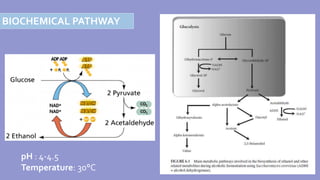
The document provides an overview of ethanol fermentation, highlighting its significance as a biofuel and alcoholic beverage, with 80% of fuel-grade production in the US derived from fermentation using various feedstocks like sugarcane and corn. It details the fermentation process, including microbial involvement, conditioning, and the biochemical pathways for converting sugars into ethanol. Additionally, it discusses both batch and continuous fermentation methods, the importance of overcoming inhibitory effects, and advancements in metabolic engineering to enhance fermentation efficiency.