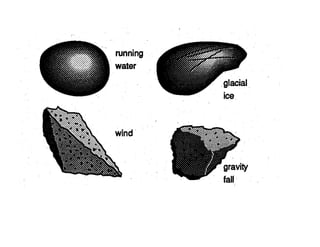
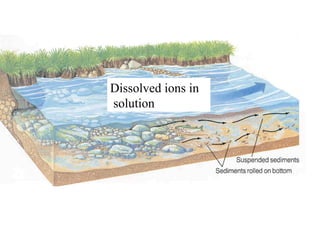
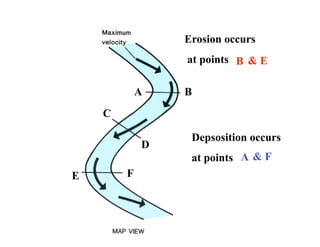
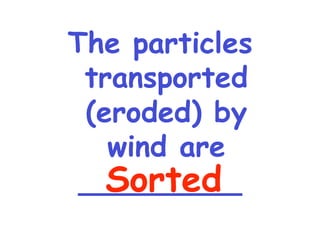
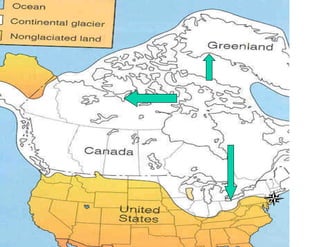
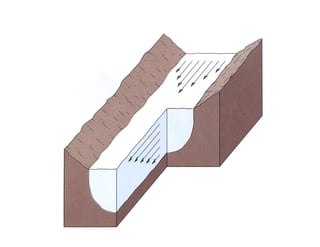
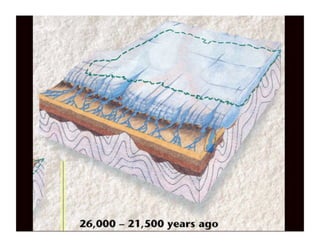
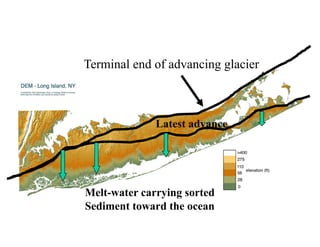
The document discusses different types of erosion caused by various agents. It describes how running water, wind, and glaciers each produce distinctive erosion features. It also explains the different ways sediments are transported by streams, including in solution, suspension, and being rolled along the stream bed. Glacial erosion leaves behind unsorted sediments and landforms like U-shaped valleys, striations, and kettle lakes.