Enzymes notes, enzyme chapter
•
0 likes•90 views
Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes are very specific and only catalyze one or a few reactions. The active site of an enzyme is where substrates bind and reactions occur. Many factors can influence an enzyme's activity, such as temperature, pH, substrate/product concentration, and inhibitors. Enzymes work by reducing the energy needed for reactions to occur and stabilizing the transition state.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Enzymes (Definition, characteristics, mechanism action, activity, stability) ...

Definition of enzyme, characteristics of enzyme, function of enzyme, mechanism action of enzyme, differences between enzyme and catalyst, activity of enzymes, stability of enzymes
Enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in living things. They have an active site that attracts and binds to specific substrate molecules. Once bound, the enzyme-substrate complex undergoes a shape change that either breaks or forms bonds in the substrate. This releases the product and returns the enzyme to its original shape to catalyze more reactions. Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for reactions and are regulated through cofactors, inhibitors, feedback inhibition, and subcellular localization.
Factors affecting enzyme activity SlideShare

This document discusses enzymes and how various factors affect their activity. It explains that enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, and that their activity is influenced by temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration. The optimum temperature and pH are described as well as how rises or falls from these can impact activity. Isoenzymes, which are variants of the same enzyme found in different tissues, are also covered. The concept of rate-limiting enzymes, which determine the overall rate of a metabolic pathway, is defined.
Enzymes

This document provides an overview of enzymes for a biology lesson. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and help speed up metabolic reactions in living organisms. It explains that enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of reactions and outlines several key points about how enzymes function, including that they have an active site that substrates bind to, and that temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors can affect reaction rates. The objectives of the lesson are to explain enzymes, how they catalyze reactions, and factors that influence reaction rates.
Enzymes dr.khushbu

This document provides information on enzymes, including their structure, function, classification, and regulation. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without undergoing permanent change. Enzymes are classified according to the type of chemical reaction they catalyze using the Enzyme Commission system with four digit codes. Enzyme activity can be regulated through various mechanisms including allosteric regulation, covalent modification, proteolytic cleavage, and induction/repression of enzyme synthesis.
Enzymes

Enzymes are globular proteins that regulate and speed up metabolic reactions in cells. They lower the activation energy needed for reactions to occur at normal body temperatures. Enzymes have an active site that binds specifically to substrates, catalyzing their conversion to products. The substrate fits into the active site like a key in a lock (lock-and-key model), though the induced fit model suggests the active site changes shape to better accommodate the substrate. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on factors like temperature, pH, enzyme and substrate concentrations - each enzyme works best within a specific range of conditions.
Enzymes

This document discusses key concepts around biochemical processes and enzymes. It defines metabolism as thousands of chemical reactions in organisms that give off heat depending on metabolic rate. Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy. Anabolic reactions join atoms and molecules to build complex structures and require energy. Reactions are controlled by biochemical pathways using enzymes. Mitochondria produce ATP through energy-releasing reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions using specific active sites without being used up in the process. Factors like pH, temperature, enzyme and substrate concentrations can affect enzyme activity.
06 Enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They can catalyze both catabolic reactions that break down molecules, and anabolic reactions that build molecules up. Enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules and a regulatory region that can be influenced by cofactors, coenzymes, or inhibitors. The binding of a substrate to an enzyme's active site is described by either the lock-and-key or induced-fit models. Factors like pH, temperature, enzyme and substrate concentrations can affect an enzyme's activity level.
Recommended
Enzymes (Definition, characteristics, mechanism action, activity, stability) ...

Definition of enzyme, characteristics of enzyme, function of enzyme, mechanism action of enzyme, differences between enzyme and catalyst, activity of enzymes, stability of enzymes
Enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in living things. They have an active site that attracts and binds to specific substrate molecules. Once bound, the enzyme-substrate complex undergoes a shape change that either breaks or forms bonds in the substrate. This releases the product and returns the enzyme to its original shape to catalyze more reactions. Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for reactions and are regulated through cofactors, inhibitors, feedback inhibition, and subcellular localization.
Factors affecting enzyme activity SlideShare

This document discusses enzymes and how various factors affect their activity. It explains that enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, and that their activity is influenced by temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration. The optimum temperature and pH are described as well as how rises or falls from these can impact activity. Isoenzymes, which are variants of the same enzyme found in different tissues, are also covered. The concept of rate-limiting enzymes, which determine the overall rate of a metabolic pathway, is defined.
Enzymes

This document provides an overview of enzymes for a biology lesson. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and help speed up metabolic reactions in living organisms. It explains that enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of reactions and outlines several key points about how enzymes function, including that they have an active site that substrates bind to, and that temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors can affect reaction rates. The objectives of the lesson are to explain enzymes, how they catalyze reactions, and factors that influence reaction rates.
Enzymes dr.khushbu

This document provides information on enzymes, including their structure, function, classification, and regulation. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without undergoing permanent change. Enzymes are classified according to the type of chemical reaction they catalyze using the Enzyme Commission system with four digit codes. Enzyme activity can be regulated through various mechanisms including allosteric regulation, covalent modification, proteolytic cleavage, and induction/repression of enzyme synthesis.
Enzymes

Enzymes are globular proteins that regulate and speed up metabolic reactions in cells. They lower the activation energy needed for reactions to occur at normal body temperatures. Enzymes have an active site that binds specifically to substrates, catalyzing their conversion to products. The substrate fits into the active site like a key in a lock (lock-and-key model), though the induced fit model suggests the active site changes shape to better accommodate the substrate. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on factors like temperature, pH, enzyme and substrate concentrations - each enzyme works best within a specific range of conditions.
Enzymes

This document discusses key concepts around biochemical processes and enzymes. It defines metabolism as thousands of chemical reactions in organisms that give off heat depending on metabolic rate. Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy. Anabolic reactions join atoms and molecules to build complex structures and require energy. Reactions are controlled by biochemical pathways using enzymes. Mitochondria produce ATP through energy-releasing reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions using specific active sites without being used up in the process. Factors like pH, temperature, enzyme and substrate concentrations can affect enzyme activity.
06 Enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They can catalyze both catabolic reactions that break down molecules, and anabolic reactions that build molecules up. Enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules and a regulatory region that can be influenced by cofactors, coenzymes, or inhibitors. The binding of a substrate to an enzyme's active site is described by either the lock-and-key or induced-fit models. Factors like pH, temperature, enzyme and substrate concentrations can affect an enzyme's activity level.
Enzymes

The document defines key terms related to enzymes including substrate, active site, and cofactors. It describes the lock and key and induced fit models of how enzymes bind to substrates. Environmental factors like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration can affect the rate of enzymatic reactions. Cofactors and coenzymes are required for some enzymatic reactions. Competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors can regulate enzyme activity. Examples are given of enzymatic uses in industry, detergents, food, and diagnosing/treating diseases.
Enzyme mechanism of action & kinetics

