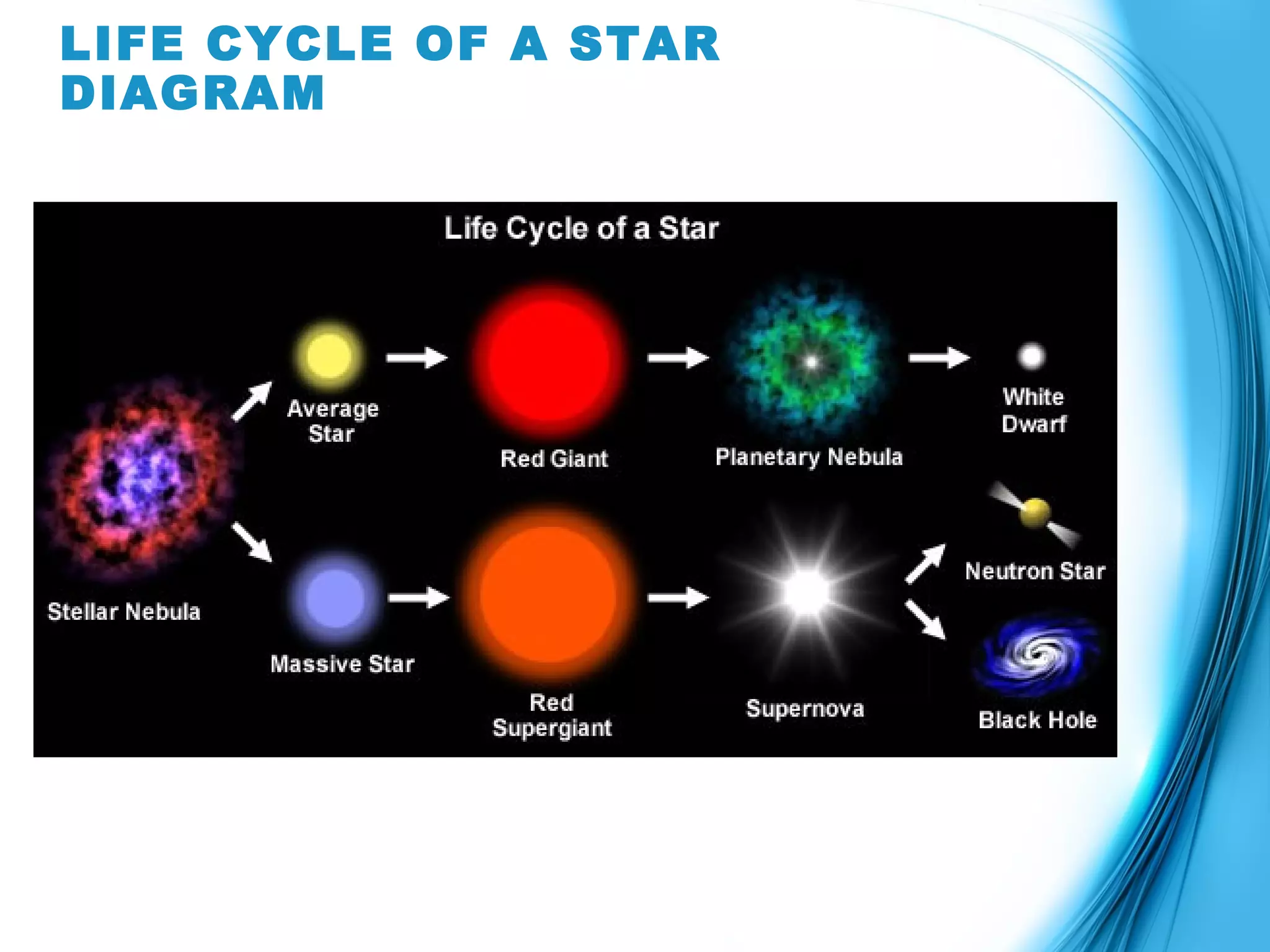
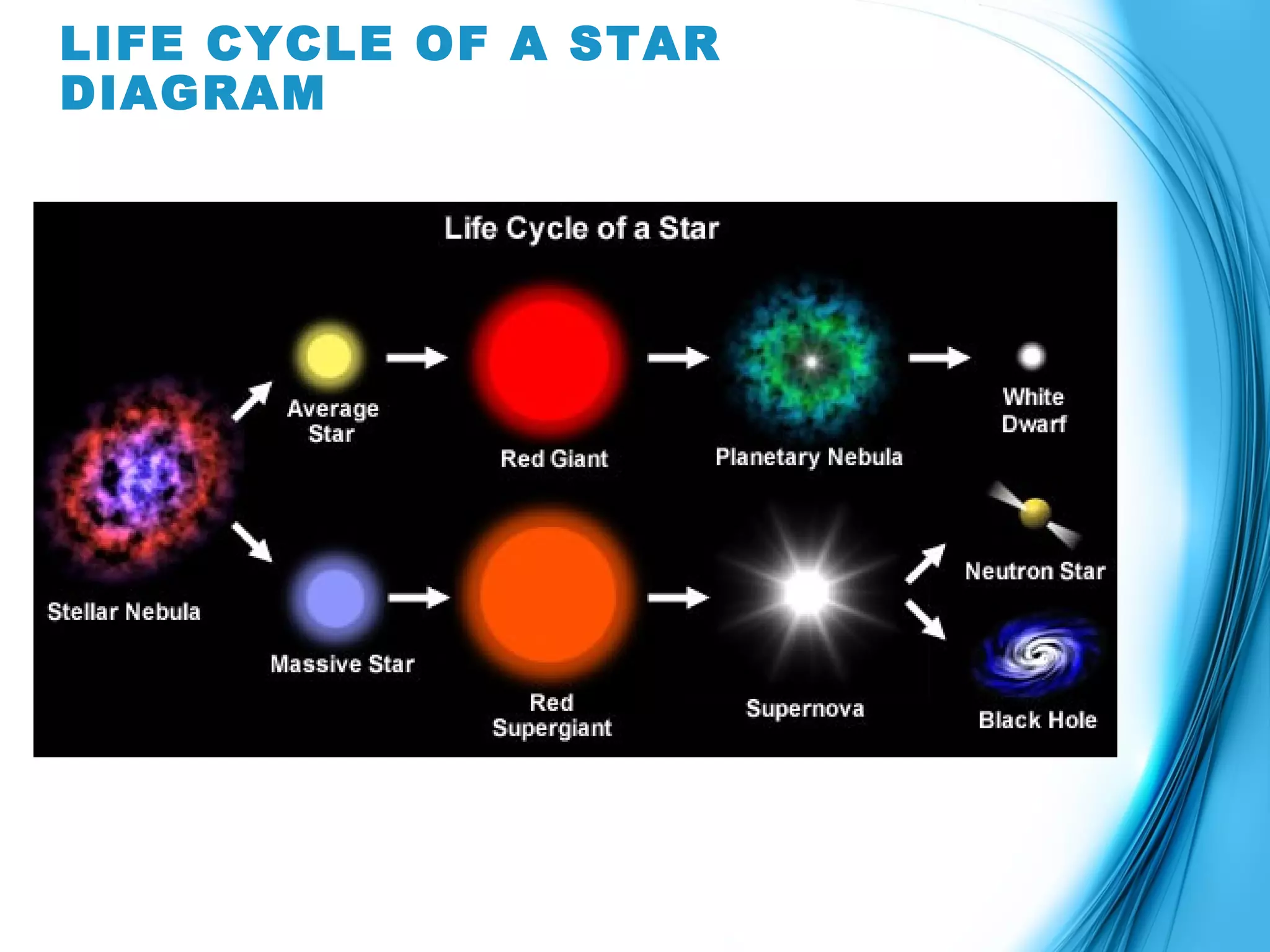
Stars are born from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Over billions of years, stars progress through various stages as they age. Lower mass stars begin as protostars and become main sequence stars fueled by nuclear fusion. As their hydrogen runs out, they become red giants and eventually white dwarfs. Higher mass stars explode as supernovae at the end of their lives, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.