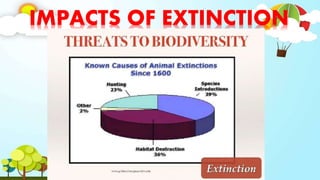
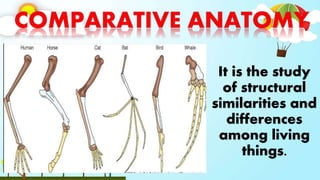
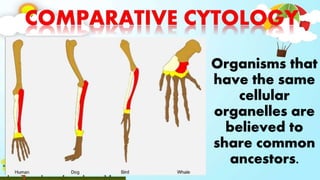
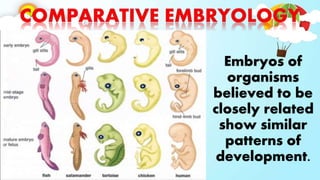
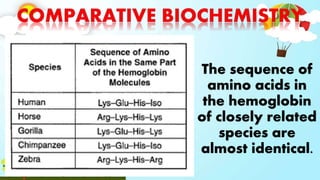
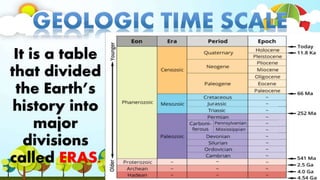
The document discusses biodiversity and the causes and impacts of species extinction. It defines key terms like species diversity, genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, habitat destruction, overhunting, invasive species, pollution, and more. It also discusses the importance of adaptation and how adaptive traits are acquired. The end includes a quiz to test understanding.