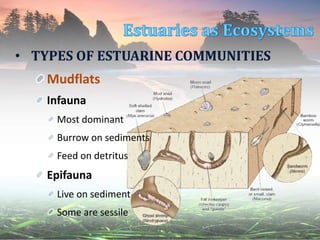
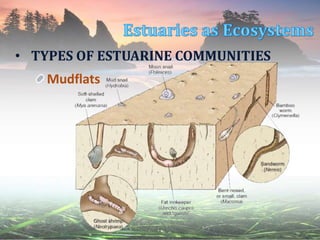
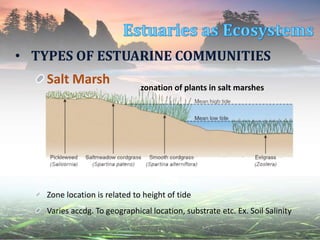
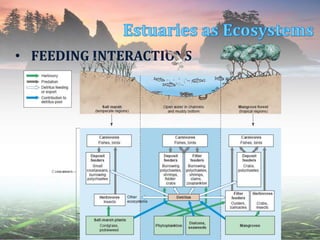
This document describes different estuarine communities, including open water, mudflats, salt marshes, mangrove forests, and other communities like seagrass beds and oyster reefs. It discusses the characteristic species found in each community and their roles, like cordgrass and fiddler crabs in salt marshes or red, black, and white mangroves in mangrove forests. However, many estuarine communities are being destroyed by human activities like reclamation, dredging, shrimp farming, and coastal development.