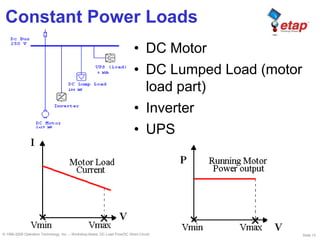
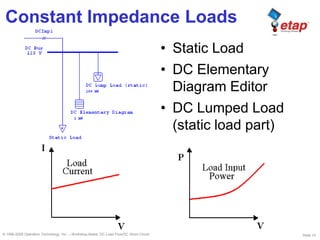
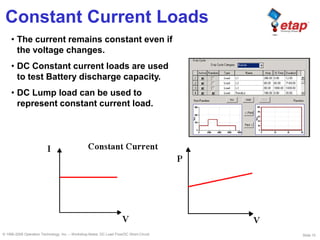
This document discusses DC load flow and short-circuit analysis. It describes why these studies are important for reliable DC systems and outlines the various models used to represent different DC system elements like batteries, chargers, loads, and branches in the studies. The purpose of DC load flow is to determine operating voltages and currents while DC short-circuit aims to find maximum fault currents to verify protection equipment ratings. Models include constant power, impedance and current loads as well as voltage and current sources for generators and converters.