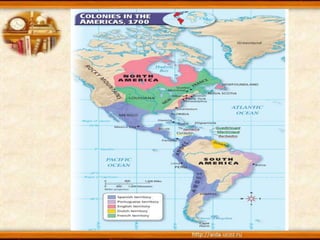
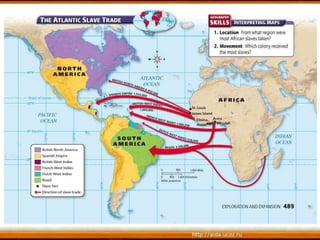
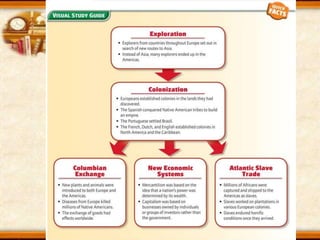
The document discusses the exploration and expansion of Western Europe during the 1400s and 1500s. Driven by desires for wealth, glory, and spreading religion, European explorers embarked on voyages of discovery aided by advances in shipbuilding and navigation technologies. This led to the establishment of European colonies in lands like North America, as well as the violent conquest of indigenous peoples. It resulted in the Columbian Exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between Europe and the Americas. The creation of colonies also established new patterns of trade and the economic system of mercantilism. Between the 1500s-1800s, millions of Africans were captured and sold into slavery, establishing the brutal Atlantic slave trade.