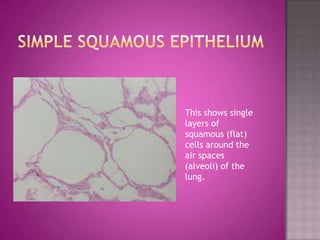
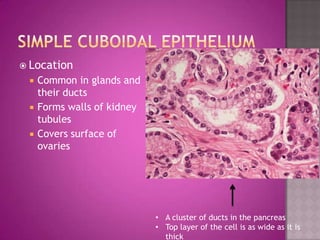
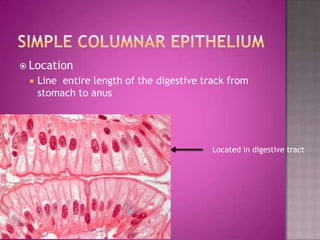
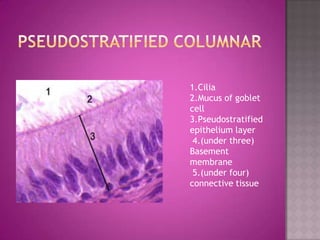
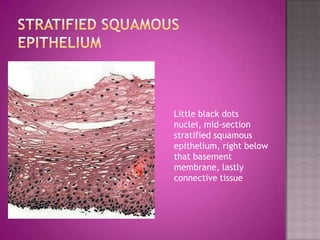
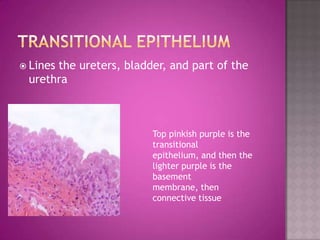
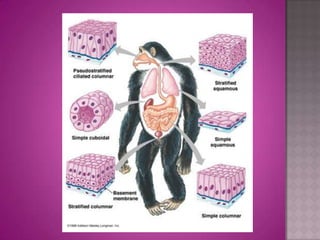
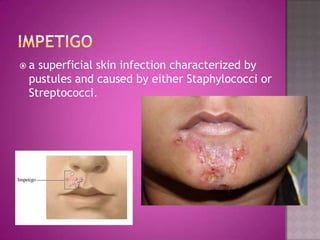
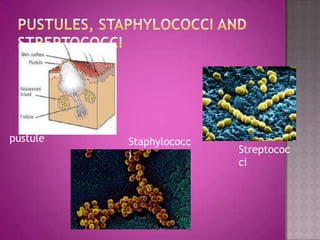
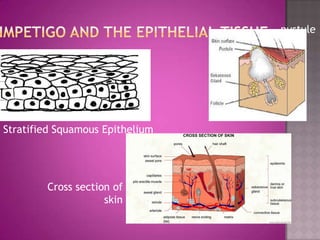
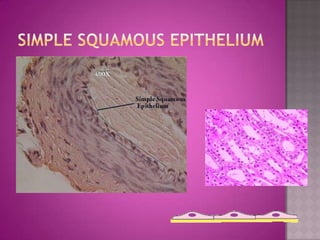
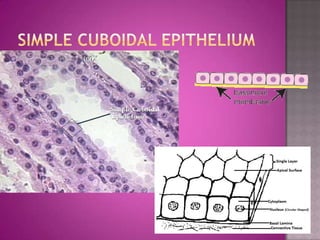
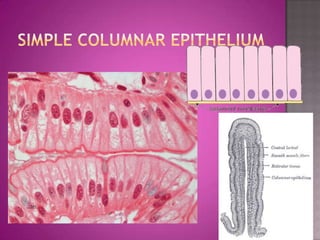
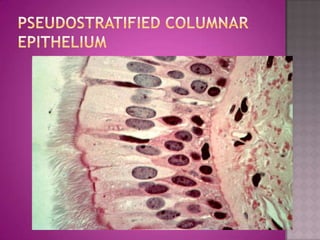
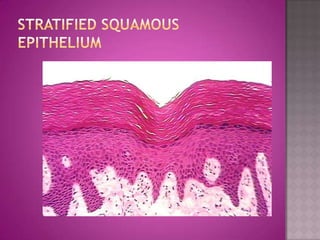
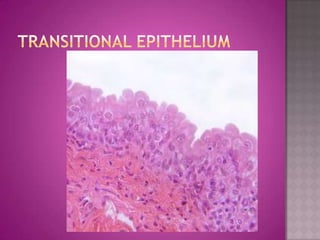
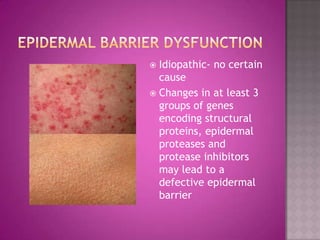
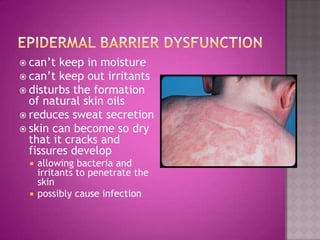
This document discusses different types of epithelial tissues. It describes three types of epithelial layers - simple, stratified, and pseudostratified/transitional. The different cell shapes that can make up the top layer are also defined. Specific locations and examples of each type of epithelium are provided.