The document summarizes key aspects of enzyme action and kinetics. It defines substrates and enzymes, and describes the lock and key and induced fit models of enzyme-substrate binding. It then explains enzyme kinetics using the Michaelis-Menten equation, defining terms like Vmax and Km. Finally, it discusses factors that affect enzyme activity such as enzyme/substrate concentration, inhibitors, temperature, and pH.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action

This document discusses the mechanism of enzyme action through a learning outcome and several sections. It begins with introducing the topic of enzyme mechanisms and defining enzymes as biological catalysts for cellular reactions. It then explains the "lock and key" hypothesis for enzyme action, where a specific substrate molecule binds to the active site of an enzyme, forming an unstable enzyme-substrate complex. This allows the substrate to be converted into products, which then leave the active site so the enzyme can catalyze another reaction. The document assessments students' understanding with multiple choice and short answer questions about enzyme specificity and how temperature affects reaction rates.
Enzyme

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions. They are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze and have a complex three-dimensional globular structure. Enzymes specifically bind to substrates through their active sites to lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding up the formation of products. The mechanism of enzyme action was originally proposed to be lock-and-key binding, but is now understood to involve induced fit, where the enzyme and substrate mutually adjust their shapes for catalysis. Enzymes can be regulated by various factors like substrate concentration, temperature, pH, inhibitors, and activators.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein molecules that act as catalysts to speed up biological reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. They have specific active sites that substrates bind to, either breaking substrates apart or joining them together. The structure of the active site determines the specific substrate an enzyme can act on. While the lock and key model depicted a simple binding, the induced fit model better explains how enzymes and substrates may slightly change shape to promote reactions. Environmental factors like temperature, pH, and cofactors can impact an enzyme's activity by potentially denaturing its structure.
B.Sc. Biochem II Biomolecule I U 4 Enzyme

1. Enzymes are complex proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions in living cells. They do this by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur.
2. The Michaelis-Menten kinetic model describes enzyme kinetics. It states that the enzyme first binds to the substrate to form an enzyme-substrate complex, and this complex then breaks down to release products and free up the enzyme.
3. The Michaelis-Menten equation relates the initial reaction rate to substrate concentration. It produces a hyperbolic curve that describes the typical saturation kinetics seen with many enzymes.
Chap 10 enzyme

Enzymes are protein molecules produced by living organisms that act as biological catalysts, controlling and accelerating biochemical reactions in cells. They do this by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. Enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules. The binding can cause a slight change in the enzyme's shape through an induced fit mechanism to better bind the substrate and catalyze the reaction. An enzyme's activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration.
Powerpoint enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve specificity by fitting substrate molecules into their active sites. Factors like temperature, pH, and substrate/enzyme concentration can affect the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Temperature and pH can cause enzymes to denature if they exceed the optimal range, altering the protein structure and disabling catalytic activity. Higher substrate concentrations allow more reactions to occur until all active sites are occupied, while more enzymes provide more active sites for substrates to bind to, both increasing reaction rate.
الانزيمات د.مصطفى طه محمد Enzymes

The document discusses enzymes and how they function. It provides information on:
- Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts and lower the activation energy of chemical reactions.
- Enzymes have a specific three-dimensional structure with an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules.
- The lock and key model describes how the substrate fits into the active site like a key in a lock, and the enzyme catalyzes the reaction to convert the substrate to products.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. Their three-dimensional structure, including amino acid sequence and folding, determines the specific reaction they catalyze. The active site is where substrates bind and undergo reaction. Factors like temperature, pH, enzyme/substrate concentrations, and inhibitors can affect the reaction rate by impacting substrate binding or enzyme structure. Feedback inhibition allows some enzymes to precisely control metabolic pathways.
AS Level Biology - 3) Enzymes

Enzymes are biological catalysts. They play some of the most important roles in the processes of life sustenance. They are presence even at the tiniest level of metabolism - acting as the lubricant for life to progress smoothly. Without enzymes, complex life would not be possible.
Enzymes (An Introductory Approach)

1. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
2. Enzymes have specific active sites that substrates bind to, and can break down or join substrates.
3. Enzymes are proteins but some are RNA molecules called ribozymes, and their activity is affected by temperature, pH, substrate concentration and other factors.
Enzymes

This document provides an overview of enzymes and enzyme kinetics. It discusses how enzymes were discovered to catalyze reactions through the work of Buchner and Pasteur. It also describes Michaelis-Menten kinetics and how enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors. Different types of inhibition - competitive, noncompetitive, and irreversible - are explained. Finally, it briefly introduces enzyme-linked cell surface receptors and common features of receptor serine/threonine kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases.
Enzyme inhibition

Enzyme introduction, Enzyme inhibition, Irreversible inhibition, reversible inhibition, competitive inhibition, noncompetitive inhibition, uncompetitive inhibition, examples for different types of inhibition, uses of enzyme inhibition in medicinal purpose, allosteric enzymes, allosteric activation, allosteric inhibition, pictorial explanation, graphical explanation.
Chapter 5 Enzymes Lesson 2 - Characteristics of enzymes

Enzymes found in biological washing powders help clean clothes by breaking down stains. Enzymes work best within a certain temperature and pH range, and can become denatured outside of this range, losing their effectiveness. Different enzymes have different optimal conditions, so washing powders may contain enzymes that function at higher temperatures to remove tougher stains.
Enzyme’s activity

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and have many applications in industry. In the human body, enzymes are involved in essential processes like DNA replication and protein synthesis. Industrially, enzymes are used in detergents, textiles, and food processing. This document discusses the importance and mechanisms of enzyme activity, including how enzymes lower activation energy and use specific active sites. It also covers measuring enzyme activity, factors that affect it like temperature and pH, and examples of their use in industries like cheese and wine production.
enzymes

Enzymes are complex proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions in living cells. They speed up reactions by lowering their activation energy. Each enzyme is specific and only catalyzes one reaction. Enzyme function can be affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and inhibitor concentrations, and the presence of cofactors. There are different models that describe how enzymes specifically bind to substrates, such as the lock-and-key and induced fit hypotheses.
Enzymes by Dr. Aritri Bir

This document discusses enzymes and enzymology. It begins by defining what an enzyme is and explaining enzyme nomenclature and classification. It then discusses the structural organization of enzymes and different types of cofactors. The mechanisms of enzyme action and factors that affect enzyme kinetics are also explained. Different topics within enzymology are then explored in more detail, including enzyme inhibition mechanisms and how enzyme activity is regulated through various methods like allosteric regulation, covalent modification, and controlling enzyme synthesis and degradation. Clinical applications of enzymes are also briefly covered.
Enzymes&biocatalysis

Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions in living cells without undergoing a change themselves. They are usually proteins but can also be RNA. Many enzymes require non-protein cofactors like metal ions or organic molecules to be active. There are over 75,000 known enzymes that are classified and named based on the reactions they catalyze. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing more molecules to reach the transition state. Their activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and can be inhibited by other molecules. Feedback inhibition regulates enzyme activity by inhibiting enzymes using their own end products.
Allosteric and feedback regulation

This document discusses allosteric and feedback regulation of enzymes. It defines allosteric enzymes as having sites besides the active site that can bind non-substrate molecules and influence enzyme activity. Two main models of allosteric regulation are described: the symmetrical model and sequential model. Allosteric effectors can be homotropic, which are substrates, or heterotropic, which are regulatory molecules other than substrates that activate or inhibit the enzyme. Examples of allosteric regulation and feedback inhibition are given.
ENZYMES -enzymes biochemistry.slideshare.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They achieve catalysis through four main mechanisms: proximity of substrates, acid-base catalysis, catalysis by strain, and covalent catalysis. Enzymes are highly specific and contain an active site that binds substrates in a way that lowers their activation energy and facilitates the formation of products.
1s.ENZYMES.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They facilitate reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. Enzymes achieve specificity through their active sites, which are complementary in shape and chemical properties to their substrates. Factors like temperature, pH, and inhibitors can impact an enzyme's activity. There are several mechanisms of enzyme action and regulation, including competitive and non-competitive inhibition, as well as allosteric regulation through effectors binding at distinct sites. Precise control of enzymes is crucial for metabolic processes in cells and organisms.
More Related Content
What's hot
Enzymes

The document defines key terms related to enzymes including substrate, active site, and cofactors. It describes the lock and key and induced fit models of how enzymes bind to substrates. Environmental factors like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration can affect the rate of enzymatic reactions. Cofactors and coenzymes are required for some enzymatic reactions. Competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors can regulate enzyme activity. Examples are given of enzymatic uses in industry, detergents, food, and diagnosing/treating diseases.
Enzyme mechanism of action & kinetics

The document summarizes key aspects of enzyme action and kinetics. It defines substrates and enzymes, and describes the lock and key and induced fit models of enzyme-substrate binding. It then explains enzyme kinetics using the Michaelis-Menten equation, defining terms like Vmax and Km. Finally, it discusses factors that affect enzyme activity such as enzyme/substrate concentration, inhibitors, temperature, and pH.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action

This document discusses the mechanism of enzyme action through a learning outcome and several sections. It begins with introducing the topic of enzyme mechanisms and defining enzymes as biological catalysts for cellular reactions. It then explains the "lock and key" hypothesis for enzyme action, where a specific substrate molecule binds to the active site of an enzyme, forming an unstable enzyme-substrate complex. This allows the substrate to be converted into products, which then leave the active site so the enzyme can catalyze another reaction. The document assessments students' understanding with multiple choice and short answer questions about enzyme specificity and how temperature affects reaction rates.
Enzyme

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions. They are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze and have a complex three-dimensional globular structure. Enzymes specifically bind to substrates through their active sites to lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding up the formation of products. The mechanism of enzyme action was originally proposed to be lock-and-key binding, but is now understood to involve induced fit, where the enzyme and substrate mutually adjust their shapes for catalysis. Enzymes can be regulated by various factors like substrate concentration, temperature, pH, inhibitors, and activators.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein molecules that act as catalysts to speed up biological reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. They have specific active sites that substrates bind to, either breaking substrates apart or joining them together. The structure of the active site determines the specific substrate an enzyme can act on. While the lock and key model depicted a simple binding, the induced fit model better explains how enzymes and substrates may slightly change shape to promote reactions. Environmental factors like temperature, pH, and cofactors can impact an enzyme's activity by potentially denaturing its structure.
B.Sc. Biochem II Biomolecule I U 4 Enzyme

1. Enzymes are complex proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions in living cells. They do this by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur.
2. The Michaelis-Menten kinetic model describes enzyme kinetics. It states that the enzyme first binds to the substrate to form an enzyme-substrate complex, and this complex then breaks down to release products and free up the enzyme.
3. The Michaelis-Menten equation relates the initial reaction rate to substrate concentration. It produces a hyperbolic curve that describes the typical saturation kinetics seen with many enzymes.
Chap 10 enzyme

Enzymes are protein molecules produced by living organisms that act as biological catalysts, controlling and accelerating biochemical reactions in cells. They do this by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. Enzymes have an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules. The binding can cause a slight change in the enzyme's shape through an induced fit mechanism to better bind the substrate and catalyze the reaction. An enzyme's activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration.
Powerpoint enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve specificity by fitting substrate molecules into their active sites. Factors like temperature, pH, and substrate/enzyme concentration can affect the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Temperature and pH can cause enzymes to denature if they exceed the optimal range, altering the protein structure and disabling catalytic activity. Higher substrate concentrations allow more reactions to occur until all active sites are occupied, while more enzymes provide more active sites for substrates to bind to, both increasing reaction rate.
الانزيمات د.مصطفى طه محمد Enzymes

The document discusses enzymes and how they function. It provides information on:
- Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts and lower the activation energy of chemical reactions.
- Enzymes have a specific three-dimensional structure with an active site that binds to specific substrate molecules.
- The lock and key model describes how the substrate fits into the active site like a key in a lock, and the enzyme catalyzes the reaction to convert the substrate to products.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. Their three-dimensional structure, including amino acid sequence and folding, determines the specific reaction they catalyze. The active site is where substrates bind and undergo reaction. Factors like temperature, pH, enzyme/substrate concentrations, and inhibitors can affect the reaction rate by impacting substrate binding or enzyme structure. Feedback inhibition allows some enzymes to precisely control metabolic pathways.
AS Level Biology - 3) Enzymes

Enzymes are biological catalysts. They play some of the most important roles in the processes of life sustenance. They are presence even at the tiniest level of metabolism - acting as the lubricant for life to progress smoothly. Without enzymes, complex life would not be possible.
Enzymes (An Introductory Approach)

1. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
2. Enzymes have specific active sites that substrates bind to, and can break down or join substrates.
3. Enzymes are proteins but some are RNA molecules called ribozymes, and their activity is affected by temperature, pH, substrate concentration and other factors.
Enzymes

This document provides an overview of enzymes and enzyme kinetics. It discusses how enzymes were discovered to catalyze reactions through the work of Buchner and Pasteur. It also describes Michaelis-Menten kinetics and how enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inhibitors. Different types of inhibition - competitive, noncompetitive, and irreversible - are explained. Finally, it briefly introduces enzyme-linked cell surface receptors and common features of receptor serine/threonine kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases.
Enzyme inhibition

