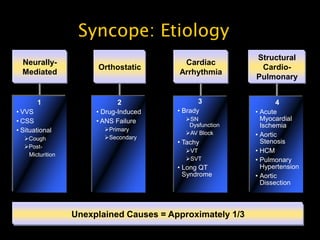
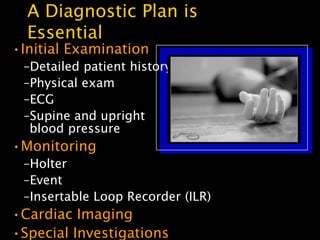
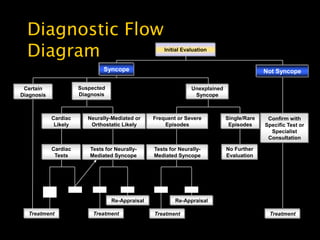
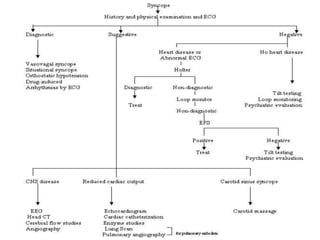
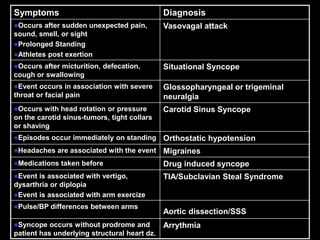
This document discusses the evaluation of syncope in adults. Syncope is defined as a brief, self-limited loss of consciousness due to decreased blood flow to the brain. The causes of syncope can be categorized as neurally-mediated, orthostatic, cardiac, or structural/cardiopulmonary. A thorough history, physical exam, and diagnostic testing are needed to determine the underlying cause and guide treatment. The history provides clues to distinguish syncope from other conditions and identify risk factors, while the physical exam focuses on vital signs and signs of end-organ damage or dysfunction.