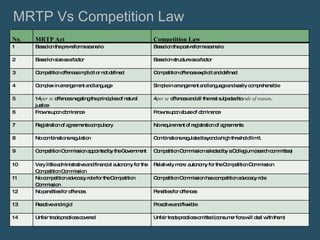
The document discusses the evolution of competition laws in India from the MRTP Act of 1969 to the current Competition Act of 2002. It provides details on the key provisions and changes made by amendments over time to the MRTP Act in 1991 and 1984, as well as the introduction of the Competition Act in 2002. It also summarizes a key case related to the MRTP Commission's powers to examine mergers and compares some of the major differences between the MRTP Act and the Competition Act.