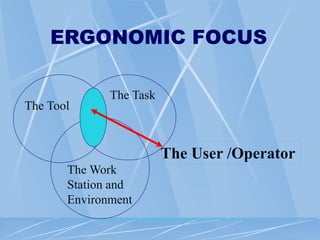
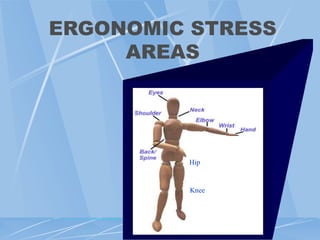
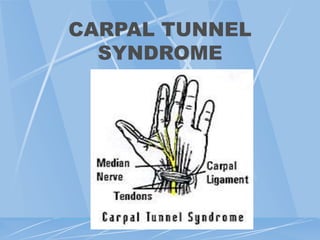
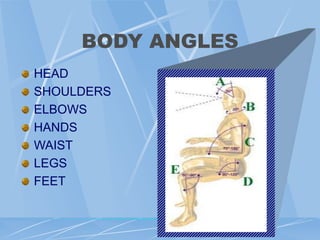
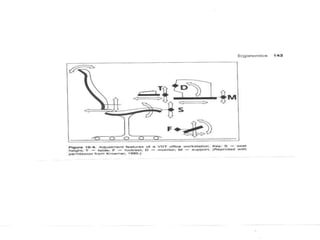
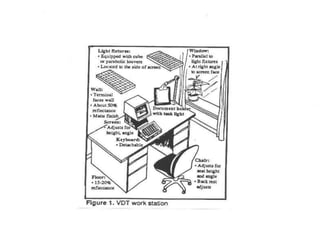
This document provides an overview of ergonomics and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) for a workplace training. It defines ergonomics as fitting the job to the worker. The goal of the training is to minimize injuries from physical and psychological stresses while maximizing productivity. MSDs are discussed, including common causes like repetitive motions, awkward postures, and vibration. Signs and symptoms of MSDs are outlined. The document covers administrative, work practice, and engineering controls that can be implemented as solutions. Exercises are demonstrated to relieve ergonomic stresses.