The document discusses immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genetics. It describes:
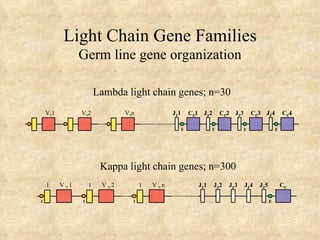
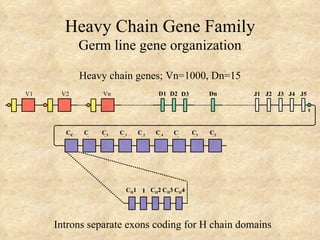
1) The organization of light and heavy chain gene loci, including multiple V, D, and J genes.
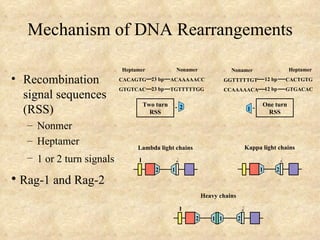
2) The mechanisms of V(D)J recombination and junctional diversity that generate antibody diversity prior to antigen exposure.
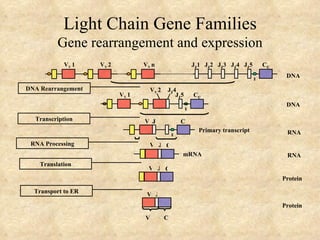
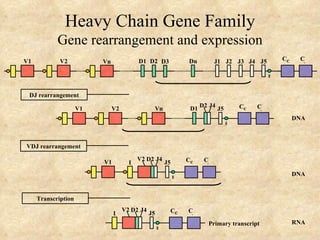
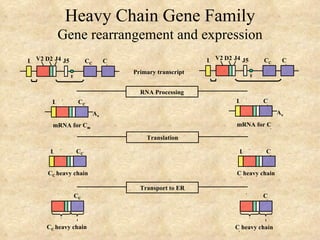
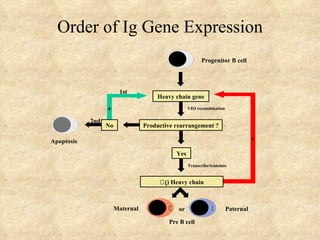
3) The processes of heavy and light chain gene rearrangement and expression that produce a single antibody specificity per B cell.