Enzyme introduction, Enzyme inhibition, Irreversible inhibition, reversible inhibition, competitive inhibition, noncompetitive inhibition, uncompetitive inhibition, examples for different types of inhibition, uses of enzyme inhibition in medicinal purpose, allosteric enzymes, allosteric activation, allosteric inhibition, pictorial explanation, graphical explanation.
Chapter 5 Enzymes Lesson 2 - Characteristics of enzymes

Enzymes found in biological washing powders help clean clothes by breaking down stains. Enzymes work best within a certain temperature and pH range, and can become denatured outside of this range, losing their effectiveness. Different enzymes have different optimal conditions, so washing powders may contain enzymes that function at higher temperatures to remove tougher stains.
Enzyme’s activity

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and have many applications in industry. In the human body, enzymes are involved in essential processes like DNA replication and protein synthesis. Industrially, enzymes are used in detergents, textiles, and food processing. This document discusses the importance and mechanisms of enzyme activity, including how enzymes lower activation energy and use specific active sites. It also covers measuring enzyme activity, factors that affect it like temperature and pH, and examples of their use in industries like cheese and wine production.
enzymes

Enzymes are complex proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions in living cells. They speed up reactions by lowering their activation energy. Each enzyme is specific and only catalyzes one reaction. Enzyme function can be affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and inhibitor concentrations, and the presence of cofactors. There are different models that describe how enzymes specifically bind to substrates, such as the lock-and-key and induced fit hypotheses.
Enzymes by Dr. Aritri Bir

This document discusses enzymes and enzymology. It begins by defining what an enzyme is and explaining enzyme nomenclature and classification. It then discusses the structural organization of enzymes and different types of cofactors. The mechanisms of enzyme action and factors that affect enzyme kinetics are also explained. Different topics within enzymology are then explored in more detail, including enzyme inhibition mechanisms and how enzyme activity is regulated through various methods like allosteric regulation, covalent modification, and controlling enzyme synthesis and degradation. Clinical applications of enzymes are also briefly covered.
Enzymes&biocatalysis

Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions in living cells without undergoing a change themselves. They are usually proteins but can also be RNA. Many enzymes require non-protein cofactors like metal ions or organic molecules to be active. There are over 75,000 known enzymes that are classified and named based on the reactions they catalyze. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing more molecules to reach the transition state. Their activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and can be inhibited by other molecules. Feedback inhibition regulates enzyme activity by inhibiting enzymes using their own end products.
Allosteric and feedback regulation

This document discusses allosteric and feedback regulation of enzymes. It defines allosteric enzymes as having sites besides the active site that can bind non-substrate molecules and influence enzyme activity. Two main models of allosteric regulation are described: the symmetrical model and sequential model. Allosteric effectors can be homotropic, which are substrates, or heterotropic, which are regulatory molecules other than substrates that activate or inhibit the enzyme. Examples of allosteric regulation and feedback inhibition are given.
What's hot (20)
Chapter 5 Enzymes Lesson 2 - Characteristics of enzymes

Chapter 5 Enzymes Lesson 2 - Characteristics of enzymes
Similar to Enzymes notes, enzyme chapter
ENZYMES -enzymes biochemistry.slideshare.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They achieve catalysis through four main mechanisms: proximity of substrates, acid-base catalysis, catalysis by strain, and covalent catalysis. Enzymes are highly specific and contain an active site that binds substrates in a way that lowers their activation energy and facilitates the formation of products.
1s.ENZYMES.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They facilitate reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. Enzymes achieve specificity through their active sites, which are complementary in shape and chemical properties to their substrates. Factors like temperature, pH, and inhibitors can impact an enzyme's activity. There are several mechanisms of enzyme action and regulation, including competitive and non-competitive inhibition, as well as allosteric regulation through effectors binding at distinct sites. Precise control of enzymes is crucial for metabolic processes in cells and organisms.
Enzymes bph

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions and stabilizing transition states. Enzymes require cofactors like metal ions or organic coenzymes to function. The active site of an enzyme binds specifically to substrates to catalyze reactions. Many factors influence enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, substrate and product concentration.
MAIN PPT- ENZYMES.pptx

Enzymes are biological catalysts that are usually proteins and speed up biochemical reactions. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes are very specific and only catalyze one type of reaction. The active site of an enzyme binds to specific substrates. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like pH, temperature, and substrate/product concentration. There are two main models for enzyme activity - the lock and key model suggests a rigid enzyme structure that substrates fit into, while the induced fit model suggests substrates cause enzyme structures to change shape for binding. Enzymes can be inhibited competitively by substrates that resemble their real substrates or non-competitively by other molecules.
Enzyme unit 4 5

In this Slide share detail discussion about classification of enzyme inhibition as well cofactor and coenzyme
ENZYME - by rahil (ciu)

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions by lowering their activation energy. They have highly specific active sites that substrates bind to, forming enzyme-substrate complexes and converting substrates into products. Each enzyme has a recommended name based on its substrate or action, and a systematic name describing its chemical reaction. Enzyme activity can be regulated by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and allosteric effectors. Covalent modifications and controlling enzyme synthesis levels also regulate activity.
Enzymes 

Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biological reactions. They do this by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing substrates to more easily react and form products. Enzymes have a specific active site where substrates bind so they can catalyze reactions. While enzymes speed up reactions, their activity can be affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and inhibitor concentration, and cofactors.
Enzymes

This document provides an overview of enzymes. It discusses that enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions in living cells without changing themselves. The document describes the different components of enzyme molecules, including the protein component called the apoenzyme and various cofactors that can be organic compounds, inorganic ions, or prosthetic groups. It also discusses the active site of enzymes and mechanisms of enzyme action, such as induced fit and lock and key models. Additionally, it covers factors that affect enzyme activity like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration. The document summarizes different types of enzyme inhibition including competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive inhibition. Finally, it discusses mechanisms of regulating enzyme activity, including controlling enzyme
Enzyme And Metabolism

This document provides an overview of enzymes and metabolism. It defines enzymes as proteins that catalyze chemical reactions and discusses the lock-and-key and induced-fit models of enzyme action. It also explains factors that influence enzyme activity such as pH and temperature, and describes the roles of coenzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
Enzyme activity

This document discusses enzymes and their catalytic properties. It begins by explaining that enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions by lowering their activation energy. It then discusses the chemical nature of enzymes as proteins made of amino acid chains. The document covers several factors that affect enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, and concentration of enzymes and substrates. It also discusses enzyme specificity and inhibition. Key terms related to enzymes and their reactions are defined.
Enzymes

