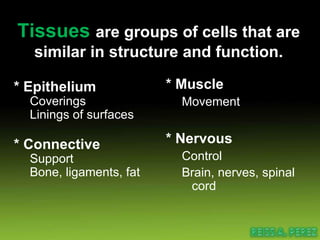
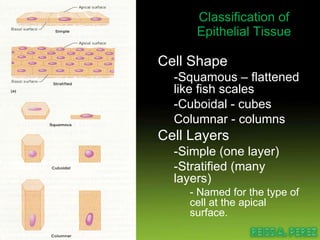
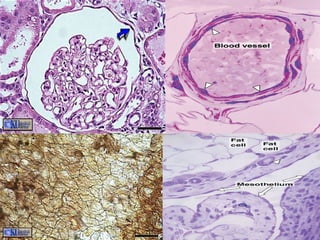
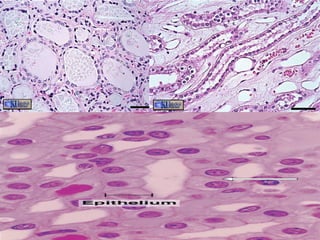
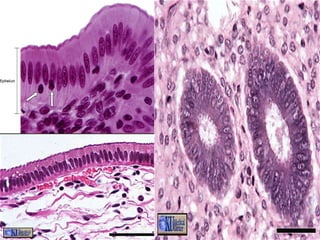
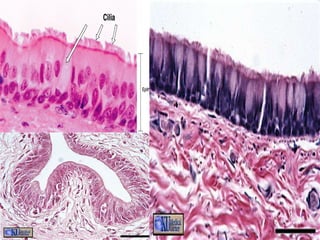
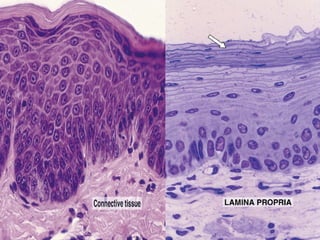
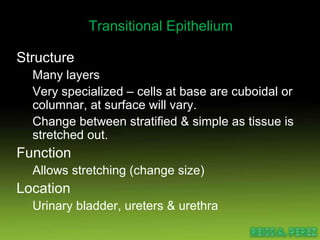
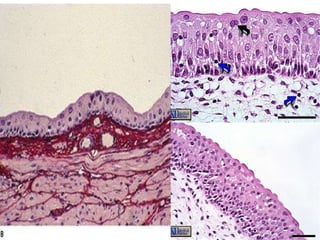
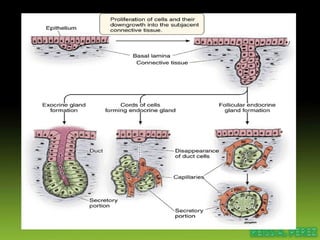
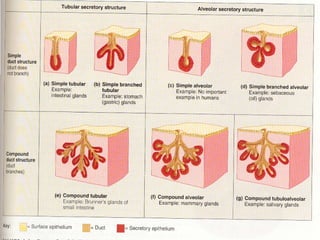
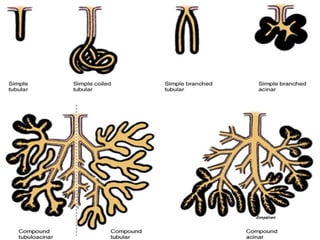
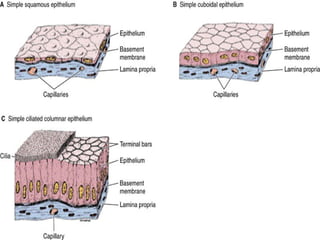
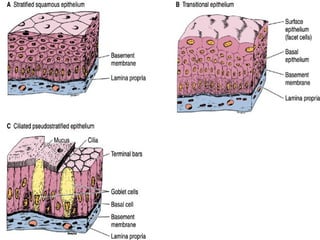
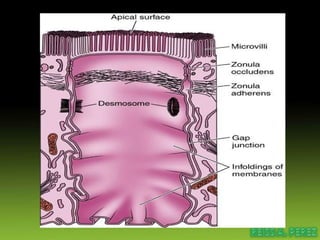
Epithelial tissue forms protective coverings and linings throughout the body. It is classified based on cell shape and layering. Simple epithelia are single-layered and include squamous, cuboidal, and columnar cells. Stratified epithelia have multiple layers and include squamous and transitional cells. Glands are classified by shape and include exocrine glands that secrete through ducts and endocrine glands that secrete directly into blood. Apical surfaces of epithelial cells may have microvilli, stereocilia, or cilia to increase absorption.