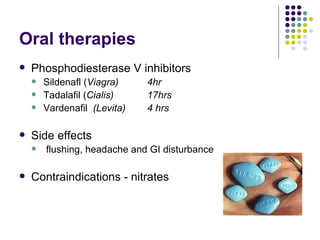
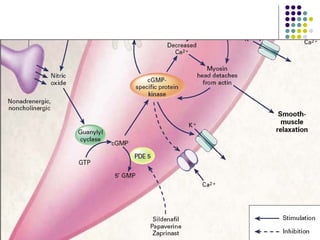
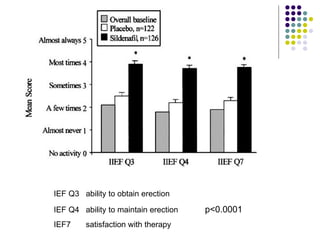
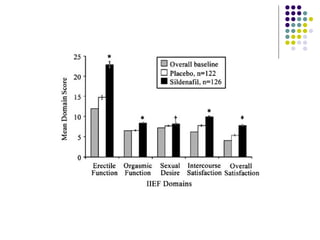
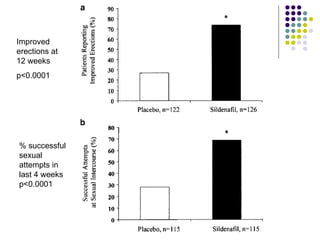
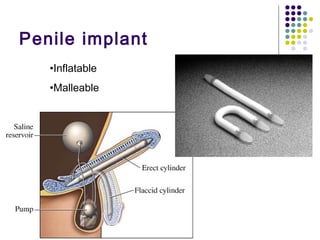
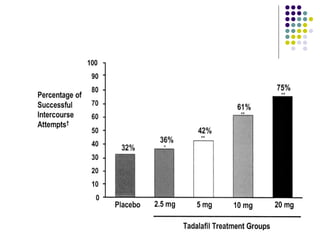
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is common, affecting over 150 million men worldwide. It is a marker for other neurovascular complications in diabetes. The causes of ED include vascular, neurological, endocrine, and psychological factors. Treatments include oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, vacuum devices, intracavernosal injections, testosterone replacement, and psychosexual counseling. Managing associated conditions and hormonal deficiencies can effectively treat ED.