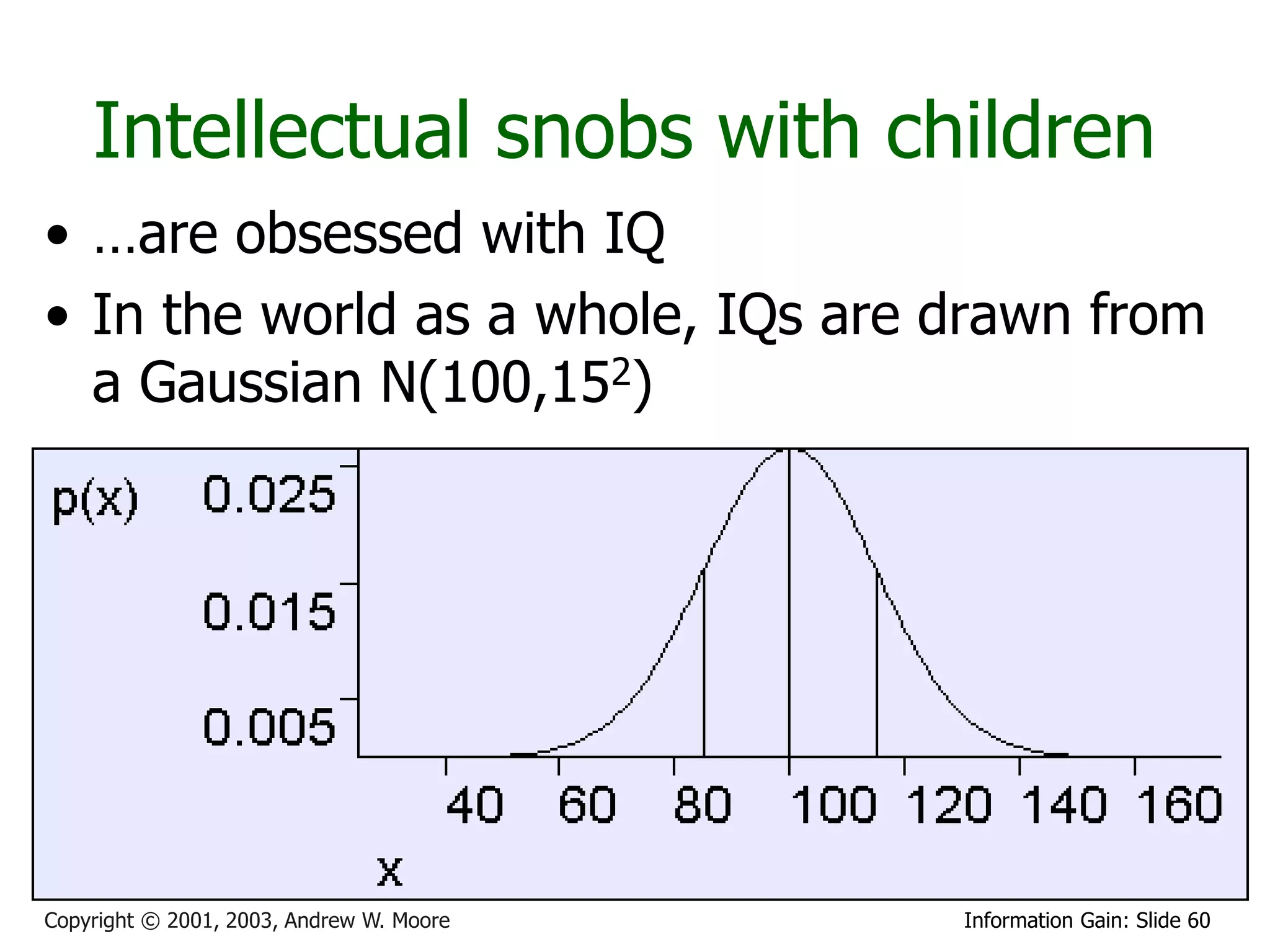
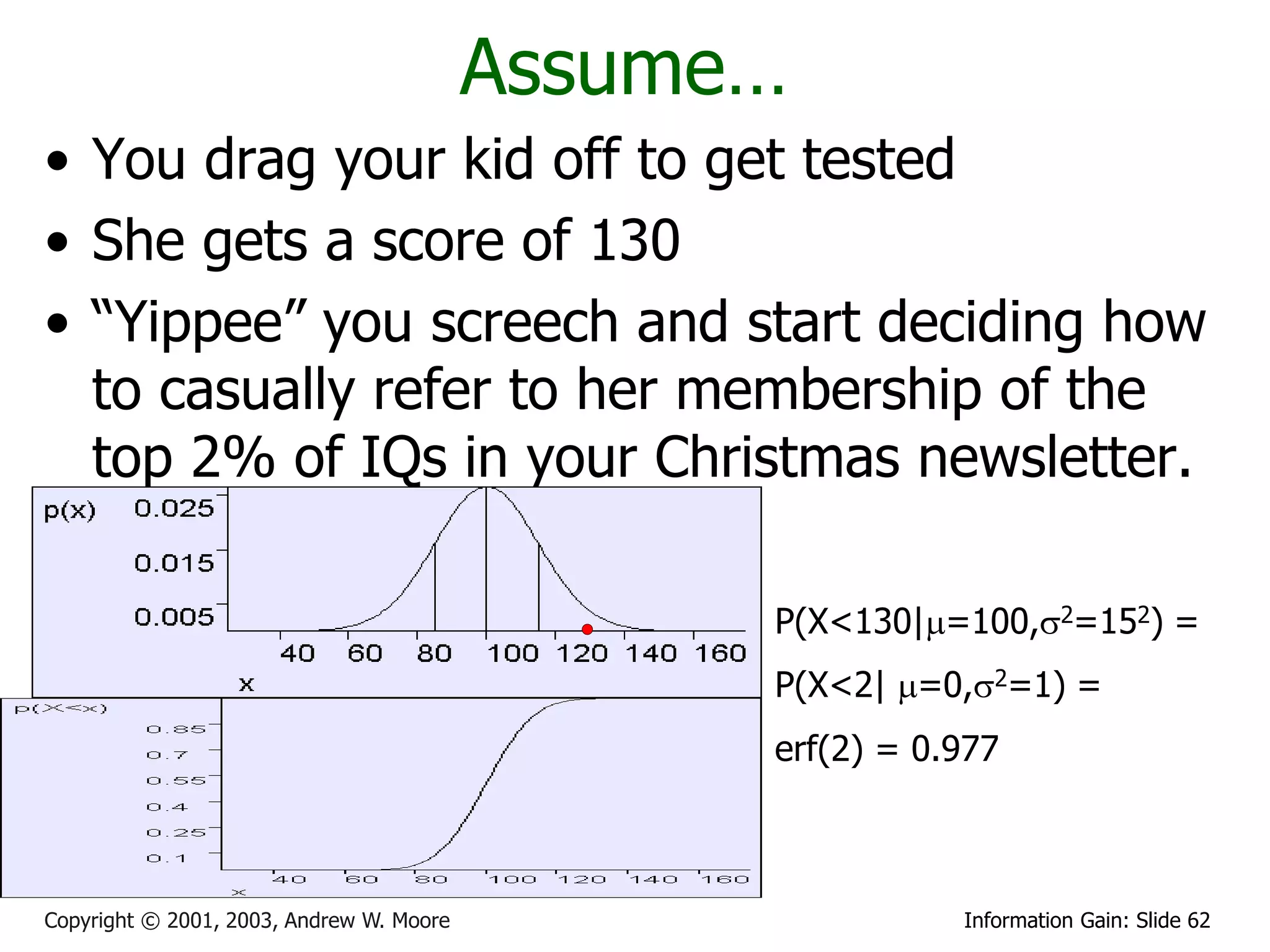
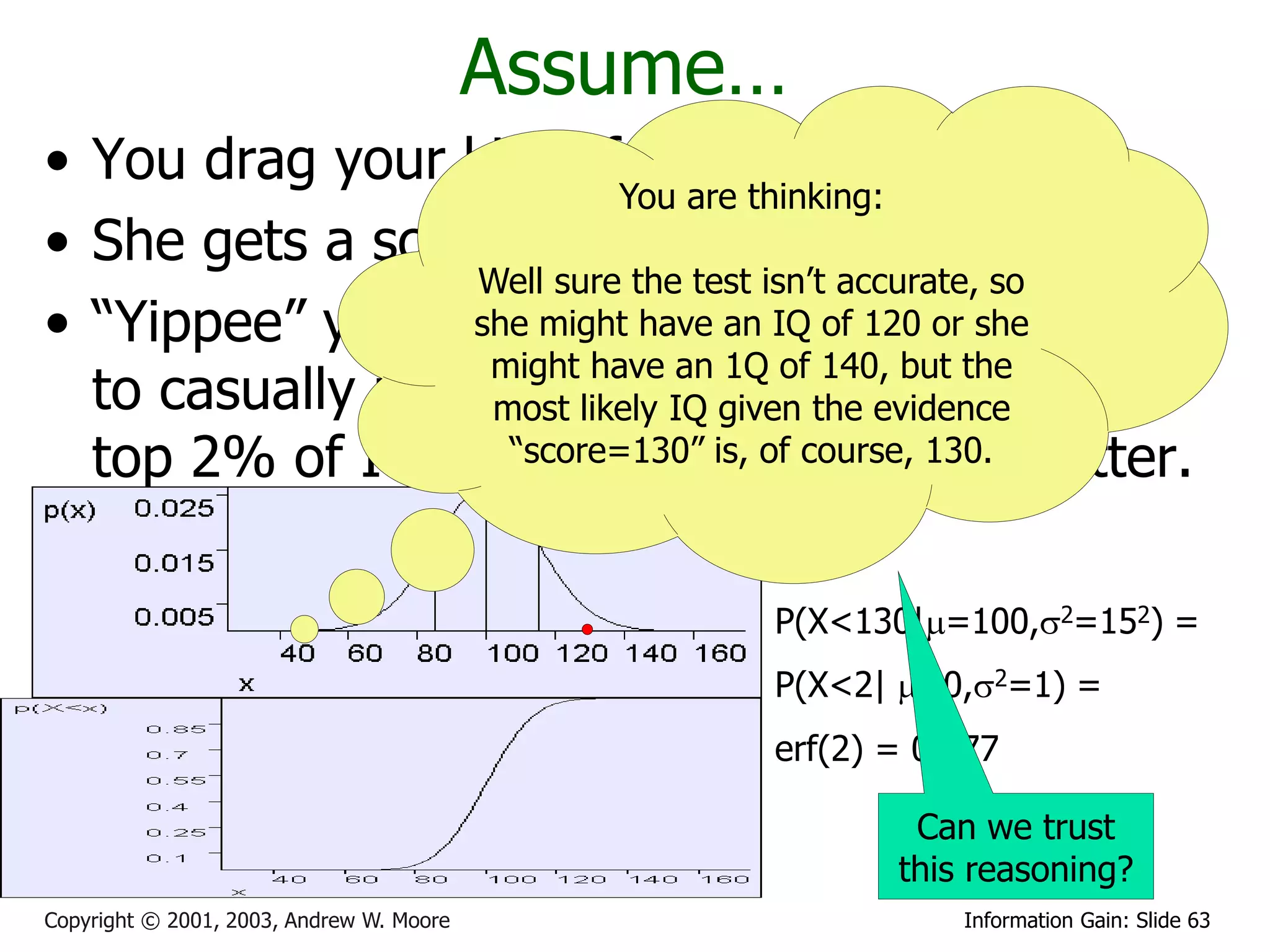
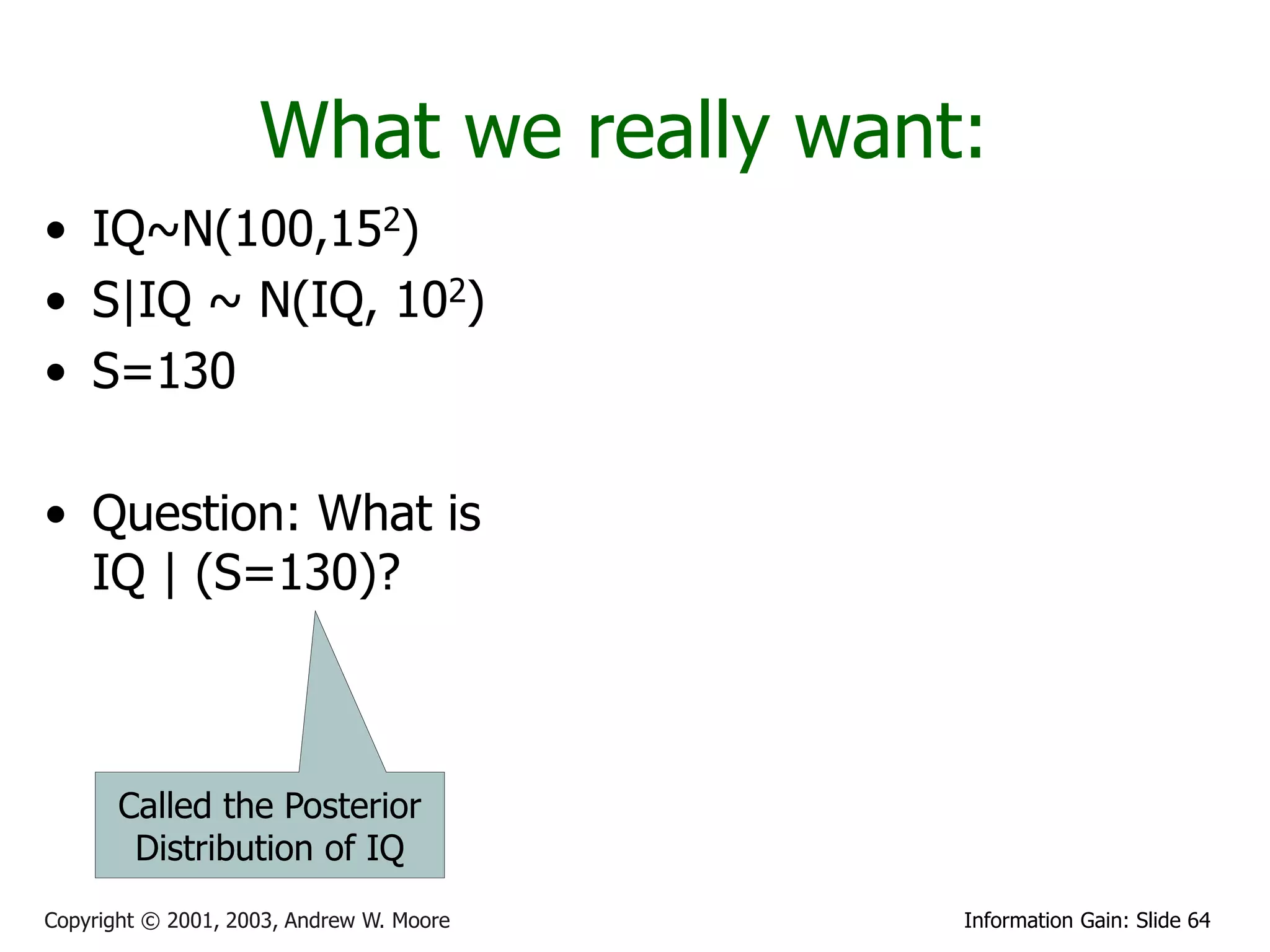
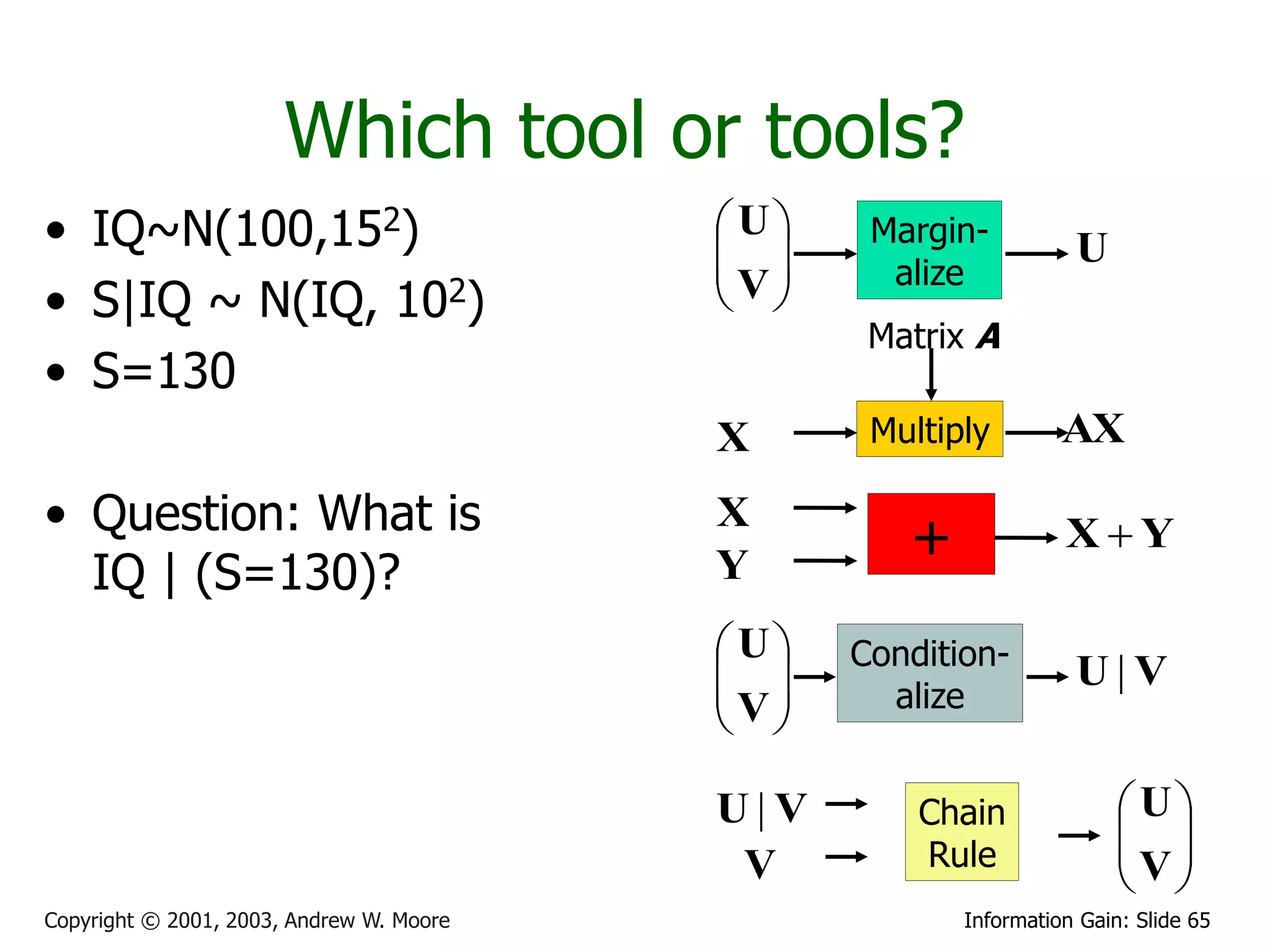
