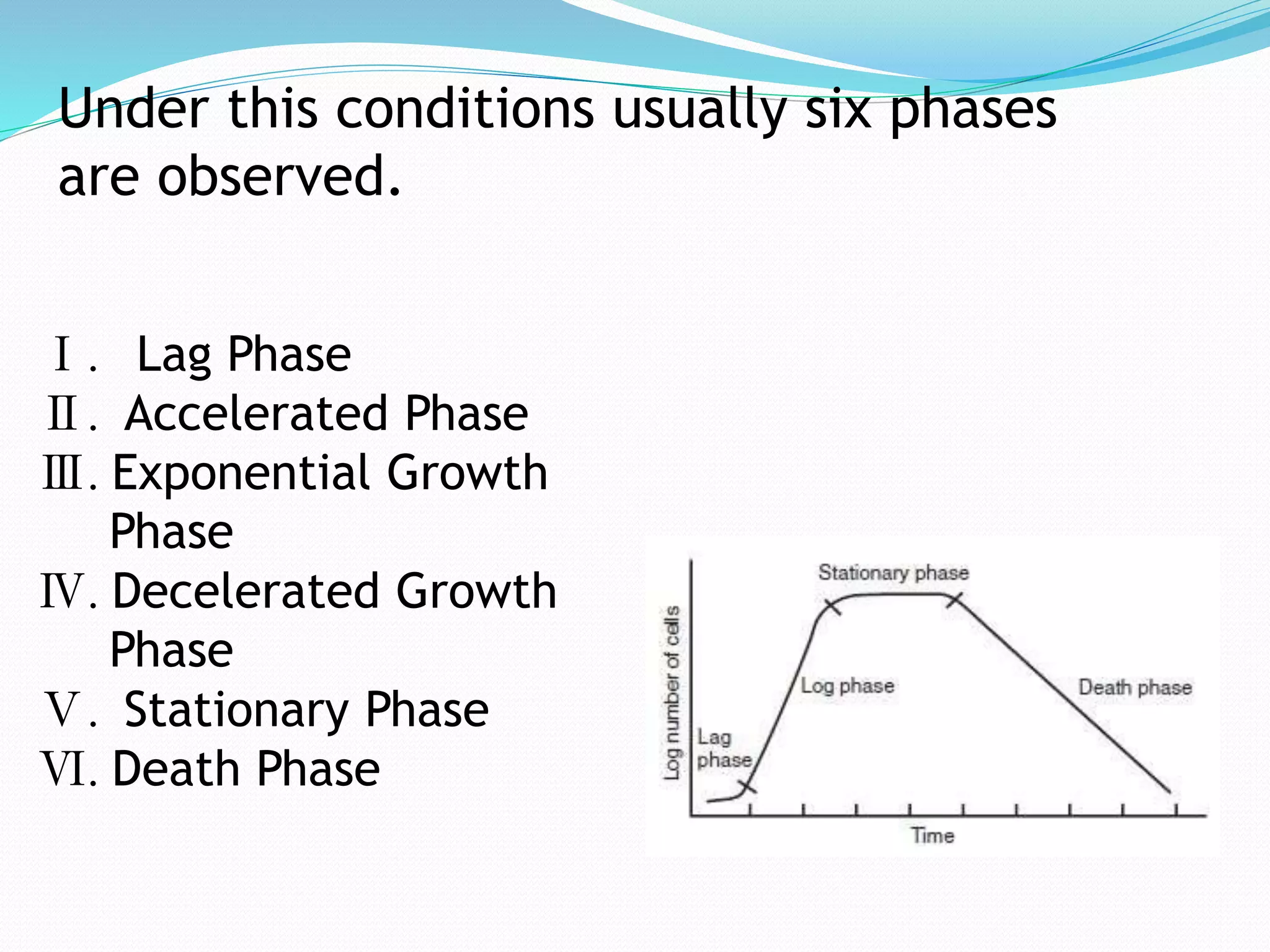
This document discusses types of microbial culture and growth kinetics. It describes three types of microbial culture: batch culture, fed-batch culture, and continuous culture. For batch culture, it outlines the six phases of microbial growth: lag phase, accelerated phase, exponential growth phase, decelerated growth phase, stationary phase, and death phase. Fed-batch culture involves incrementally adding nutrients over time to prolong the log and stationary phases. Continuous culture maintains a steady cell population by continuously adding and removing medium. The advantages of continuous culture are that it avoids downtime between batches and produces more consistent yields, while its disadvantages include greater difficulty maintaining sterility and potential cell loss.