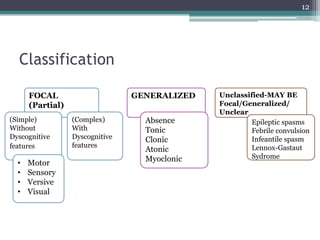
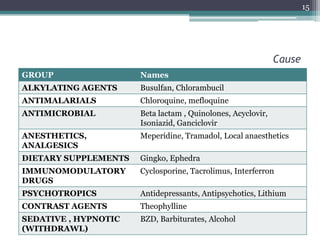
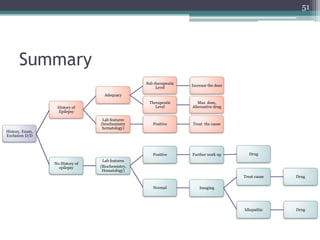
This document provides an overview of epilepsy, including its pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnostic approach, and management. It discusses how epilepsy results from an imbalance between excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system. Seizures occur due to factors that lower the seizure threshold or precipitate an attack. Diagnosis involves obtaining a medical history, clinical examination, and tests like EEG and imaging. Treatment primarily involves antiepileptic drugs to control seizures, though surgery may be an option for refractory cases. Proper management of epilepsy requires long-term medical treatment as well as attention to any psychiatric comorbidities.