Embed presentation
Download to read offline


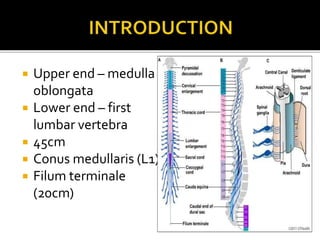

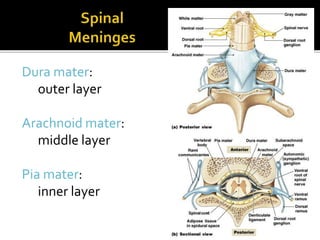
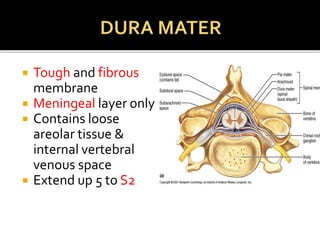

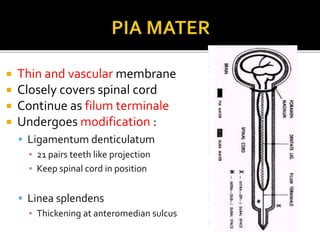
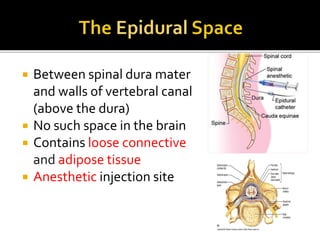

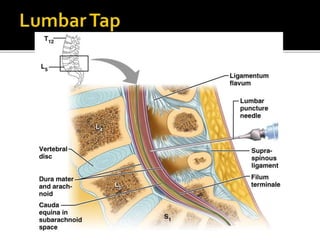
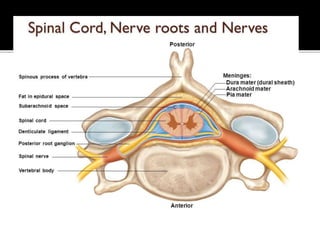


This document summarizes key information about the spinal meninges and epidural space. It lists the three meningeal layers - dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater - and describes their structures and functions in protecting the spinal cord. It also explains the epidural space located between the dura mater and vertebral wall, which is the site of anesthetic injection. Finally, it identifies the subdural and subarachnoid spaces filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and notes that a lumbar tap procedure withdraws CSF from the lower lumbar region for diagnosis.













