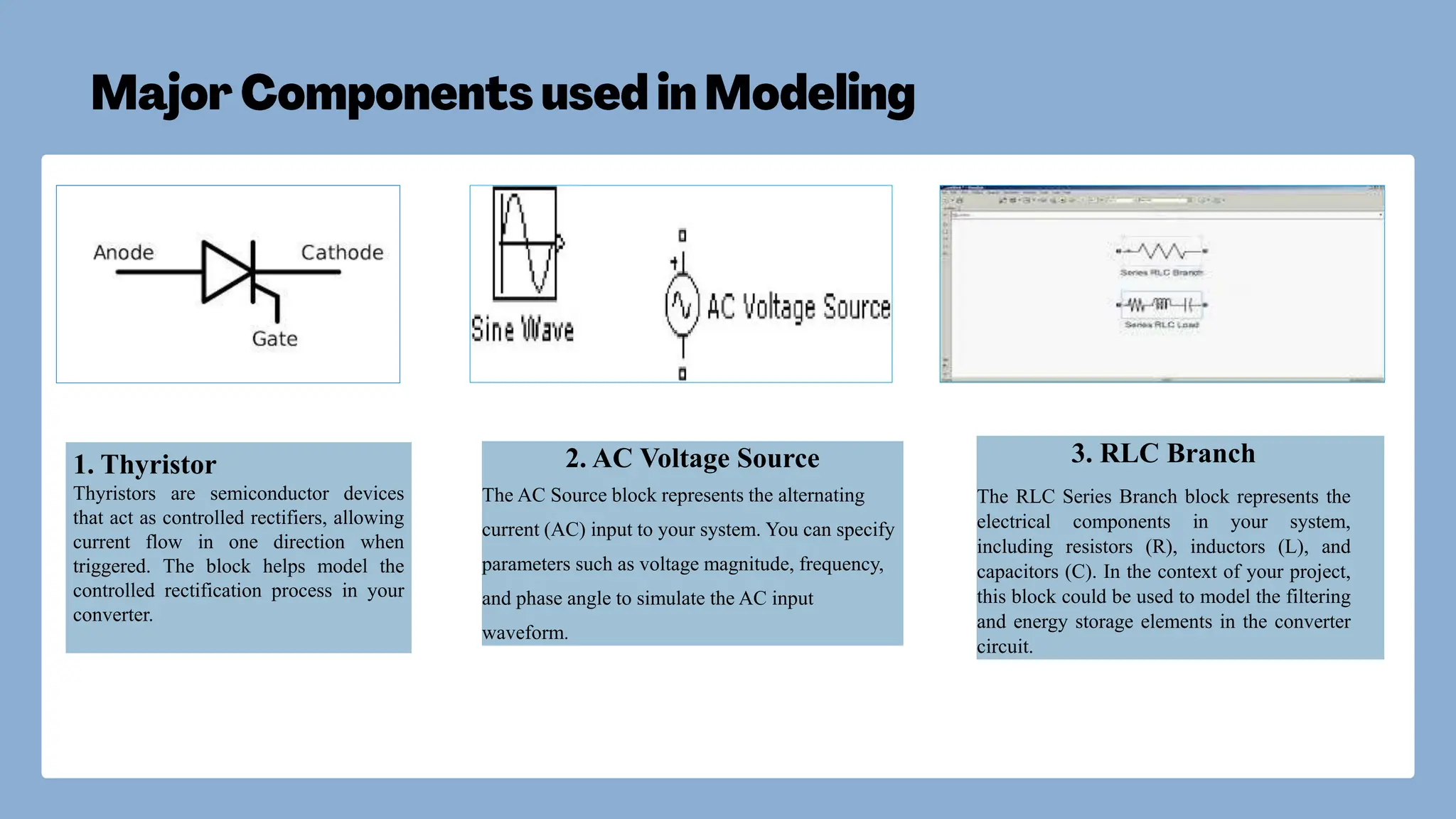
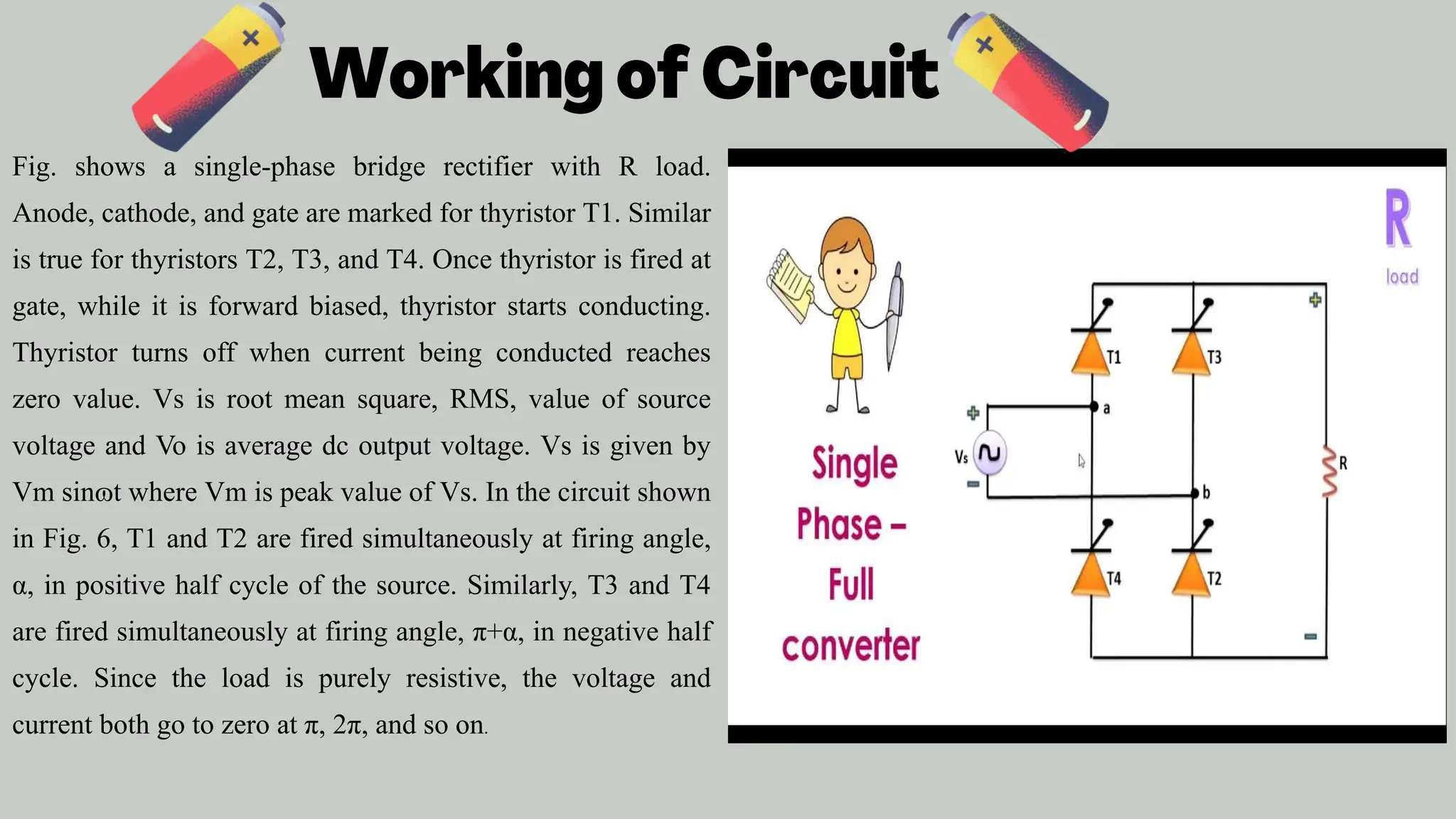
The document discusses the design and simulation of a single-phase AC to DC converter using MATLAB Simulink, emphasizing the role of thyristors in controlled rectification. It outlines the importance of AC to DC conversion for various applications, including electric vehicles and battery charging, while detailing the conversion principles and simulation methodologies. The project successfully demonstrated effective power regulation through the manipulation of firing angles, resulting in stable DC output.