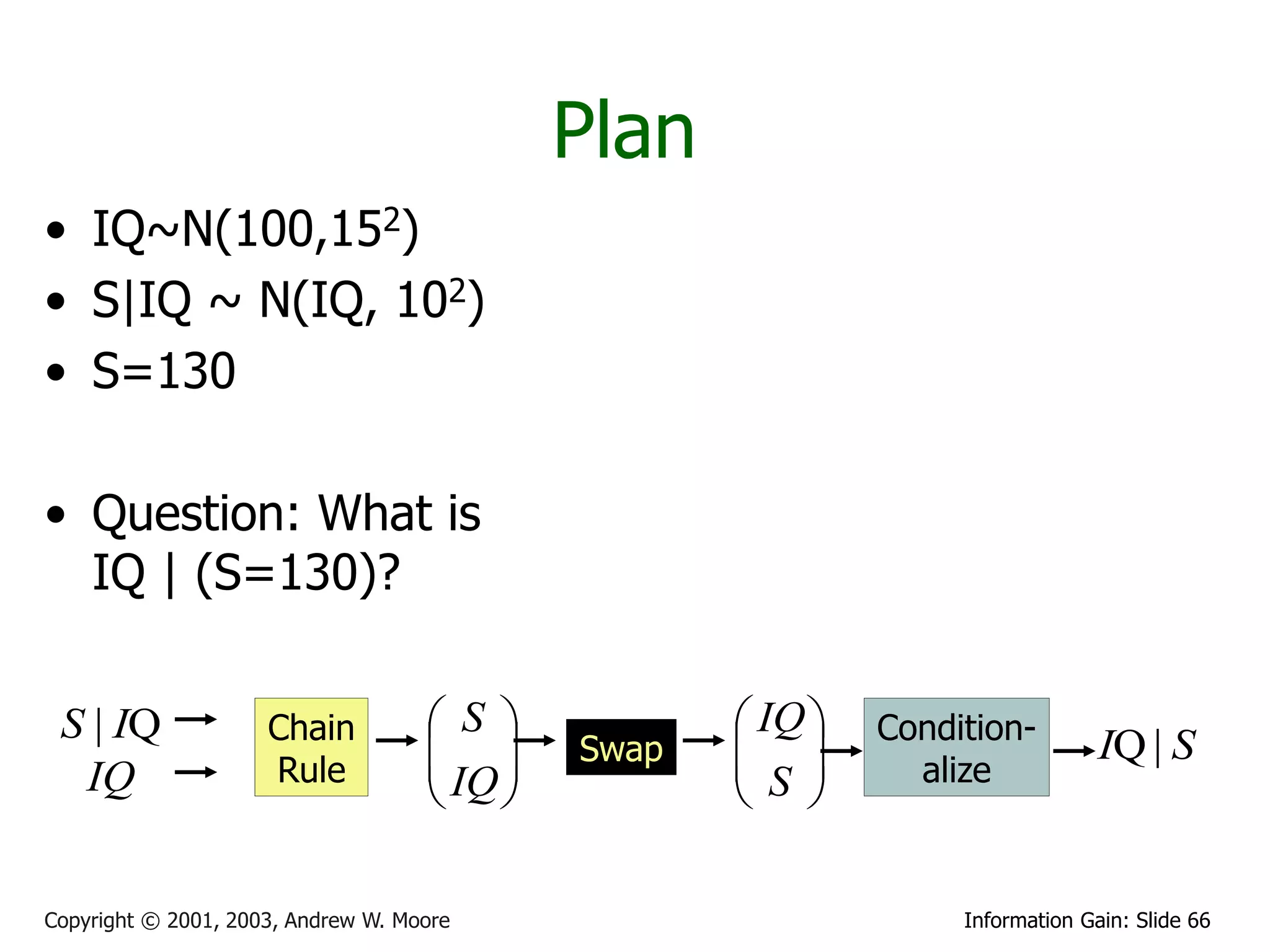
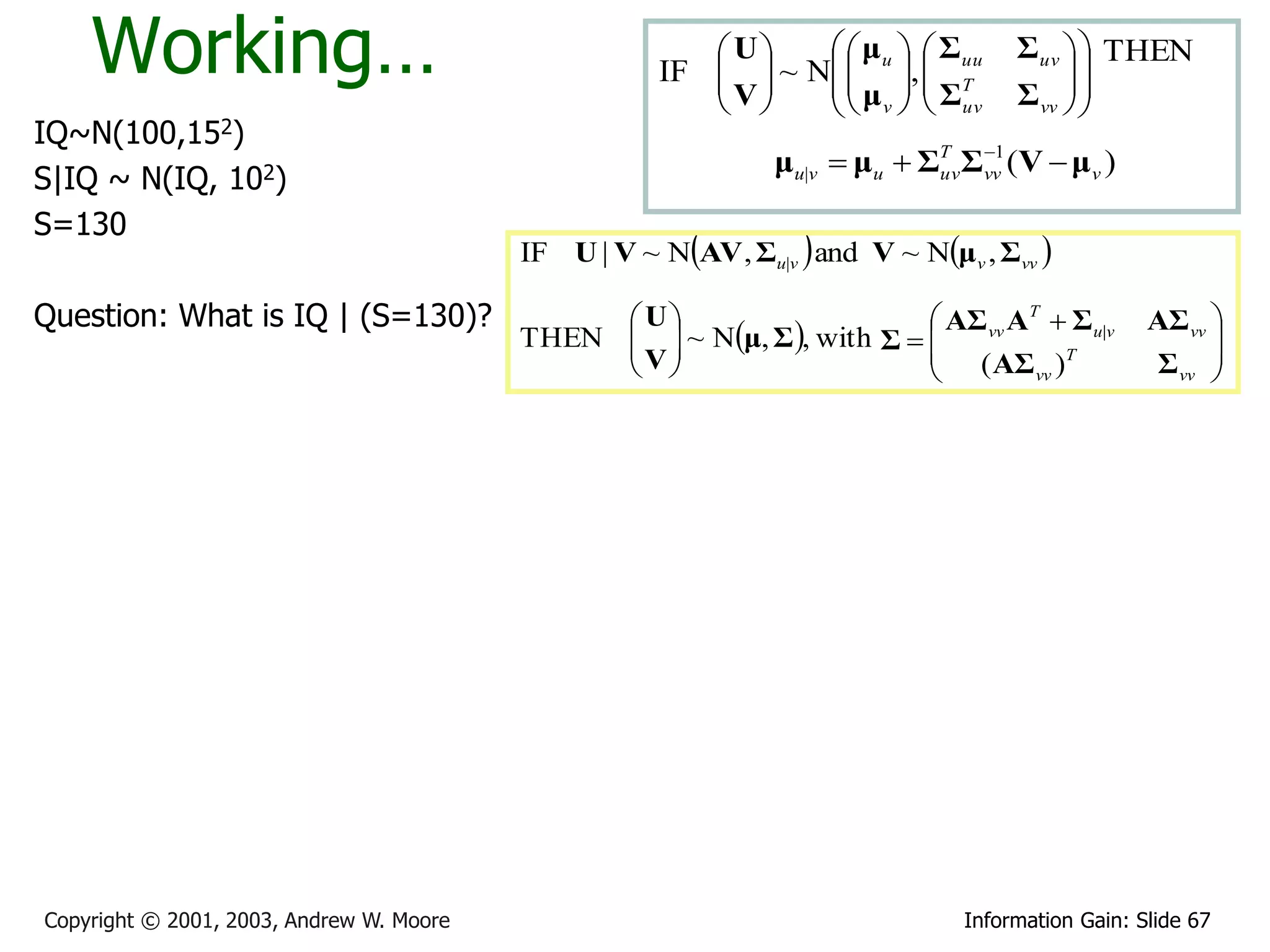
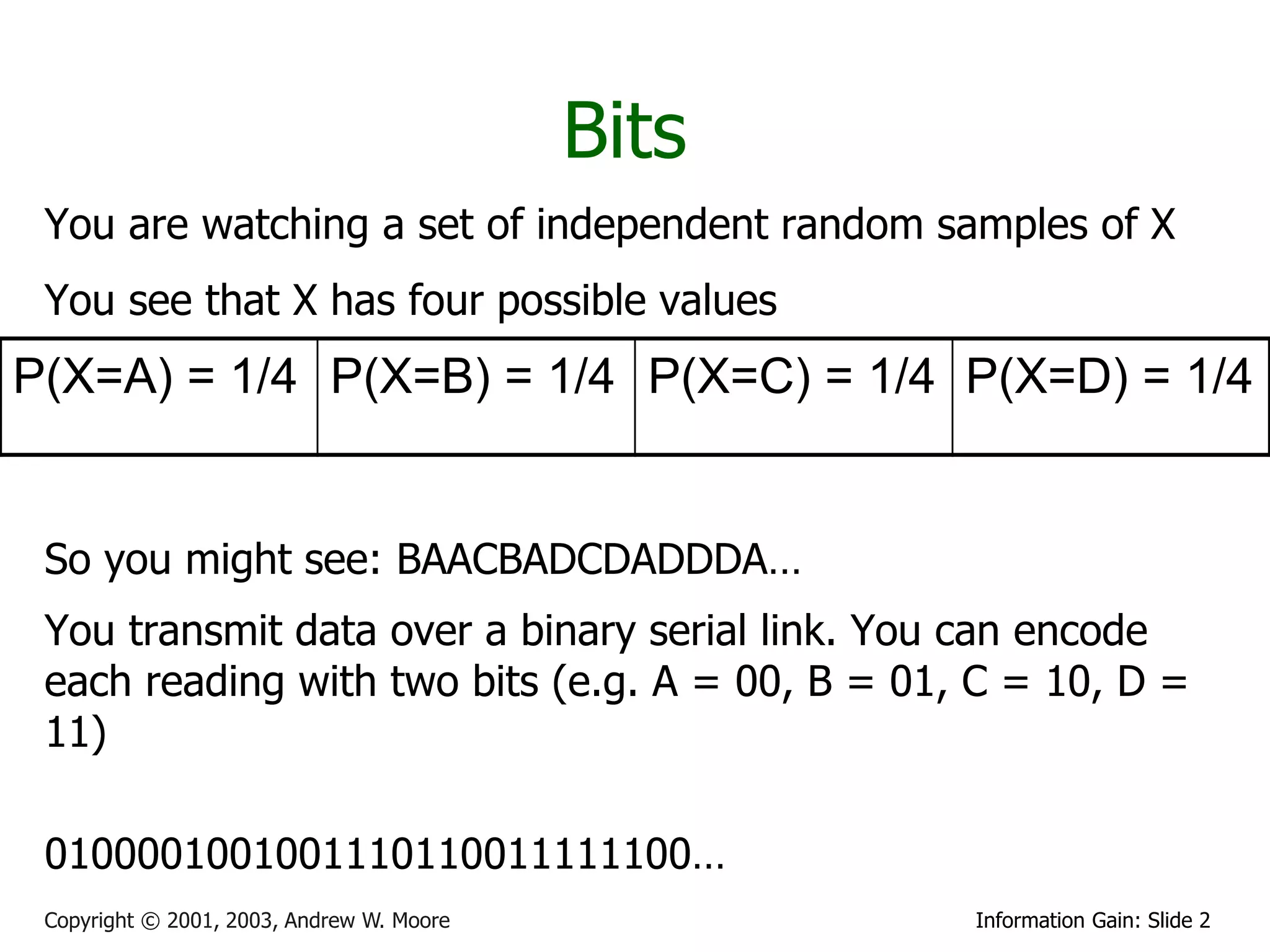
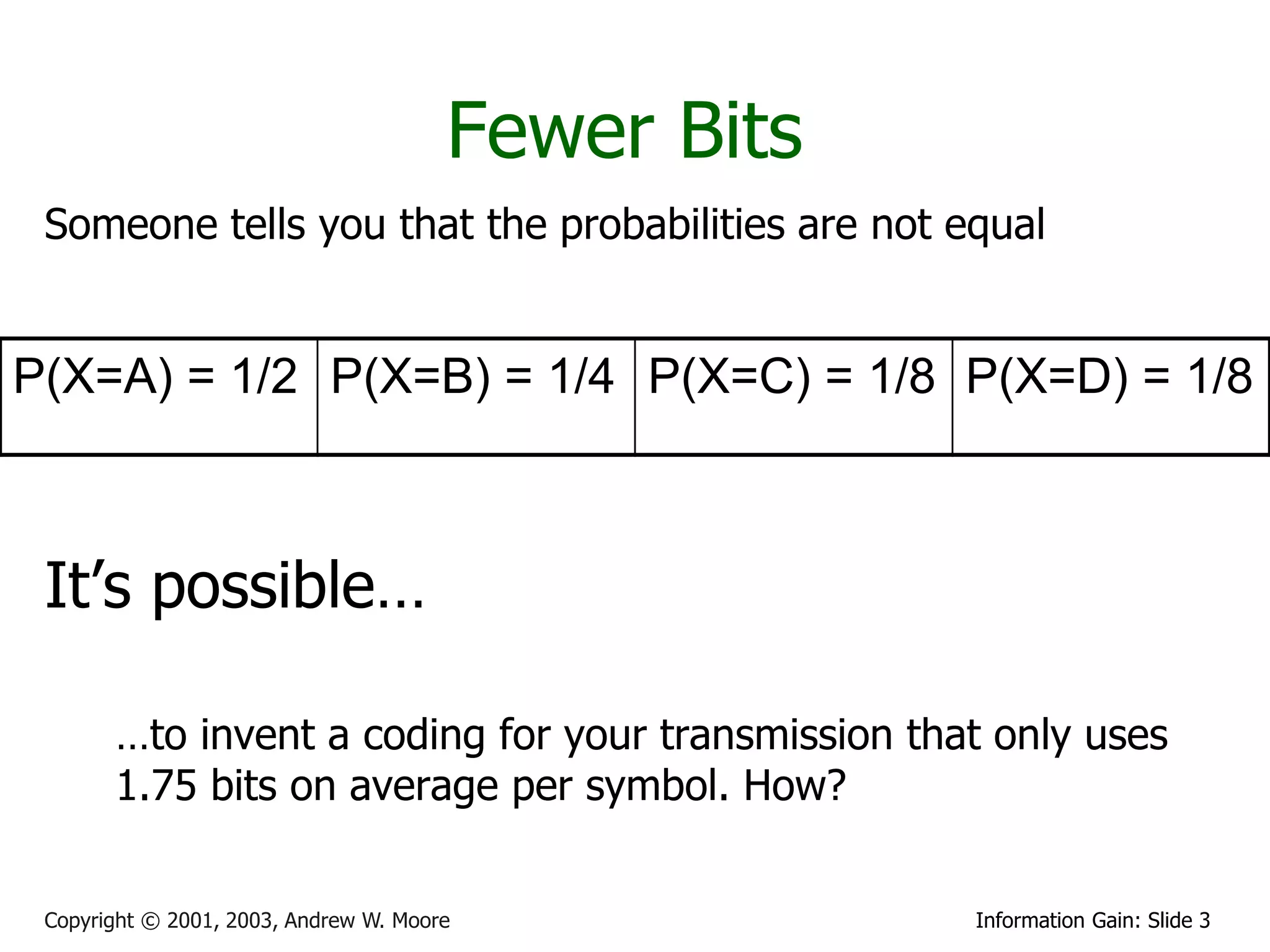
