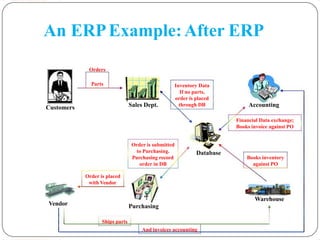
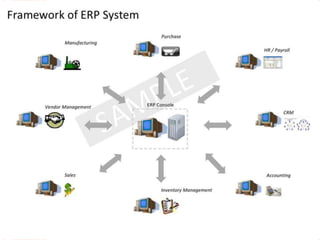
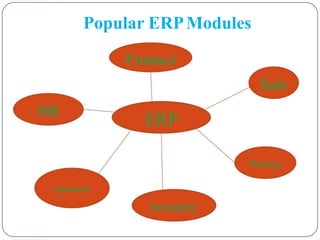
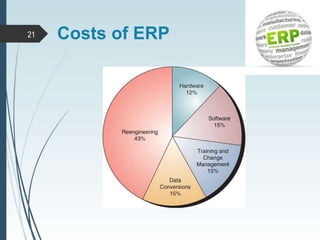
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate various business functions and departments into a single system with a shared database. ERP systems combine databases for planning, manufacturing, sales, marketing and other departments. They provide many benefits like standardized processes, reduced inventory costs, and integrated financial and customer information. Implementing an ERP system involves analyzing current business processes, customizing the ERP modules to match, training employees, and integrating the new system to replace old standalone systems. Major challenges are limitations of the software, changes to employee roles, and resistance to change from employees.