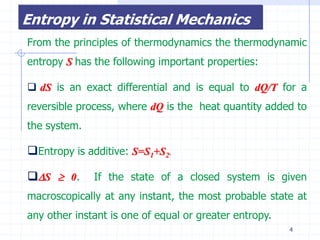
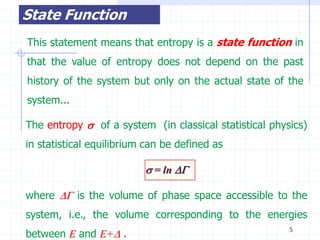
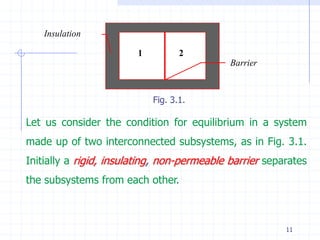
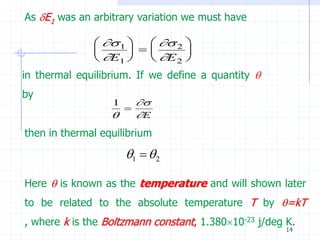
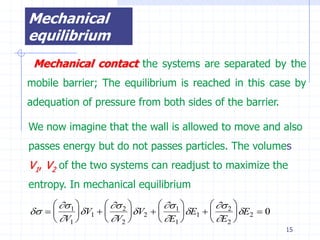
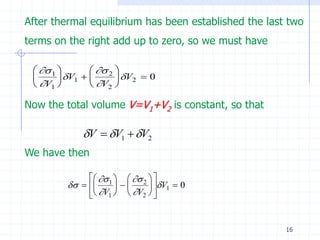
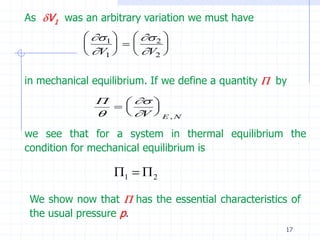
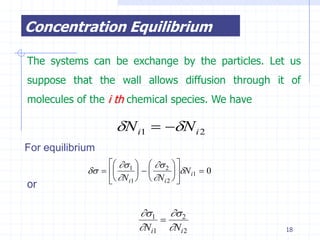
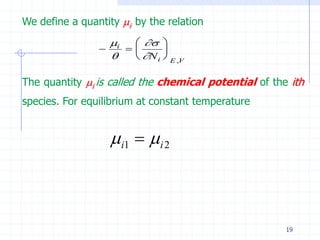
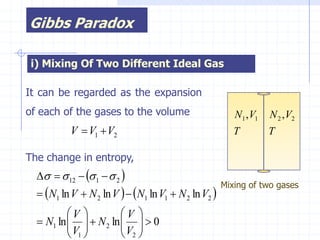
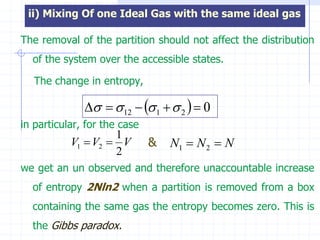
The document discusses entropy from statistical and thermodynamic perspectives. It defines entropy statistically as the natural logarithm of the number of microscopic configurations of a system. The document outlines how entropy is a state function that always increases for irreversible processes according to the second law of thermodynamics. It also discusses how entropy is additive for combined systems and how the conditions of thermal, mechanical, and chemical equilibrium can be defined in terms of entropy being maximized. The Gibbs paradox regarding mixing of ideal gases is also summarized.