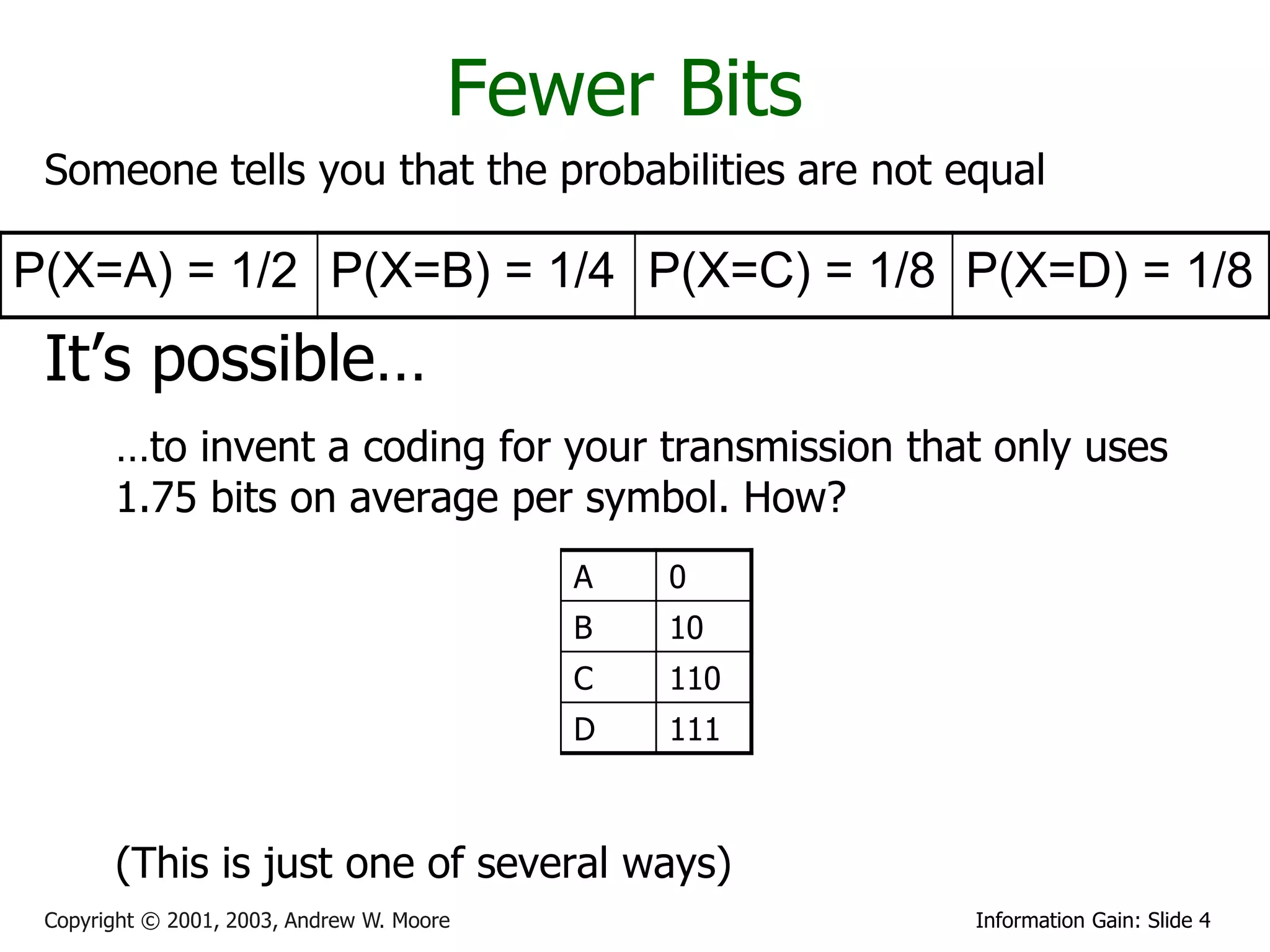
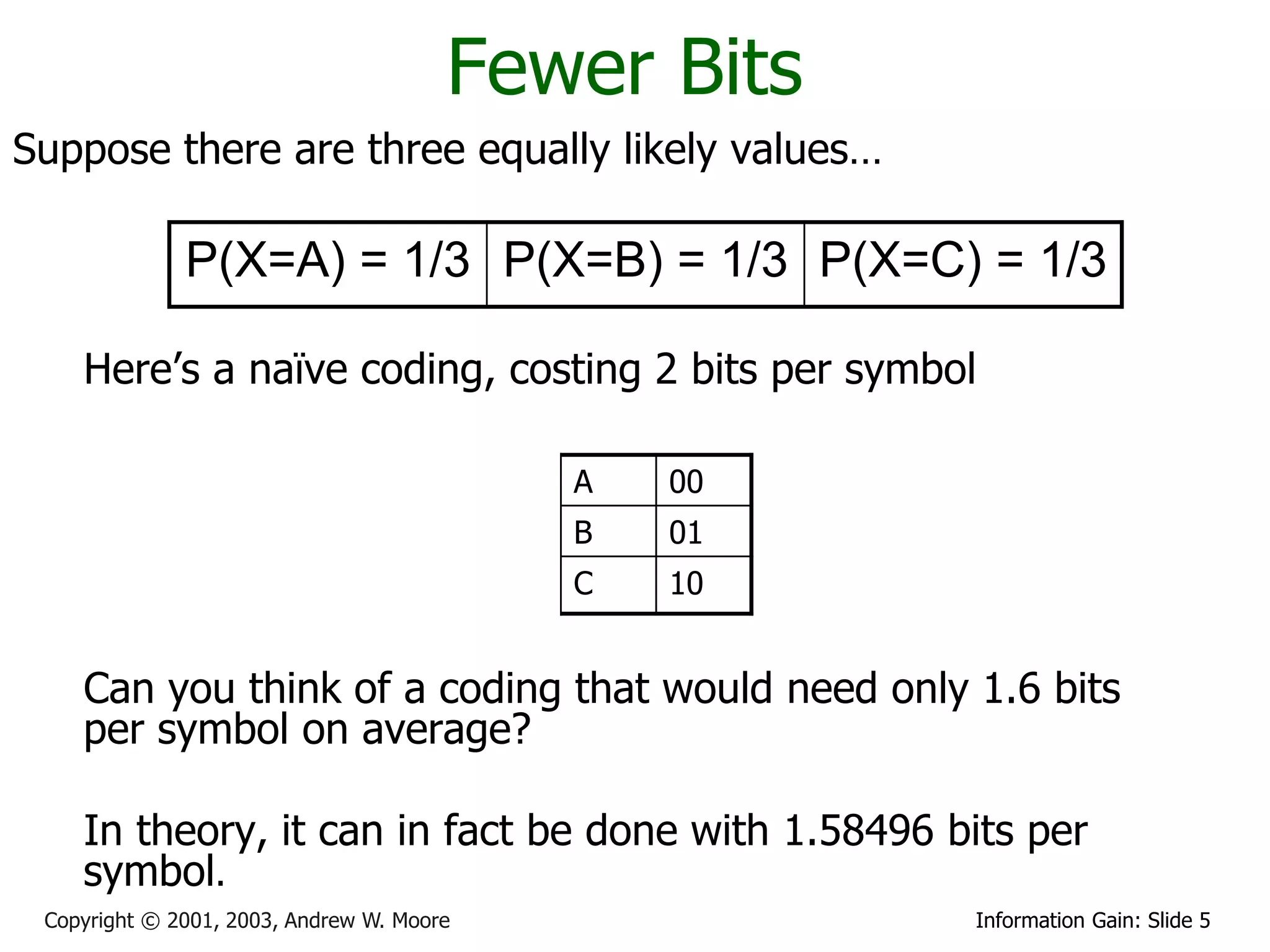
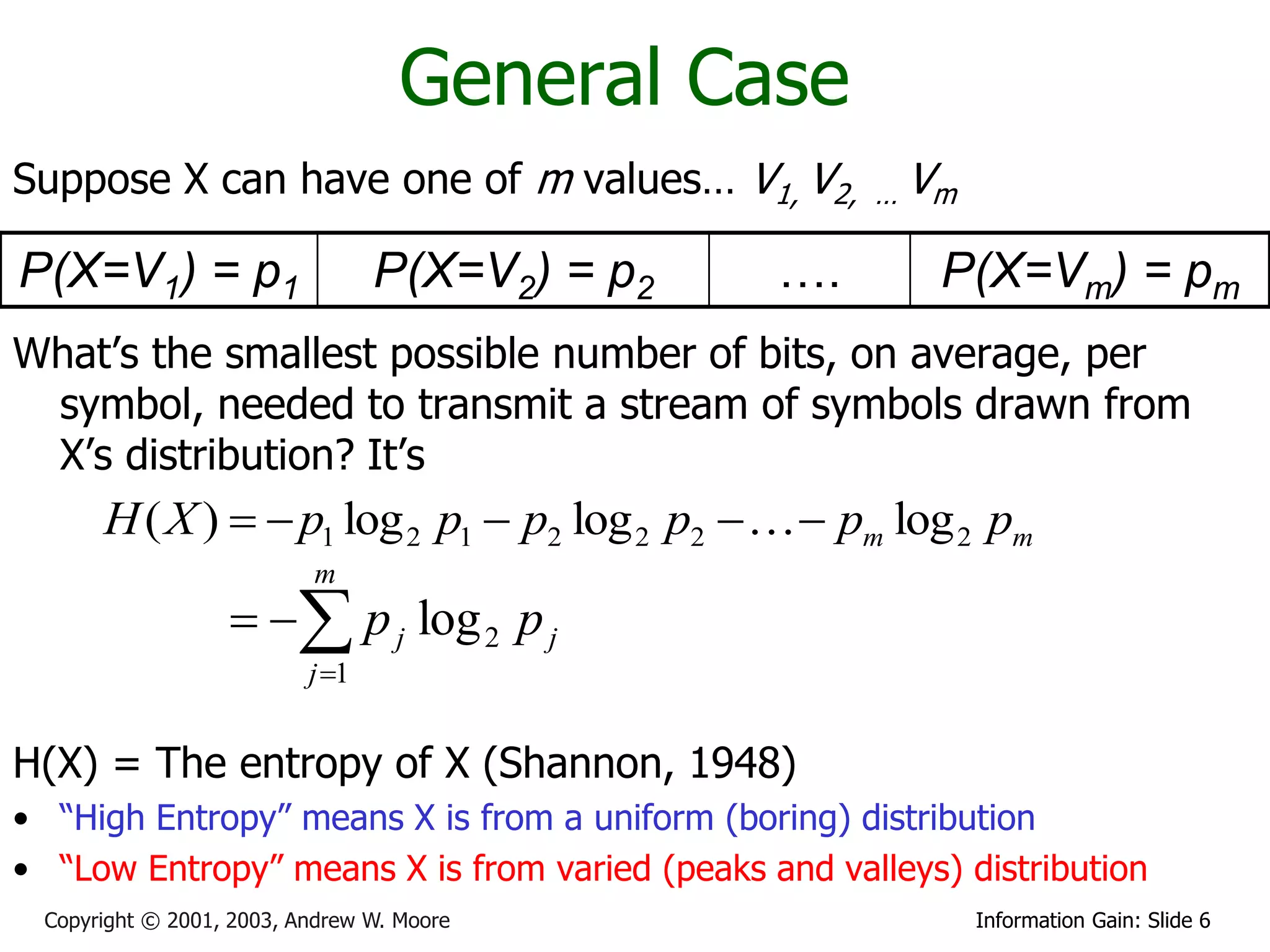
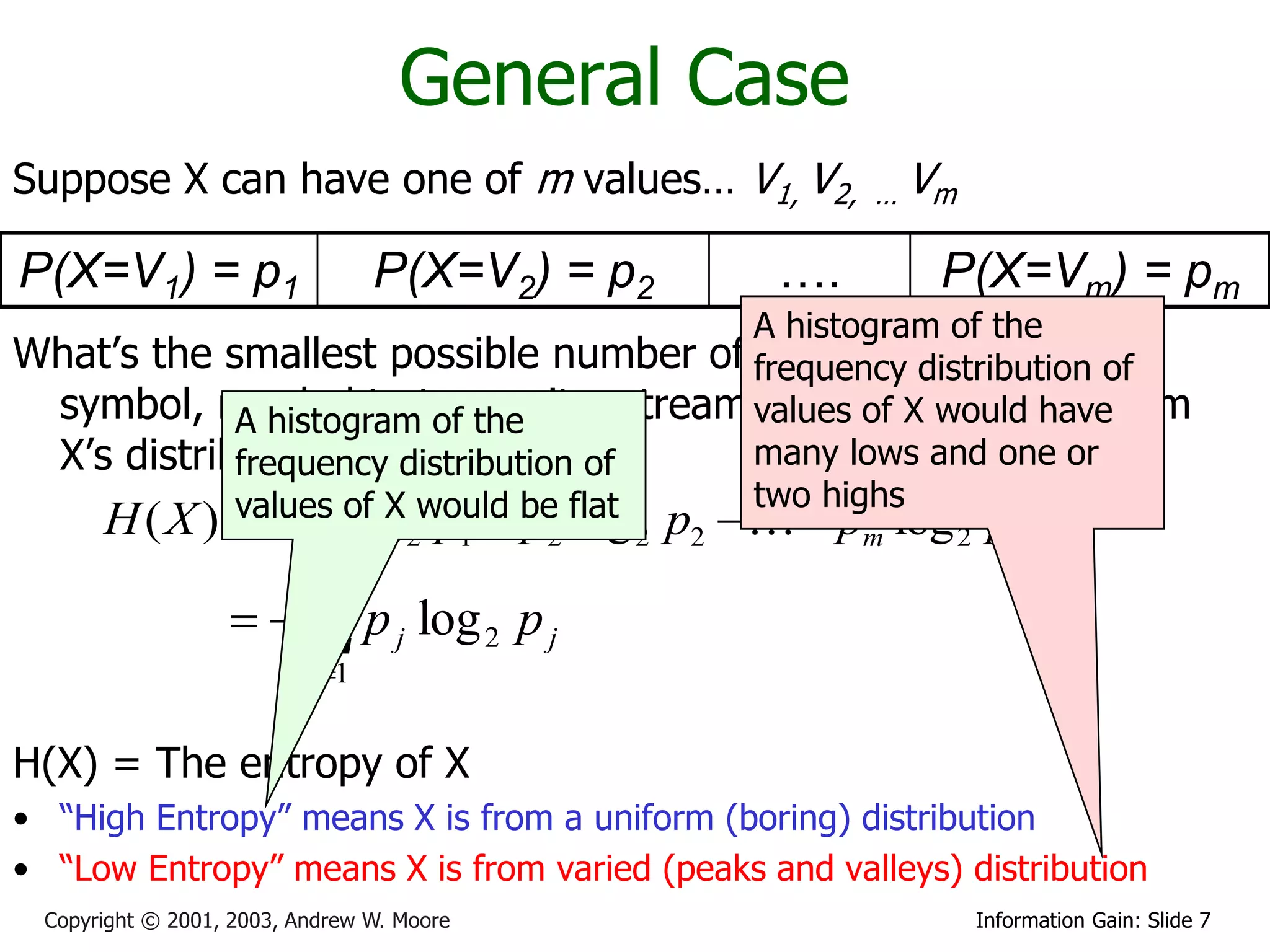
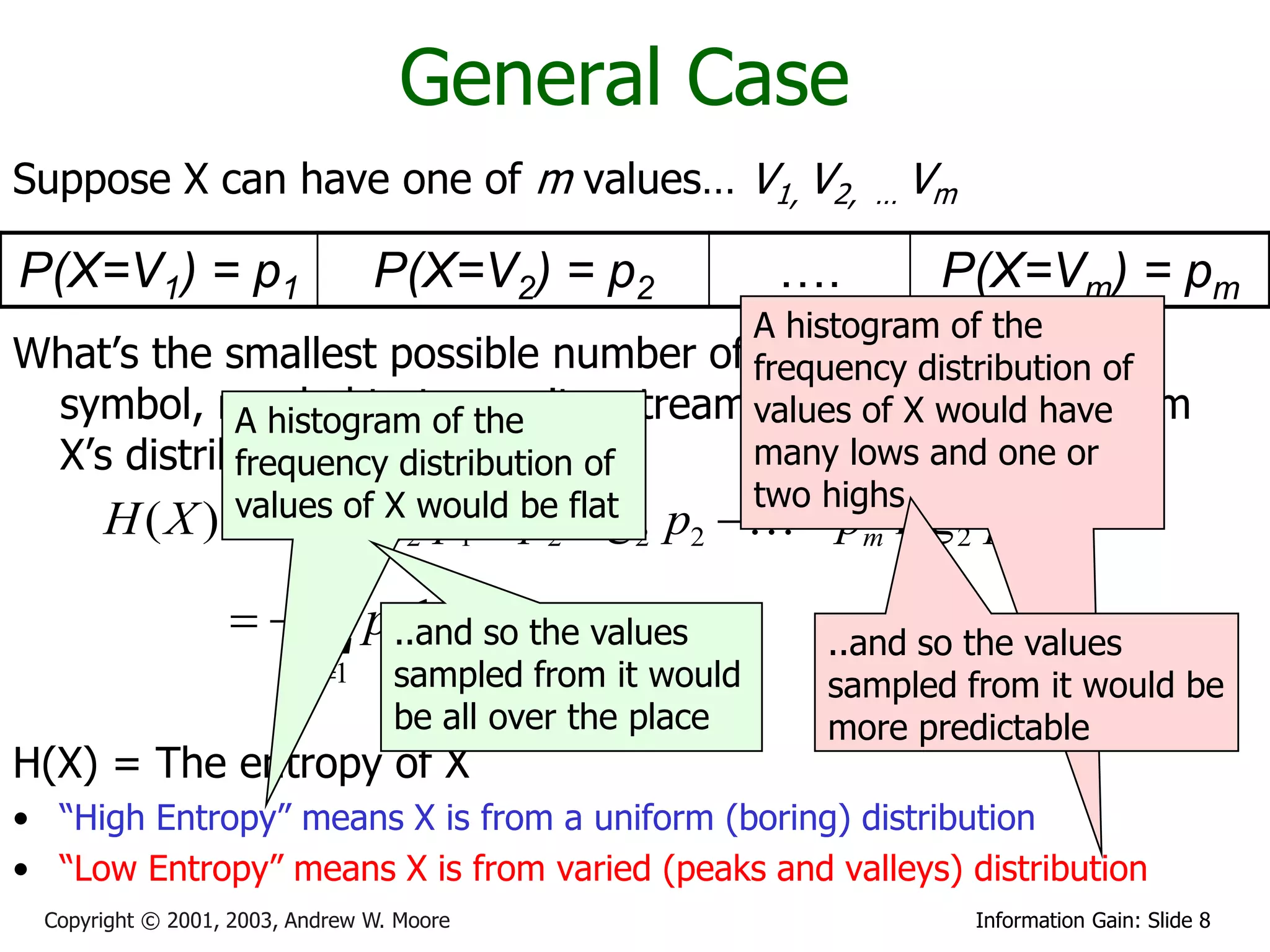
