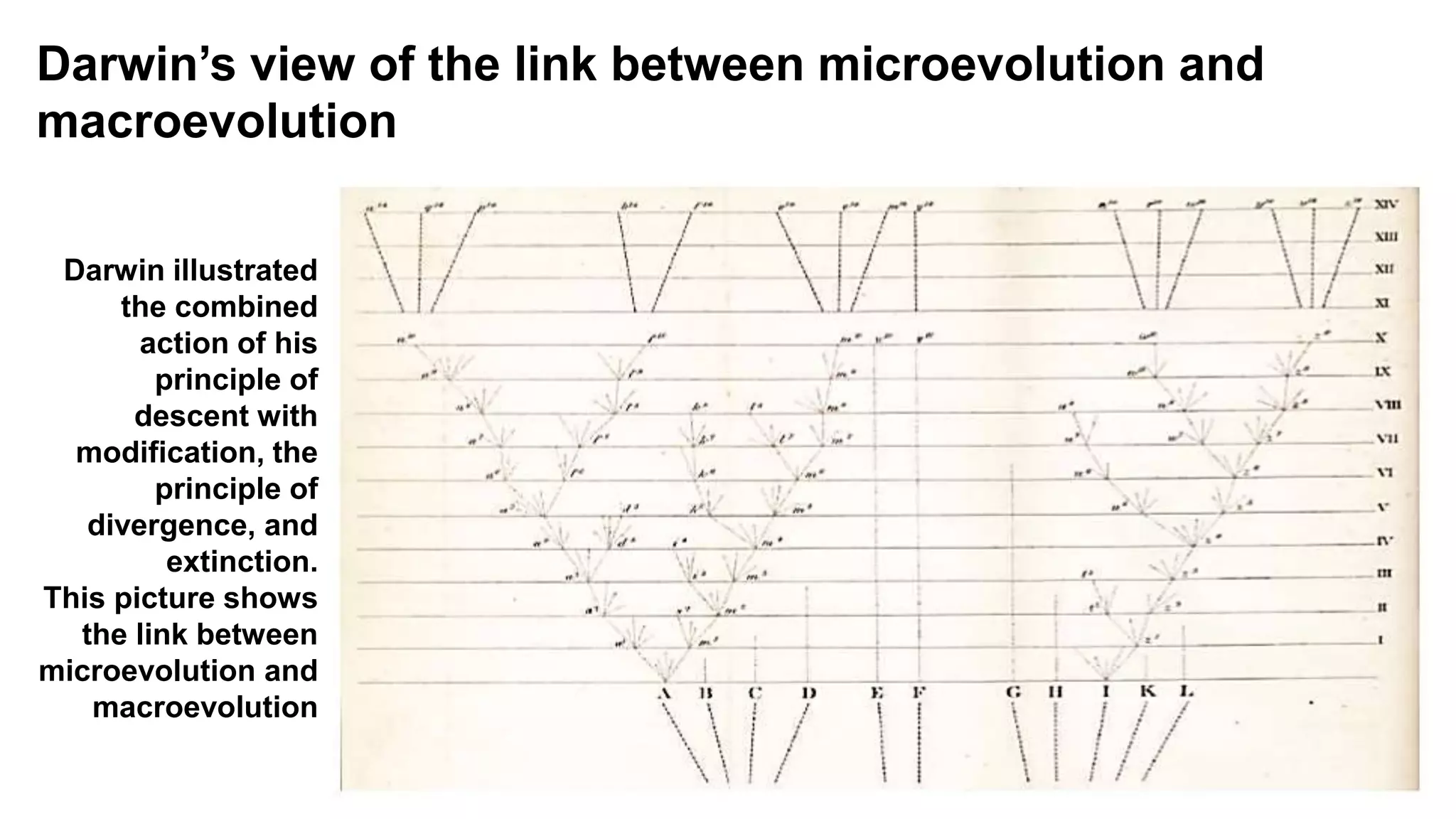
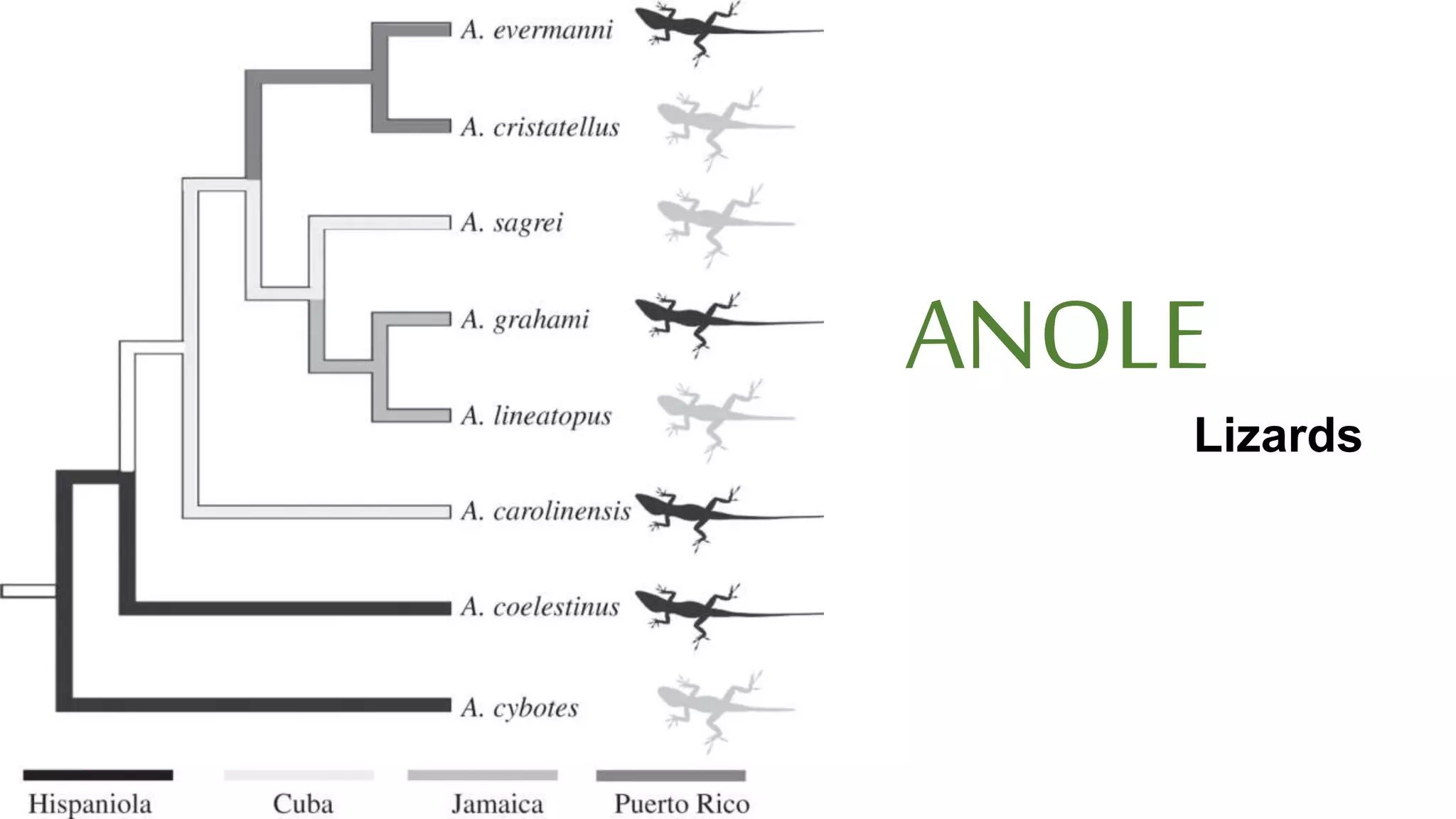
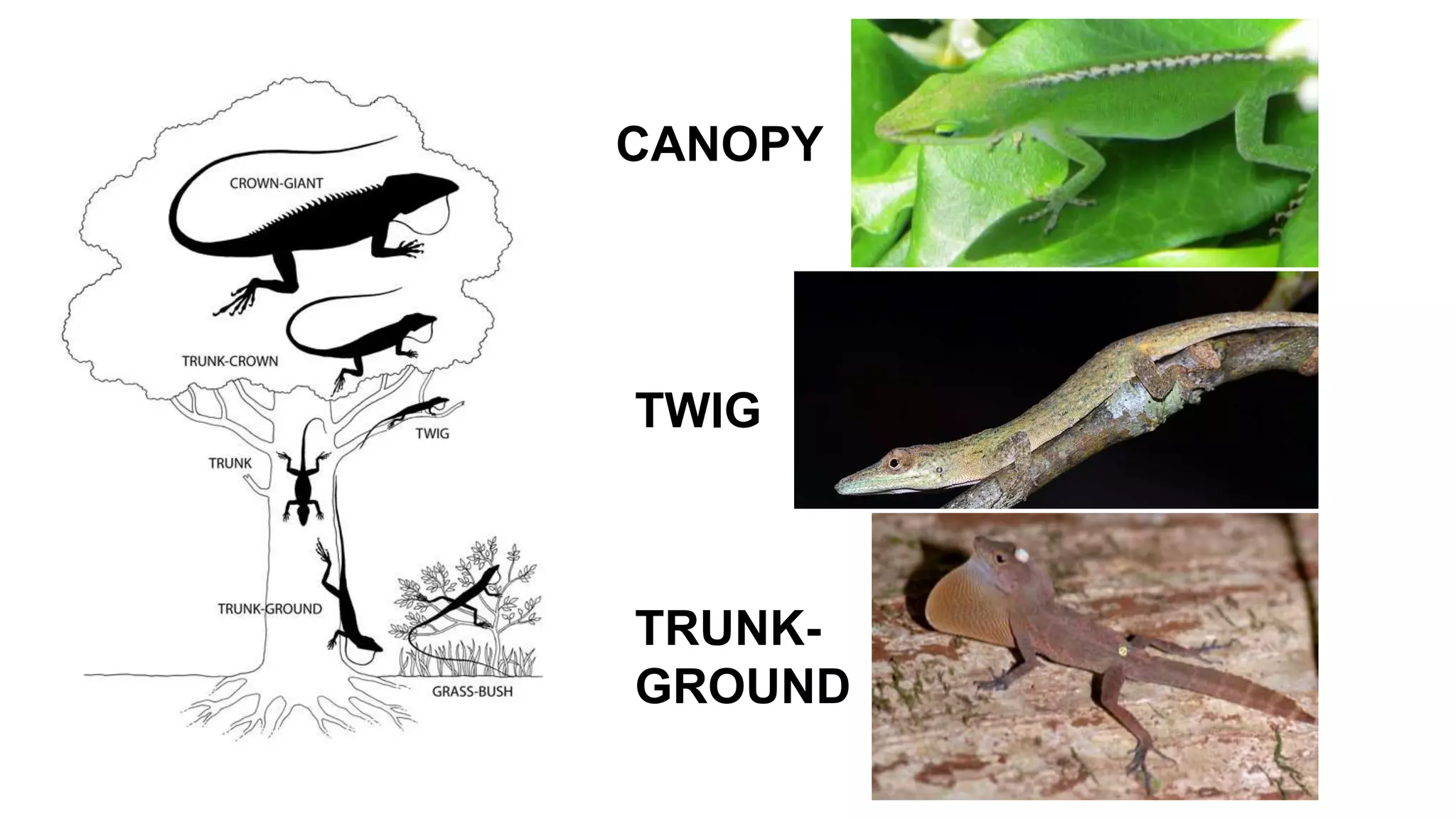
The document discusses Darwin's theories on evolution, emphasizing the relationship between microevolution and macroevolution. It explains concepts such as adaptation, speciation, and extinction, and explores the struggle for existence as a key factor in evolutionary processes. The text also highlights contributions from figures like George Cuvier and Jonathan B. Losos in understanding evolutionary dynamics.