Here are the comparisons requested:
Noncompetitive inhibition vs allosteric inhibition:
- Both involve binding at a site other than the active site
- However, noncompetitive inhibition directly alters the active site conformation, while allosteric inhibition induces a conformational change through binding at a distant allosteric site
Allosteric activation vs cooperativity:
- Both amplify the enzyme's response to substrates by inducing favorable conformational changes
- However, allosteric activation involves binding of an activator at an allosteric site, while cooperativity occurs through substrate binding and involves interactions between subunits rather than an allosteric effector
So in summary, noncompetitive vs allosteric inhibition compare different
ENZYMES Quick Study Notes Slides.pptx

Enzymes are usually proteins that act as catalysts for specific biochemical reactions. They facilitate reactions by lowering their activation energy. Most enzymes have globular structures and contain active sites that allow substrates to bind. Enzymes can be made only of proteins or can require cofactors like coenzymes or metal ions. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration. Enzymes demonstrate specificity for their reactions and substrates. They are regulated by inhibition or through feedback control involving allosteric enzymes and zymogens.
Kuliah biokimia enzim

This document summarizes key concepts about enzymes including:
1) Enzymes work as catalysts to lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions and increase reaction rates. They specifically bind to substrates in their active sites.
2) Environmental factors like temperature and pH can impact enzyme activity by causing enzyme denaturation at extreme levels.
3) Enzyme activity is regulated by various mechanisms including allosteric regulation, covalent modification through phosphorylation, and proteolytic activation of zymogens to active enzymes.
biochemist 5.pptx

Cellular metabolism involves enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions that break down nutrients to acquire energy for cellular functions. It consists of catabolic pathways that break down molecules and release energy (catabolism), and anabolic pathways that use energy to synthesize complex molecules (anabolism). The main catabolic pathway is cellular respiration, which includes glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and partially breaks down glucose, producing ATP. The Krebs cycle and electron transport chain occur in the mitochondria and completely oxidize pyruvate and other fuel molecules, generating much more ATP through oxidative phosphorylation as electrons are transferred to oxygen.
Kinetics of enzyme activity SlideShare

Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, increasing the rate of reactions without being used up. The Michaelis-Menten model describes enzyme kinetics, including the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) and substrate concentration when the reaction is at half Vmax (Km). Factors like temperature and pH affect enzyme activity, with optimal temperatures and pH levels before heat denatures the enzyme or pH changes disrupt its structure. Enzyme inhibitors decrease reaction rates by binding to the enzyme's active site (competitive) or altering its structure (non-competitive, uncompetitive).
enzymes-160517003157.pptxbiochemistryyyy

This document discusses enzymes and their properties. It begins by explaining that enzymes are biological catalysts that are usually proteins and that speed up biochemical reactions. It describes enzyme structure, including the active site where substrates bind. It discusses cofactors that enzymes require to function properly. The document then explains enzyme kinetics concepts like Michaelis-Menten kinetics and how temperature, pH, and substrate concentration affect reaction rates. Finally, it covers inhibition, where inhibitors bind enzymes and decrease their activity, and activation, where enzymes are converted to more active forms.
Enzymes

Contents:
Enzymes Terminologies
Enzymes Properties
Mechanism Of Enzyme Action
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Inhibition Of Enzyme
Regulation Of Enzyme Activity
2 Enzymes lec .ppt

Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions through their active sites, which bind specifically to substrate molecules. The "lock and key" and "induced fit" models describe this binding. The basic mechanism involves formation of an enzyme-substrate complex, followed by product release. Enzyme activity is affected by concentration, temperature, pH, and inhibitors. Optimum activity occurs within a limited range for each factor to prevent denaturation. Inhibitors can be competitive, noncompetitive, or uncompetitive, and reversible or irreversible.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve specificity by fitting substrates into their active sites. Enzyme activity is regulated through various mechanisms including feedback inhibition, cofactors, pH, temperature, and allosteric regulation. Inhibitors bind enzymes to reduce their activity, either reversibly or irreversibly. Enzymes have many applications in medicine including diagnostics, analytical tests, and enzyme replacement therapy.
Similar to Enzymes notes, enzyme chapter (20)
2024_Chapter_4_Edited_Cellular_Metabolism_and_Metabolic_Disorders (4).pptx

2024_Chapter_4_Edited_Cellular_Metabolism_and_Metabolic_Disorders (4).pptx
More from sandeep chandakavate
Clinical pharmacy management 

The document is a certificate stating that a student named Mr/Miss [name] with registration number [number] of the second year Diploma in Pharmacy program at Shri Sangameshwar College of Pharmacy has satisfactorily completed the required term work in Community Pharmacy & Management for the academic years [year] to [year] as prescribed in the curriculum. It is signed by the subject teacher and principal.
Pharmacology d.pharm practical manual

This certificate certifies that Mr/Miss [name] has completed the term work satisfactorily in Pharmacology for the academic year 20[xx] to 20[xx] as a second year student pursuing a Diploma in Pharmacy from SHRI SANGAMESHWAR COLLEGE OF PHARMACY SINDAGI with Register Number [number]. The certificate is signed by the Subject Teacher and Principal.
biochemistry Record book

The document is a certificate confirming that a student named Mr/Miss [name] completed their term work satisfactorily in Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology for the academic year 20[xx] to 20[xx] at SHRI SANGAMESHWAR COLLEGE OF PHARMACY SINDAGI. It is signed by the subject teacher and principal. The following pages provide details of experiments conducted, including introduction to carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids as well as various chemical identification tests and estimations performed on samples like urine, serum, and blood. Key tests mentioned include Molisch's test, Fehling's test, and Benedict's test for detecting the presence of carbohydrates.
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM

The cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels. The heart pumps blood into vessels that circulate it throughout the body to supply nutrients and oxygen and remove waste. The heart has four chambers - the right and left atria receive blood, and the right and left ventricles pump it out. Valves ensure blood flows in only one direction. The conduction system initiates and coordinates heart contractions. Cardiovascular disorders disrupt blood flow and heart function, while vessel disorders involve blockages or damage.
Proteins and amino Acids

Proteins are the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and are made up of amino acids. They perform many important structural and functional roles. There are three main levels of protein structure - primary, secondary, and tertiary. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. The secondary structure involves twisting of the chain into shapes like alpha helices and beta pleated sheets. Tertiary structure refers to the 3D conformation that a protein folds into. Some proteins have quaternary structure which involves the spatial arrangement of multiple polypeptide subunits.
biochemistry_labmannual_D.pharmacy

All d.pharmacy 2nd year printed lab record books available contact for more details 9663081078.
As per PCI syllabus d.pharm 2nd year
Vitamins and Thier functions chemistry