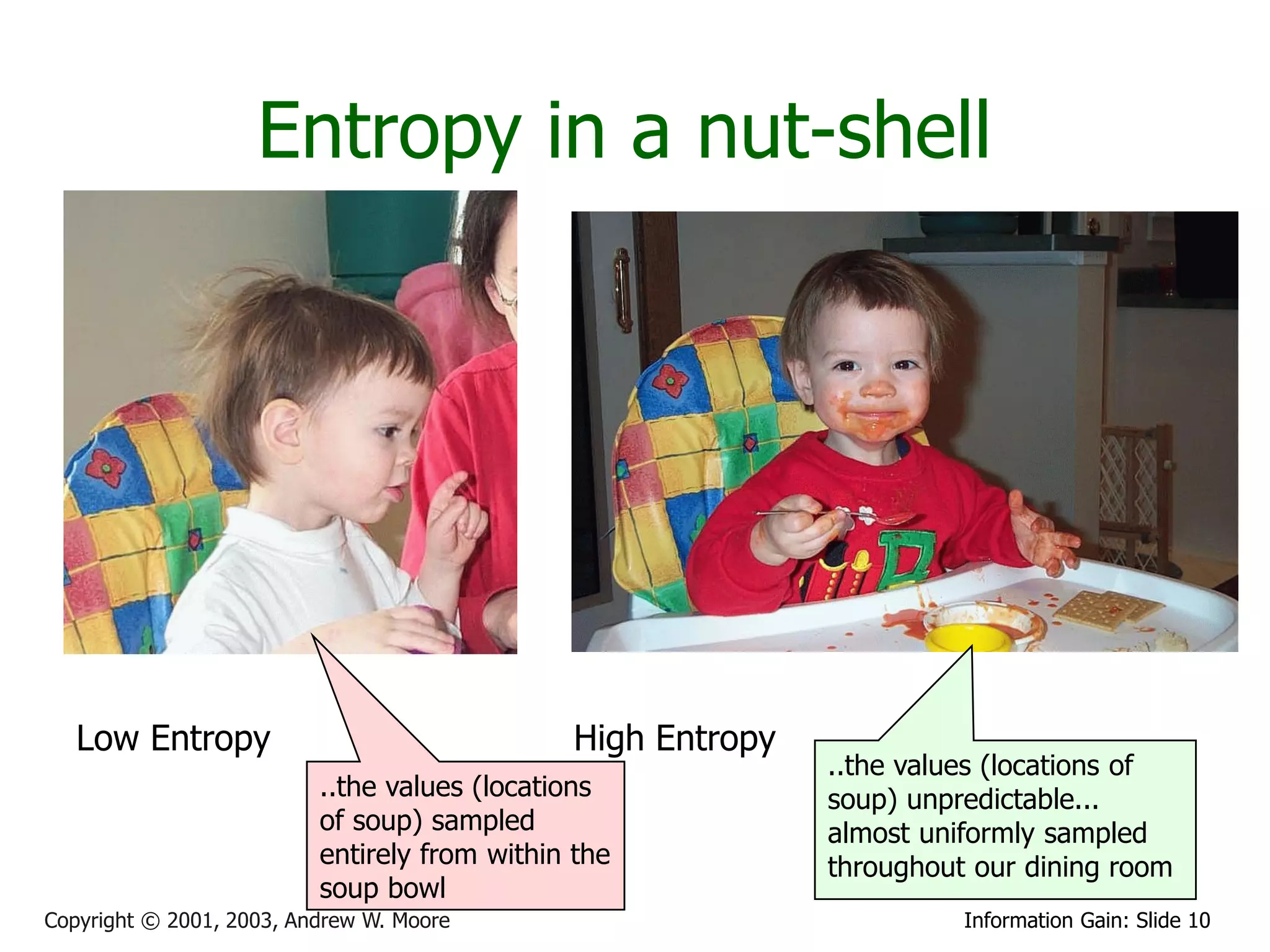
This document provides an overview of entropy and conditional entropy in information theory. It begins with examples of encoding variables with different probabilities to minimize the number of bits needed. It then defines entropy as the average number of bits needed to encode events from a probability distribution. Several example distributions are provided, along with their entropies. Finally, it defines conditional entropy as the expected entropy of a variable given knowledge of another variable.


