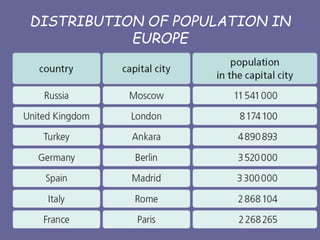
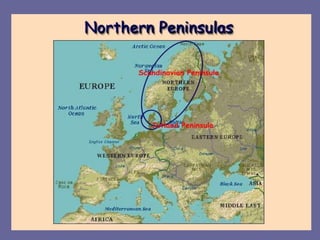
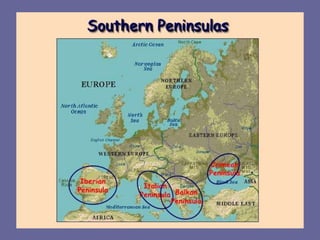
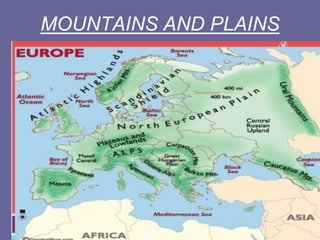
Europe has diverse geography due to its location between Asia and Africa. It contains many peninsulas and mountain ranges that divide the continent. The Alps and Pyrenees form natural borders, while rivers like the Danube flow through multiple countries. Europe's climate varies significantly from polar in the north to Mediterranean in the south. Overall, Europe's unique geography and location have shaped its development over the past 200 million years.