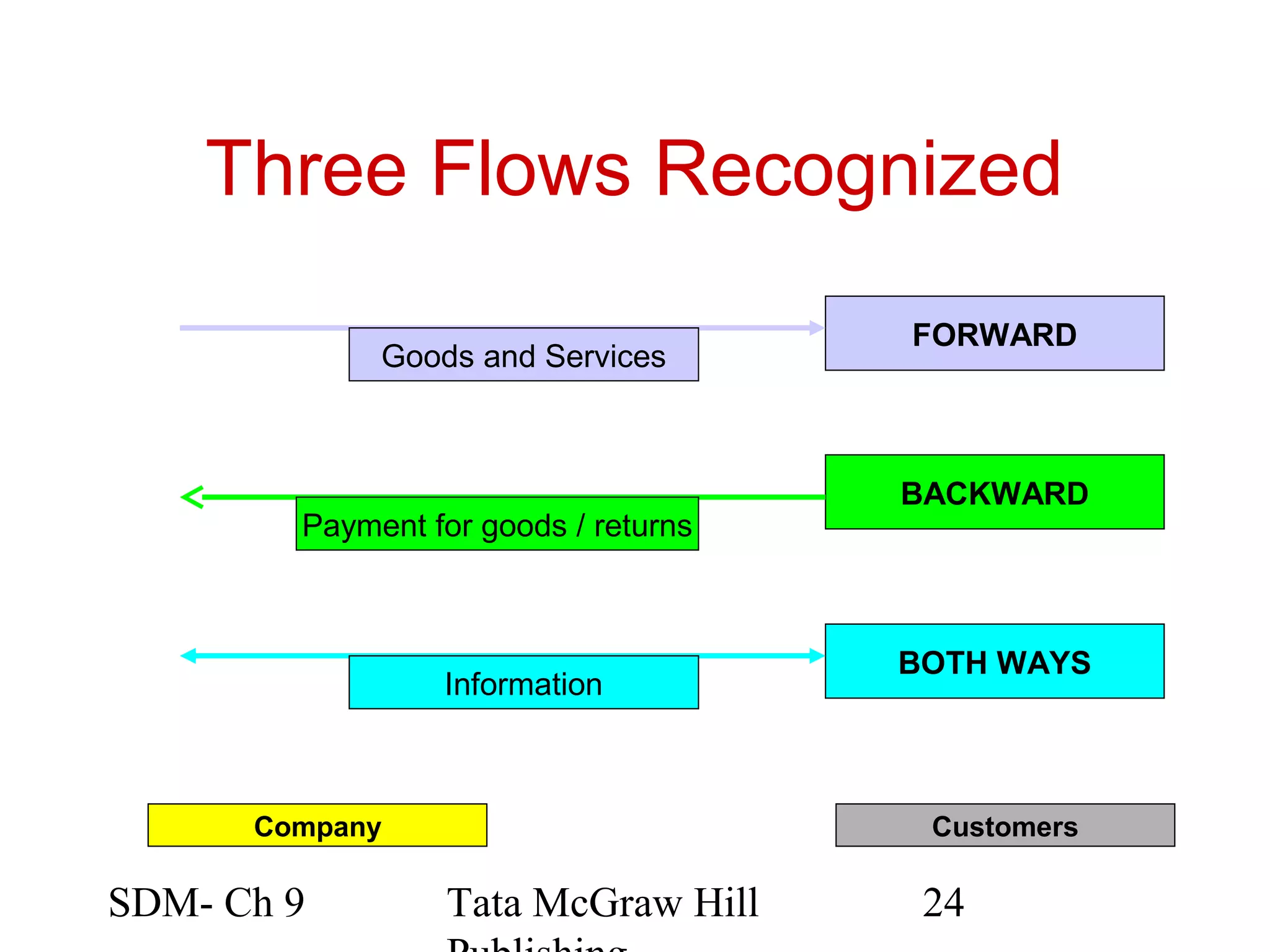
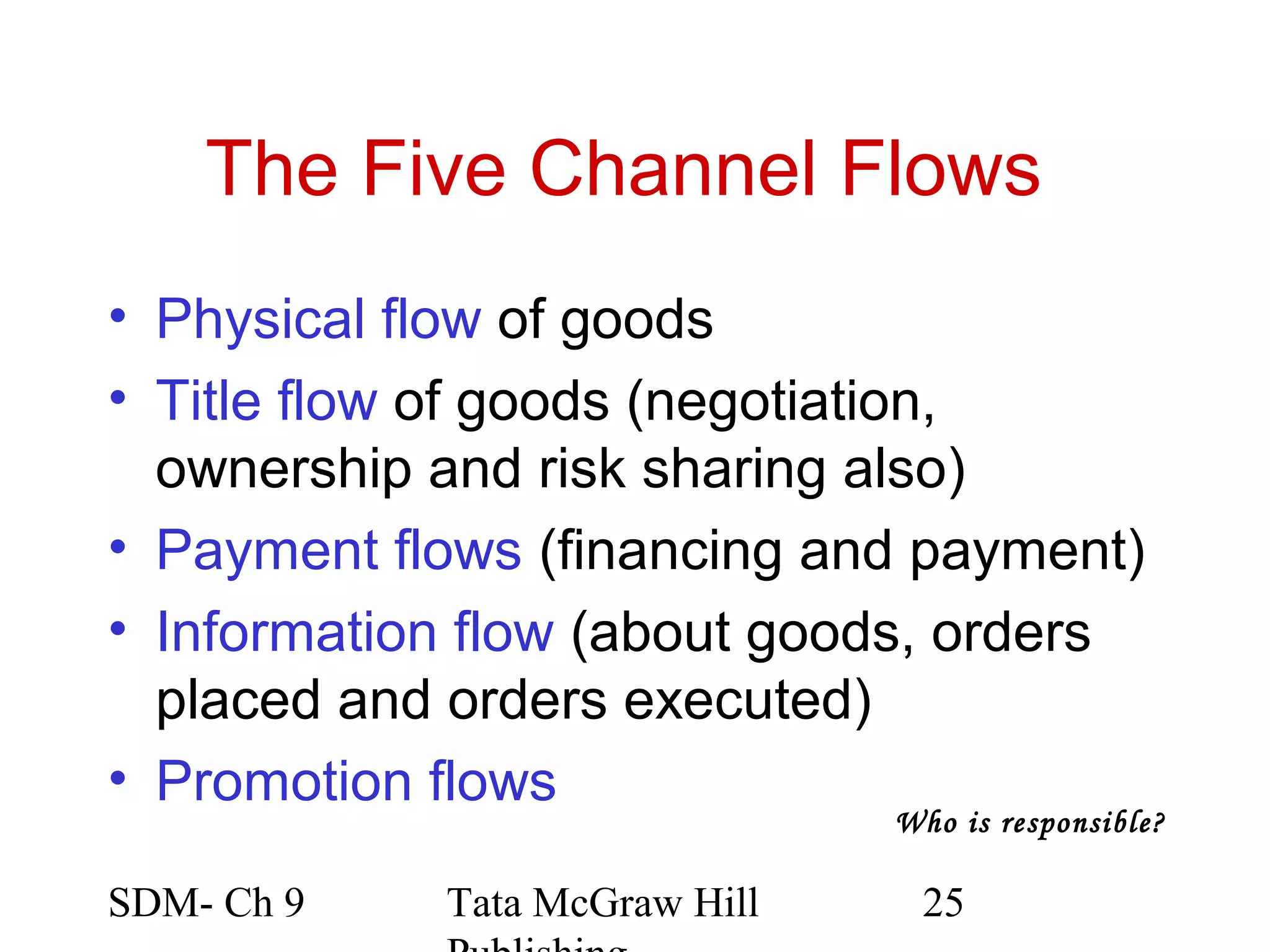
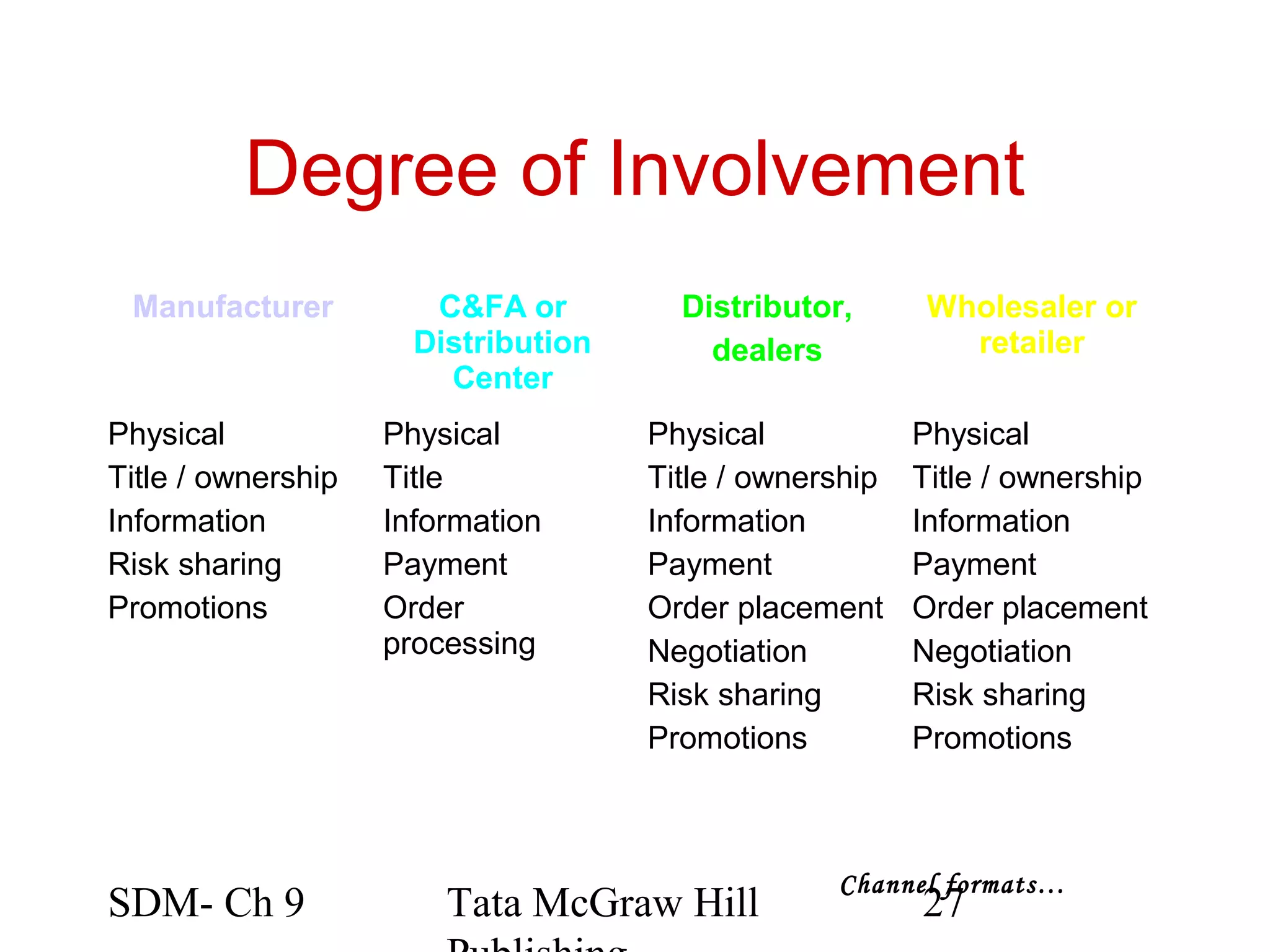
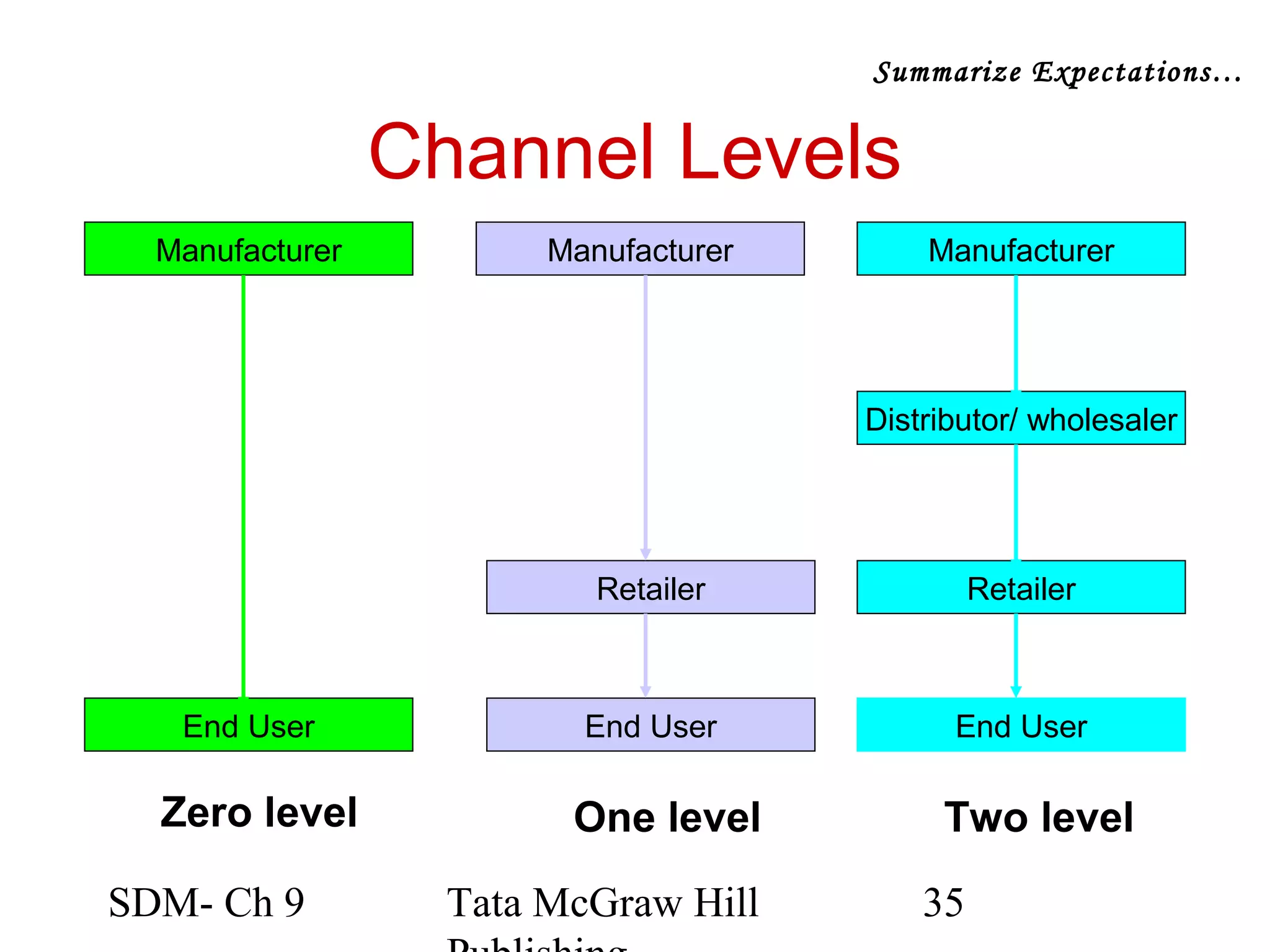
The document discusses marketing channels and channel systems. It covers key topics such as channel functions, formats, flows, levels and structures. Channel systems help address issues like spatial and temporal discrepancies. They break bulk, provide assortment and financial support. Channel flows include physical, title, payment and information flows. Common channel formats are producer, seller and service driven systems. Channel levels range from zero to multiple intermediaries. Expectations from channel systems are to efficiently deliver products and services while addressing customer needs.