Vitamins are organic compounds required in small amounts for normal growth, health and biological functions. They are classified as either fat-soluble (A, D, E, K) or water-soluble (C, B vitamins). Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed with fats and stored in tissues while water-soluble vitamins are not stored and must be continuously supplied. Each vitamin plays important roles as enzyme cofactors in critical biochemical reactions related to energy production, cell growth, immune function and more. The document provides details on the chemistry, sources, functions and requirements of several key vitamins.
Alzheimer disease

Neurodegenerative disorders are characterized by the progressive and irreversible loss of neurons in specific brain regions. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia and results from the loss of neurons in the hippocampus and cortex, leading to impairments in memory and cognitive ability. The hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease are extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles composed of tau protein. Risk factors for the disease are unknown but it is associated with brain shrinkage and neuronal loss, particularly in the hippocampus and basal forebrain. Symptoms include confusion, memory loss, impaired judgment, and personality changes.
Local anaesthetics

Local anesthetics are drugs that cause reversible loss of sensation, especially pain, in a localized area when applied topically or injected. They work by blocking sodium channels in nerve cell membranes, preventing the transmission of nerve impulses. There are two main types - esters which are metabolized rapidly and amides which have a longer duration due to slower hepatic metabolism. Common local anesthetics include lidocaine, bupivacaine, cocaine, and procaine. They have various medical uses such as nerve blocks, infiltration anesthesia, surface anesthesia and conduction blocks.
Anti Parkinsonism (PD)

Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder caused by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra. This results in reduced dopamine levels in the striatum, leading to symptoms like rigidity, tremor, and hypokinesia. Current treatment options aim to increase dopamine levels by using levodopa, dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, COMT inhibitors, or drugs like amantadine that facilitate dopamine transmission. Adverse effects include nausea, hypotension, dyskinesias, and behavioral changes with long term use.
Diuretics

This document provides an overview of diuretics, including their classification, mechanisms of action, pharmacology, and uses. It discusses urine formation through the nephron and covers various diuretic drug classes like carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, loop diuretics, thiazides, and potassium-sparing diuretics. Key points include that diuretics act primarily by inhibiting sodium transport at different nephron sites and that their primary effects impact electrolyte excretion patterns and secondary effects.
Local anaesthesia..

The document discusses local anesthetics, including their definition, properties, advantages and disadvantages, classification, mechanism of action, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, and uses. It defines local anesthesia as a loss of sensation in a circumscribed area caused by nerve ending depression or peripheral nerve conduction inhibition. It lists 10 important properties of local anesthetics like being non-irritating, not causing permanent nerve alterations, having low systemic toxicity, rapid onset, and long enough duration. The pharmacokinetics section notes that local anesthetics all cause vasodilation except cocaine, which increases absorption rate and potential toxicity.
Absorption

1) Pharmacokinetics is the quantitative study of how the body acts on drugs by examining drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion. Understanding a drug's pharmacokinetic properties helps determine dosing parameters like dosage, frequency and route of administration.
2) Drugs can be absorbed into the body through various transport mechanisms across membranes, including passive diffusion down a concentration gradient, active transport against a gradient using ATP, and carrier-mediated transport using transport proteins.
3) The three main categories of drug absorption are transcellular transport across cells, paracellular transport between cells, and endocytosis within vesicles. The document provides details on the mechanisms involved in each category.
Transgenic animals.

Transgenic animals are defined as animals that have had changes made to their genome through genetic engineering techniques. This document discusses transgenic animals, providing examples of transgenic animals such as mice and pigs that have been genetically modified. It also covers the production, maintenance, and applications of transgenic animals.
More from sandeep chandakavate (14)
Recently uploaded
Physiology of Special Chemical Sensation of Taste

Title: Sense of Taste
Presenter: Dr. Faiza, Assistant Professor of Physiology
Qualifications:
MBBS (Best Graduate, AIMC Lahore)
FCPS Physiology
ICMT, CHPE, DHPE (STMU)
MPH (GC University, Faisalabad)
MBA (Virtual University of Pakistan)
Learning Objectives:
Describe the structure and function of taste buds.
Describe the relationship between the taste threshold and taste index of common substances.
Explain the chemical basis and signal transduction of taste perception for each type of primary taste sensation.
Recognize different abnormalities of taste perception and their causes.
Key Topics:
Significance of Taste Sensation:
Differentiation between pleasant and harmful food
Influence on behavior
Selection of food based on metabolic needs
Receptors of Taste:
Taste buds on the tongue
Influence of sense of smell, texture of food, and pain stimulation (e.g., by pepper)
Primary and Secondary Taste Sensations:
Primary taste sensations: Sweet, Sour, Salty, Bitter, Umami
Chemical basis and signal transduction mechanisms for each taste
Taste Threshold and Index:
Taste threshold values for Sweet (sucrose), Salty (NaCl), Sour (HCl), and Bitter (Quinine)
Taste index relationship: Inversely proportional to taste threshold
Taste Blindness:
Inability to taste certain substances, particularly thiourea compounds
Example: Phenylthiocarbamide
Structure and Function of Taste Buds:
Composition: Epithelial cells, Sustentacular/Supporting cells, Taste cells, Basal cells
Features: Taste pores, Taste hairs/microvilli, and Taste nerve fibers
Location of Taste Buds:
Found in papillae of the tongue (Fungiform, Circumvallate, Foliate)
Also present on the palate, tonsillar pillars, epiglottis, and proximal esophagus
Mechanism of Taste Stimulation:
Interaction of taste substances with receptors on microvilli
Signal transduction pathways for Umami, Sweet, Bitter, Sour, and Salty tastes
Taste Sensitivity and Adaptation:
Decrease in sensitivity with age
Rapid adaptation of taste sensation
Role of Saliva in Taste:
Dissolution of tastants to reach receptors
Washing away the stimulus
Taste Preferences and Aversions:
Mechanisms behind taste preference and aversion
Influence of receptors and neural pathways
Impact of Sensory Nerve Damage:
Degeneration of taste buds if the sensory nerve fiber is cut
Abnormalities of Taste Detection:
Conditions: Ageusia, Hypogeusia, Dysgeusia (parageusia)
Causes: Nerve damage, neurological disorders, infections, poor oral hygiene, adverse drug effects, deficiencies, aging, tobacco use, altered neurotransmitter levels
Neurotransmitters and Taste Threshold:
Effects of serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) on taste sensitivity
Supertasters:
25% of the population with heightened sensitivity to taste, especially bitterness
Increased number of fungiform papillae
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidadeProf. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
Recomendações da OMS sobre cuidados maternos e neonatais para uma experiência pós-natal positiva.
Em consonância com os ODS – Objetivos do Desenvolvimento Sustentável e a Estratégia Global para a Saúde das Mulheres, Crianças e Adolescentes, e aplicando uma abordagem baseada nos direitos humanos, os esforços de cuidados pós-natais devem expandir-se para além da cobertura e da simples sobrevivência, de modo a incluir cuidados de qualidade.
Estas diretrizes visam melhorar a qualidade dos cuidados pós-natais essenciais e de rotina prestados às mulheres e aos recém-nascidos, com o objetivo final de melhorar a saúde e o bem-estar materno e neonatal.
Uma “experiência pós-natal positiva” é um resultado importante para todas as mulheres que dão à luz e para os seus recém-nascidos, estabelecendo as bases para a melhoria da saúde e do bem-estar a curto e longo prazo. Uma experiência pós-natal positiva é definida como aquela em que as mulheres, pessoas que gestam, os recém-nascidos, os casais, os pais, os cuidadores e as famílias recebem informação consistente, garantia e apoio de profissionais de saúde motivados; e onde um sistema de saúde flexível e com recursos reconheça as necessidades das mulheres e dos bebês e respeite o seu contexto cultural.
Estas diretrizes consolidadas apresentam algumas recomendações novas e já bem fundamentadas sobre cuidados pós-natais de rotina para mulheres e neonatos que recebem cuidados no pós-parto em unidades de saúde ou na comunidade, independentemente dos recursos disponíveis.
É fornecido um conjunto abrangente de recomendações para cuidados durante o período puerperal, com ênfase nos cuidados essenciais que todas as mulheres e recém-nascidos devem receber, e com a devida atenção à qualidade dos cuidados; isto é, a entrega e a experiência do cuidado recebido. Estas diretrizes atualizam e ampliam as recomendações da OMS de 2014 sobre cuidados pós-natais da mãe e do recém-nascido e complementam as atuais diretrizes da OMS sobre a gestão de complicações pós-natais.
O estabelecimento da amamentação e o manejo das principais intercorrências é contemplada.
Recomendamos muito.
Vamos discutir essas recomendações no nosso curso de pós-graduação em Aleitamento no Instituto Ciclos.
Esta publicação só está disponível em inglês até o momento.
Prof. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
www.agostodourado.com
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
Knee anatomy and clinical tests 2024.pdf