![Entropy of a PDF
Entropy of X H [ X ] p( x) log p( x)dx
x
Natural log (ln or loge)
The larger the entropy of a distribution…
…the harder it is to predict
…the harder it is to compress it
…the less spiky the distribution
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-11-2048.jpg)
![1
The “box” w if
p( x)
| x |
w
2
distribution 0 if
| x |
w
2
1/w
-w/2 0 w/2
w/ 2 w/ 2
1 1 1 1
H [ X ] p( x) log p( x)dx log dx log wdx log w
x x w / 2
w w w w x / 2
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-12-2048.jpg)
![1
Unit variance w if
p( x)
| x |
w
2
box distribution 0 if
| x |
w
2
E[ X ] 0
1
w2
2 3 Var[ X ]
12
3 0 3
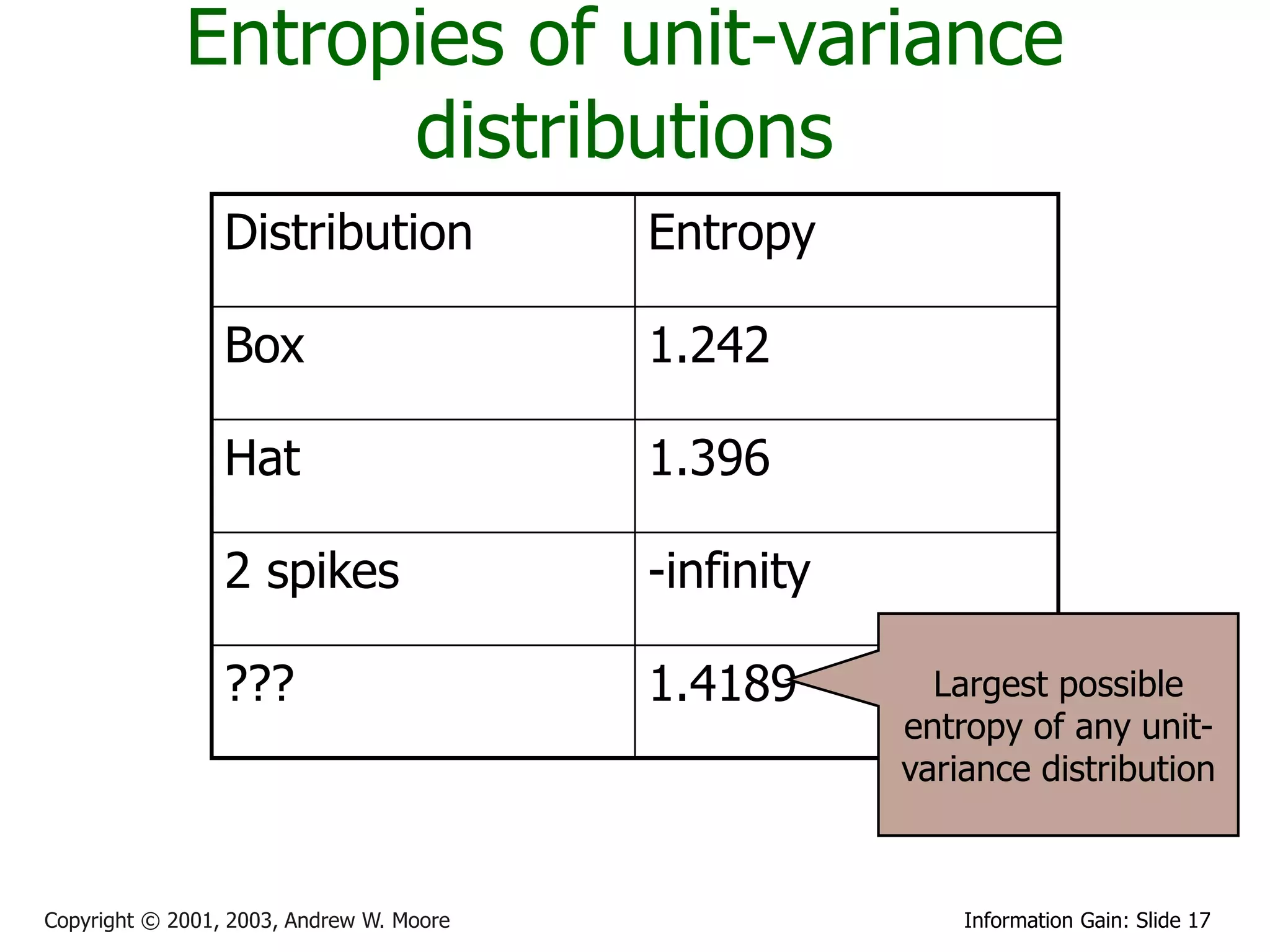
if w 2 3 then Var[ X ] 1 and H [ X ] 1.242
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-13-2048.jpg)
![The Hat w | x |
p ( x) w2
if |x| w
distribution 0
