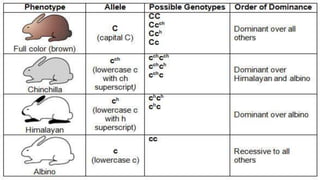
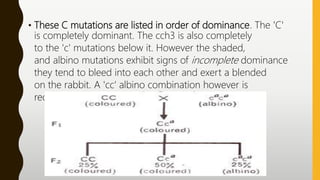
The coat color of rabbits is controlled by multiple alleles of the C gene. There are four main alleles - C for full color, Cch for chinchilla, C(H) for Himalayan, and c for albino. C is fully dominant to the other alleles. Cch is fully dominant to c. The C(H), shaded, and c alleles show incomplete dominance as their phenotypes blend together in combinations. A cc combination results in the fully recessive albino phenotype.