This includes all relevant anatomy and clinical tests compiled from standard textbooks, Campbell,netter etc..It is comprehensive and best suited for orthopaedicians and orthopaedic residents.
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA in pediatrics part one.

Abdominal trauma in pediatrics refers to injuries or damage to the abdominal organs in children. It can occur due to various causes such as falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports-related injuries, and physical abuse. Children are more vulnerable to abdominal trauma due to their unique anatomical and physiological characteristics. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness, distension, vomiting, and signs of shock. Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Management depends on the severity and may involve conservative treatment or surgical intervention. Prevention is crucial in reducing the incidence of abdominal trauma in children.
Efficacy of Avartana Sneha in Ayurveda

Avartana Sneha is a unique method of Preparation of Sneha Kalpana in Ayurveda, mainly it is indicated for the Vataja rogas.
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition TEST BANK by Stamler Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Study Guide Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Course Hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Answers Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Course hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Study Guide Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Ebook Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Questions Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Stuvia
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx

Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptxMGM SCHOOL/COLLEGE OF NURSING
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach

Explore the benefits of combining Ayurveda with conventional Parkinson's treatments. Learn how a holistic approach can manage symptoms, enhance well-being, and balance body energies. Discover the steps to safely integrate Ayurvedic practices into your Parkinson’s care plan, including expert guidance on diet, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications.
Adhd Medication Shortage Uk - trinexpharmacy.com

The UK is currently facing a Adhd Medication Shortage Uk, which has left many patients and their families grappling with uncertainty and frustration. ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a chronic condition that requires consistent medication to manage effectively. This shortage has highlighted the critical role these medications play in the daily lives of those affected by ADHD. Contact : +1 (747) 209 – 3649 E-mail : sales@trinexpharmacy.com
Top-Vitamin-Supplement-Brands-in-India List

Swisschem Dermacare provides the Top 10 Vitamin Supplement Brands in India. To know more about us give us call at our official number
How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx

STIs may cause PID. For the both disease, herbal medicine Fuyan Pill can be a solution.
Journal Article Review on Rasamanikya

Rasamanikya is a excellent preparation in the field of Rasashastra, it is used in various Kushtha Roga, Shwasa, Vicharchika, Bhagandara, Vatarakta, and Phiranga Roga. In this article Preparation& Comparative analytical profile for both Formulationon i.e Rasamanikya prepared by Kushmanda swarasa & Churnodhaka Shodita Haratala. The study aims to provide insights into the comparative efficacy and analytical aspects of these formulations for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
The Electrocardiogram - Physiologic Principles

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a quick overview of the physiological basis of a normal electrocardiogram.
Learning objectives:
1. Define an electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrocardiography
2. Describe how dipoles generated by the heart produce the waveforms of the ECG
3. Describe the components of a normal electrocardiogram of a typical bipolar lead (limb II)
4. Differentiate between intervals and segments
5. Enlist some common indications for obtaining an ECG
6. Describe the flow of current around the heart during the cardiac cycle
7. Discuss the placement and polarity of the leads of electrocardiograph
8. Describe the normal electrocardiograms recorded from the limb leads and explain the physiological basis of the different records that are obtained
9. Define mean electrical vector (axis) of the heart and give the normal range
10. Define the mean QRS vector
11. Describe the axes of leads (hexagonal reference system)
12. Comprehend the vectorial analysis of the normal ECG
13. Determine the mean electrical axis of the ventricular QRS and appreciate the mean axis deviation
14. Explain the concepts of current of injury, J point, and their significance
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 11, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 9, Human Physiology - From Cells to Systems, Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
3. Chapter 29, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
4. Electrocardiogram, StatPearls - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549803/
5. ECG in Medical Practice by ABM Abdullah, 4th edition
6. Chapter 3, Cardiology Explained, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2214/
7. ECG Basics, http://www.nataliescasebook.com/tag/e-c-g-basics
Recently uploaded (20)
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx

Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx
Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach

Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach
How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx

