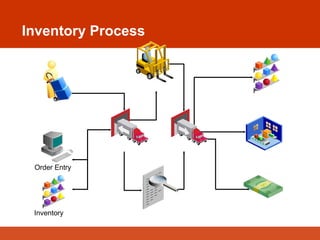
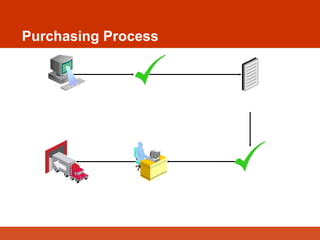
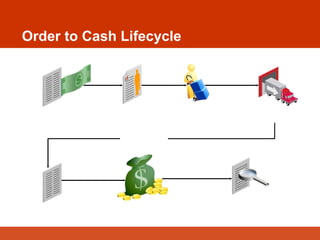
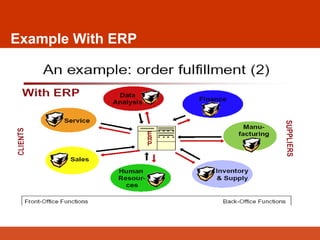
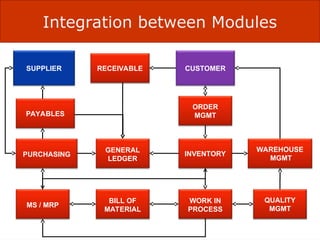
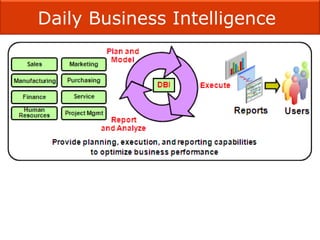
The document presents an overview of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), highlighting its significance in integrating various departments and optimizing business processes through a unified system. It covers the evolution of ERP, its functionalities, and the benefits it provides including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced information sharing. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of commitment from all organizational levels for successful ERP implementation and its potential to deliver competitive advantages.