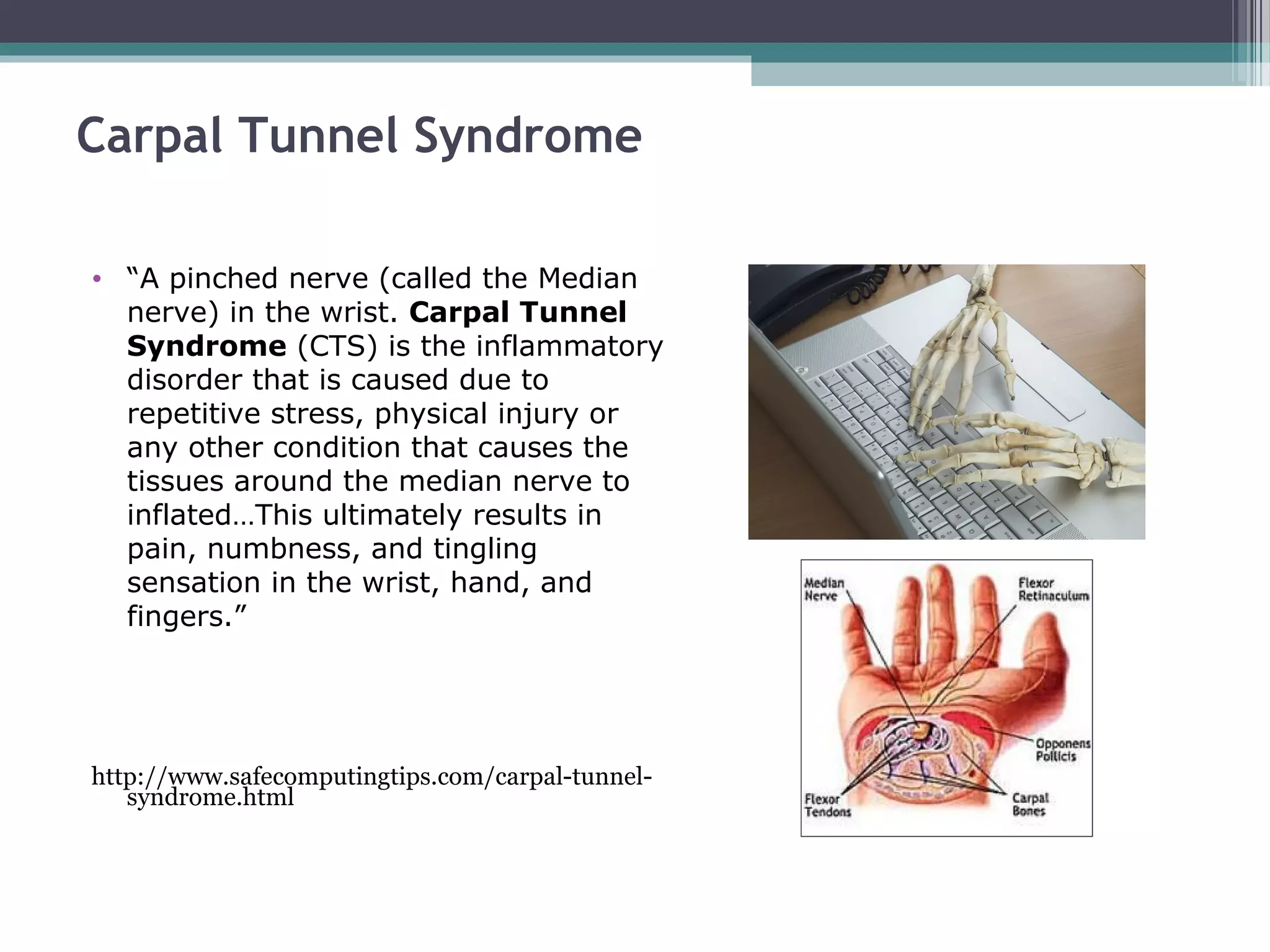
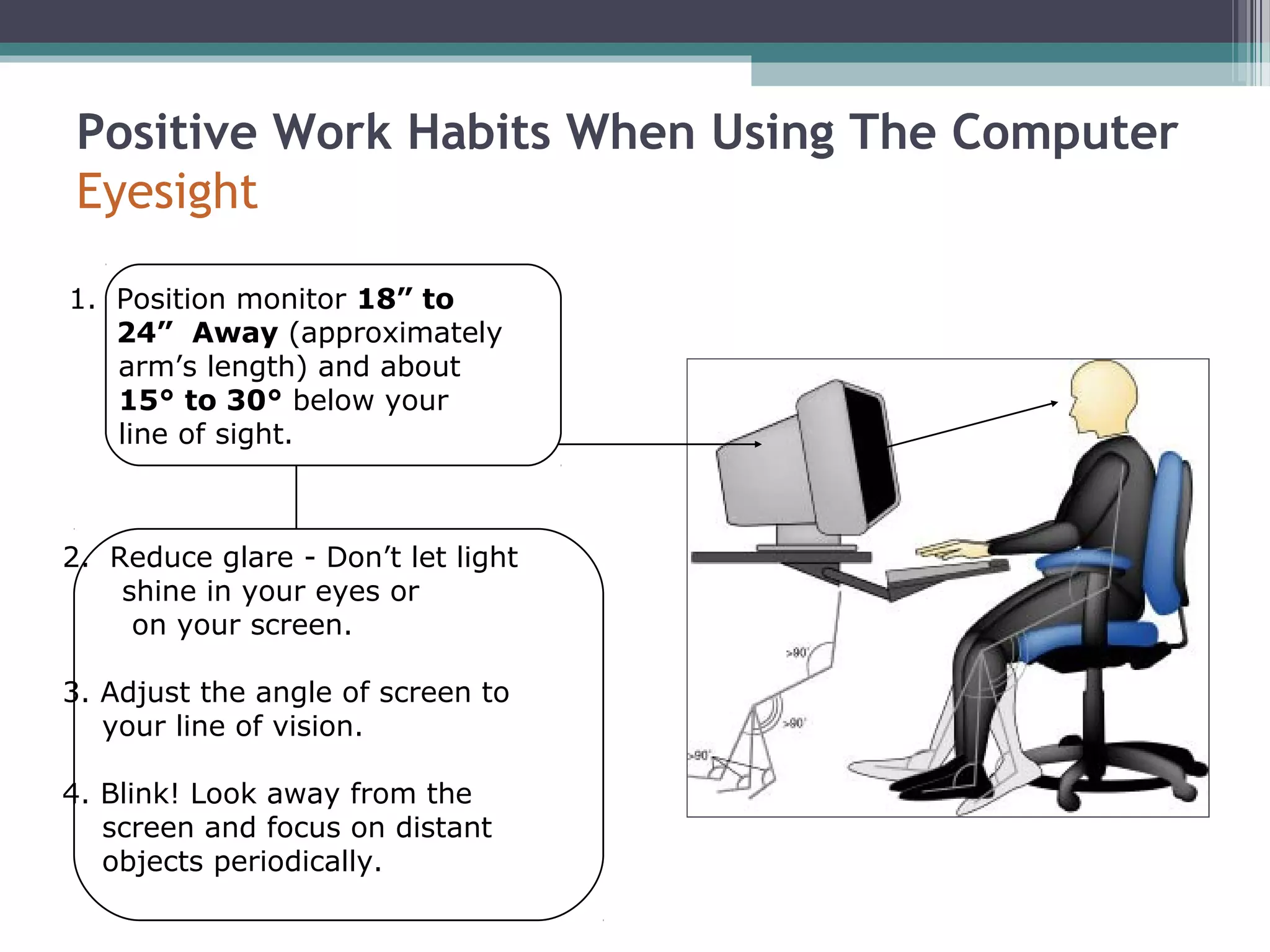
This document outlines the importance of ergonomics in using computers safely to prevent injuries like repetitive strain injury (RSI) and carpal tunnel syndrome. It provides guidelines for proper posture, equipment setup, and positive work habits while using computers. The training emphasizes the need for regular breaks and exercises to mitigate risks associated with prolonged computer use.