How STIs Influence the Development of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.pptx
Enzymes notes, enzyme chapter
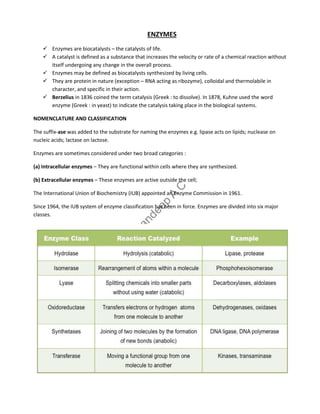
- 1. ENZYMES Enzymes are biocatalysts – the catalysts of life. A catalyst is defined as a substance that increases the velocity or rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any change in the overall process. Enzymes may be defined as biocatalysts synthesized by living cells. They are protein in nature (exception – RNA acting as ribozyme), colloidal and thermolabile in character, and specific in their action. Berzelius in 1836 coined the term catalysis (Greek : to dissolve). In 1878, Kuhne used the word enzyme (Greek : in yeast) to indicate the catalysis taking place in the biological systems. NOMENCLATURE AND CLASSIFICATION The suffix-ase was added to the substrate for naming the enzymes e.g. lipase acts on lipids; nuclease on nucleic acids; lactase on lactose. Enzymes are sometimes considered under two broad categories : (a) Intracellular enzymes – They are functional within cells where they are synthesized. (b) Extracellular enzymes – These enzymes are active outside the cell; The International Union of Biochemistry (IUB) appointed an Enzyme Commission in 1961. Since 1964, the IUB system of enzyme classification has been in force. Enzymes are divided into six major classes.
- 2. 1. Oxidoreductases : Enzymes involved in oxidation-reduction reactions. 2. Transferases : Enzymes that catalyse the transfer of functional groups. 3. Hydrolases : Enzymes that bring about hydrolysis of various compounds. 4. Lyases : Enzymes specialised in the addition or removal of water, ammonia, CO2 etc. 5. Isomerases : Enzymes involved in all the isomerization reactions. 6. Ligases : Enzymes catalysing the synthetic reactions (Greek : ligate—to bind) where two molecules are joined together and ATP is used. PROPERTIES OF ENZYMES All the enzymes are invariably proteins. Each enzyme has its own tertiary structure and specific conformation which is very essential for its catalytic activity. The functional unit of the enzyme is known as holoenzyme The enzyme is made up of apoenzyme (the protein part) and a coenzyme (non-protein organic part). Holoenzyme Apoenzyme + Coenzyme (active enzyme) (protein part) (non-protein part) FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYME ACTIVITY 1. Concentration of enzyme - As the concentration of the enzyme is increased, the velocity of the reaction proportionately increases. 2. Concentration of substrate - Increase in the substrate concentration gradually increases the velocity of enzyme reaction within the limited range of substrate levels.
- 3. 3. Effect of temperature - Velocity of an enzyme reaction increases with increase in temperature up to a maximum and then declines. A bell-shaped curve is usually observed. 4. Effect of pH - Increase in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH) considerably influences the enzyme activity and a bell-shaped curve is normally obtained. 5. Effect of product concentration - The accumulation of reaction products generally decreases the enzyme velocity. 6. Effect of activators - Some of the enzymes require certain inorganic metallic cations like Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Na+, K+ etc. for their optimum activity. Rarely, anions are also needed for enzyme activity. 7. Effect of time - Under ideal and optimal conditions (like pH, temperature etc.), the time required for an enzyme reaction is less. Variations in the time of the reaction are generally related to the alterations in pH and temperature. ACTIVE SITE The active site (or active centre) of an enzyme represents as the small region at which the substrate(s) binds and participates in the catalysis. Salient features of active site The existence of active site is due to the tertiary structure of protein resulting in three- dimensional native conformation.
- 4. The active site is made up of amino acids (known as catalytic residues) which are far from each other in the linear sequence of amino acids. Active sites are regarded as clefts or crevices or pockets occupying a small region in a big enzyme molecule. The active site is not rigid in structure and shape. It is rather flexible to promote the specific substrate binding. Generally, the active site possesses a substrate binding site and a catalytic site. The coenzymes or cofactors on which some enzymes depend are present as a part of the catalytic site. The substrate(s) binds at the active site by weak noncovalent bonds. Enzymes are specific in their function due to the existence of active sites. ENZYME INHIBITION Enzyme inhibitor is defined as a substance which binds with the enzyme and brings about a decrease in catalytic activity of that enzyme. The inhibitor may be organic or inorganic in nature. There are three broad categories of enzyme inhibition 1. Reversible inhibition. 2. Irreversible inhibition. 3. Allosteric inhibition. 1. Reversible inhibition The inhibitor binds non-covalently with enzyme and the enzyme inhibition can be reversed if the inhibitor is removed. The reversible inhibition is further sub-divided into I. Competitive inhibition II. Non-competitive inhibition Competitive inhibition : The inhibitor (I) which closely resembles the real substrate (S) is regarded as a substrate analogue. The inhibitor competes with substrate and binds at the active site of the enzyme but does not undergo any catalysis. As long as the competitive inhibitor holds the active site, the enzyme is not available for the substrate to bind. The relative concentration of the substrate and inhibitor and their respective affinity with the enzyme determines the degree of competitive inhibition. In competitive inhibition, the Km value increases whereas Vmax remains unchanged Non-competitive inhibition : The inhibitor binds at a site other than the active site on the enzyme surface. This binding impairs the enzyme function. The inhibitor has no structural resemblance with the substrate. However, there usually exists a strong affinity for the inhibitor to bind at the second site. In fact, the inhibitor does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate binding. But the catalysis is prevented, possibly due to a distortion in the enzyme conformation. Irreversible inhibition - The inhibitors bind covalently with the enzymes and inactivate them, which is irreversible. These inhibitors are usually toxic substances that poison enzymes.
- 5. COENZYMES The non-protein, organic, low molecular weight and dialysable substance associated with enzyme function is known as coenzyme. The protein part of the enzyme, on its own, is not always adequate to bring about the catalytic activity. Many enzymes require certain non- protein small additional factors, collectively referred to as cofactors for catalysis. Coenzymes are second substrates : Coenzymes are often regarded as the second substrates or co- substrates, since they have affinity with the enzyme comparable with that of the substrates. Coenzymes participate in various reactions involving transfer of atoms or groups like hydrogen, aldehyde, keto, amino, acyl, methyl, carbon dioxide etc. MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION Enzymes lower activation energy : The energy required by the reactants to undergo the reaction is known as activation energy. The reactants when heated attain the activation energy. The catalyst (or the enzyme in the biological system) reduces the activation energy and this causes the reaction to proceed at a lower temperature. The enzyme lowers energy barrier of reactants, thereby making the reaction go faster. The prime requisite for enzyme catalysis is that the substrate (S) must combine with the enzyme (E) at the active site to form enzyme- substrate complex (ES) which ultimately results in the product formation (P). MECHANISM OF ENZYME CATALYSIS The formation of an enzyme-substrate complex (ES) is very crucial for the catalysis to occur, and for the product formation. It is estimated that an enzyme catalysed reaction. The enhancement in the rate of the reaction is mainly due to four processes : 1. Acid-base catalysis; 2. Substrate strain; 3. Covalent catalysis; 4. Entropy effects. Isoenzyme - The multiple forms of an enzyme catalyzing the same reaction are isoenzymes or isozymes. They, however, differ in their physical and chemical properties which include the structure, electrophoretic and immunological properties, Km and Vmax values, pH optimum, relative susceptibility to inhibitors and degree of denaturation.