if |x| w
E[ X ] 0
1 2
w
w Var[ X ]
6
w 0 w
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-14-2048.jpg)
![Unit variance hat w | x |
p ( x) w2
if |x| w
distribution 0
if |x| w
E[ X ] 0
1 2
w
6 Var[ X ]
6
6 0 6
if w 6 then Var[ X ] 1 and H [ X ] 1.396
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-15-2048.jpg)
![Dirac Delta
The “2 spikes” ( x 1) ( x 1)
p ( x)
distribution 2
1 1 E[ X ] 0
( x 1) ( x 1)
2 2
2 Var[ X ] 1
-1 0 1
H[ X ] p( x) log p( x)dx
x
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-16-2048.jpg)
![Unit variance p( x)
1 x2
exp
2
Gaussian 2
E[ X ] 0
Var[ X ] 1
H[ X ] p( x) log p( x)dx 1.4189
x
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-18-2048.jpg)
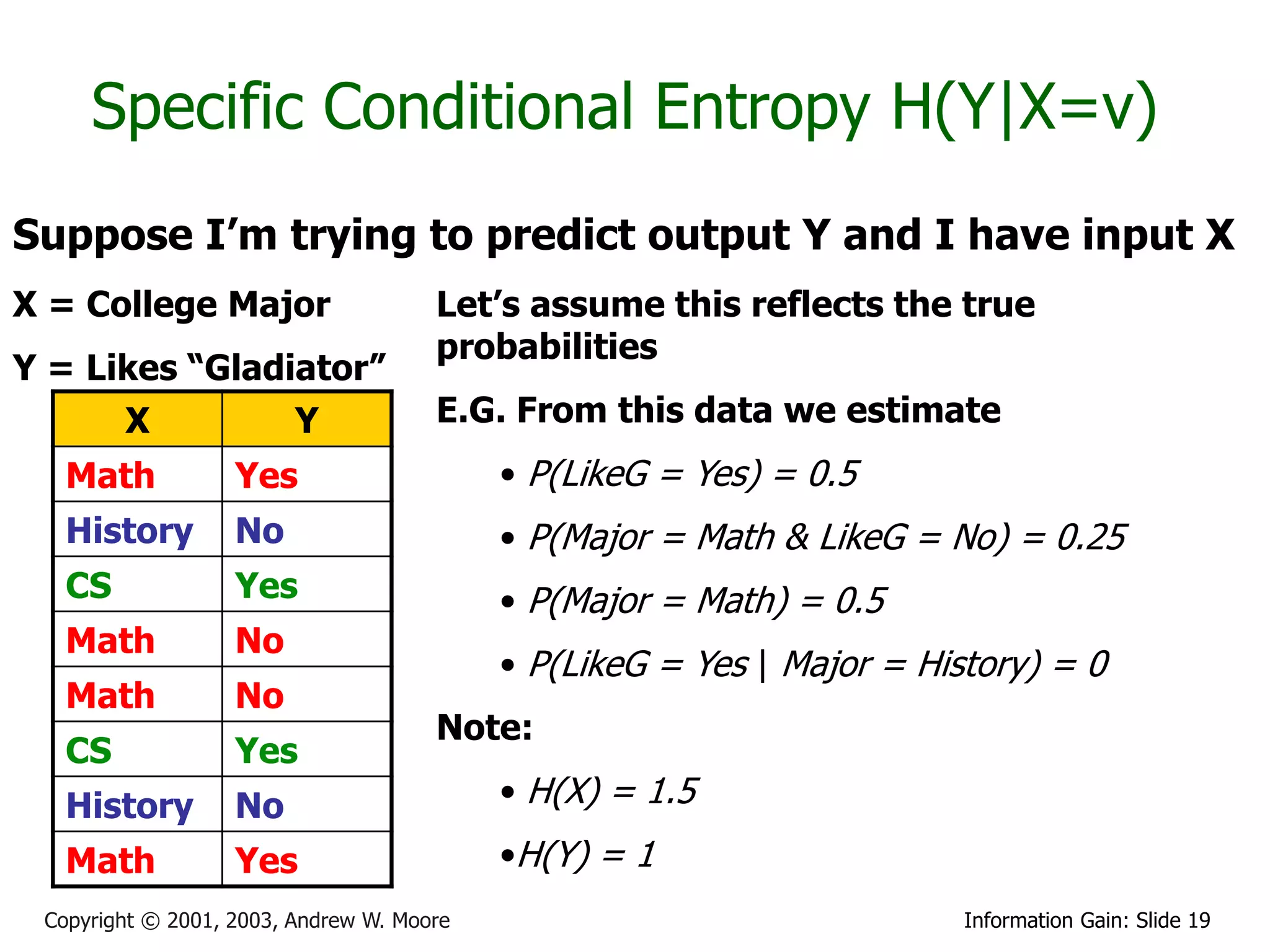
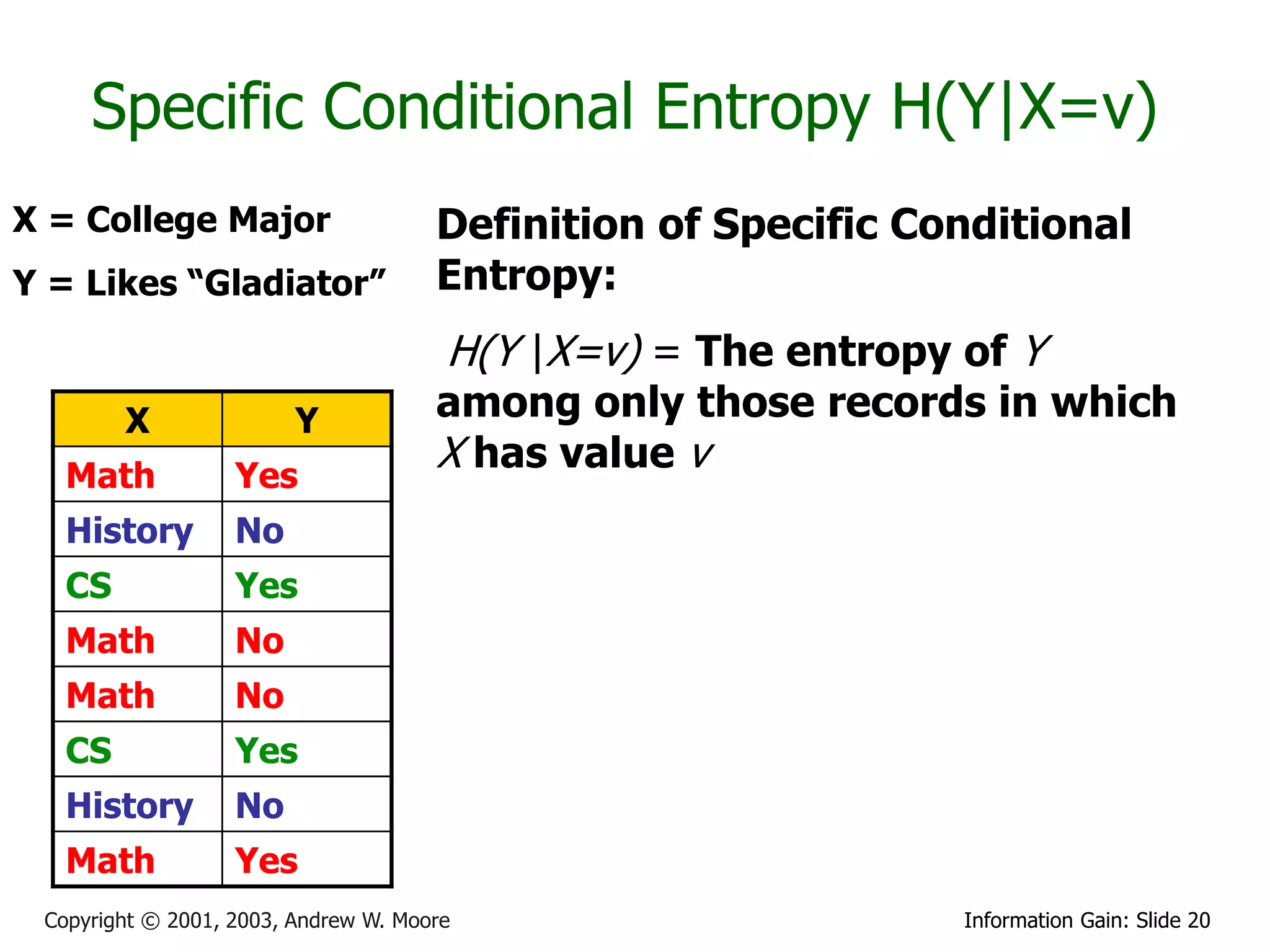
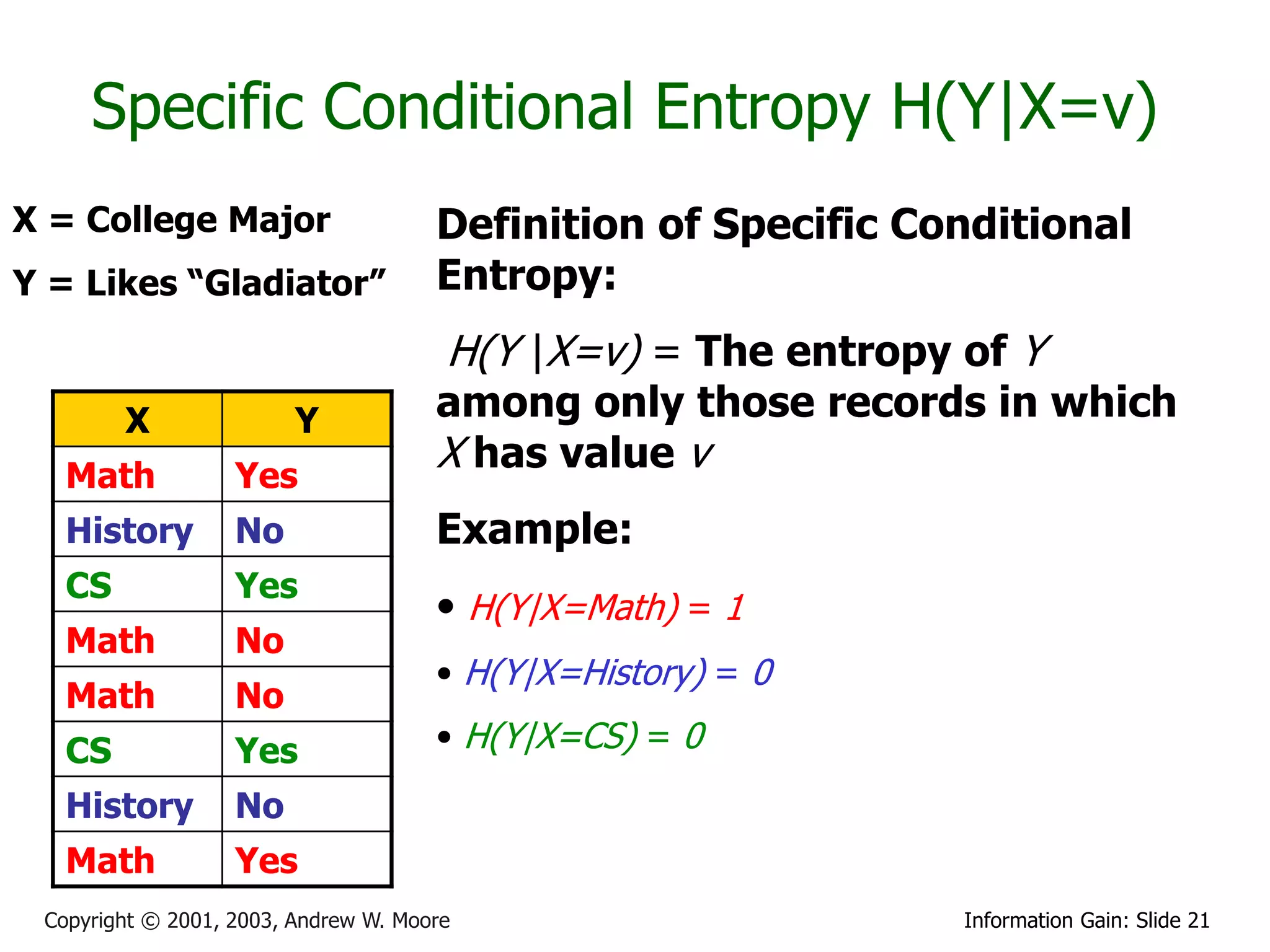
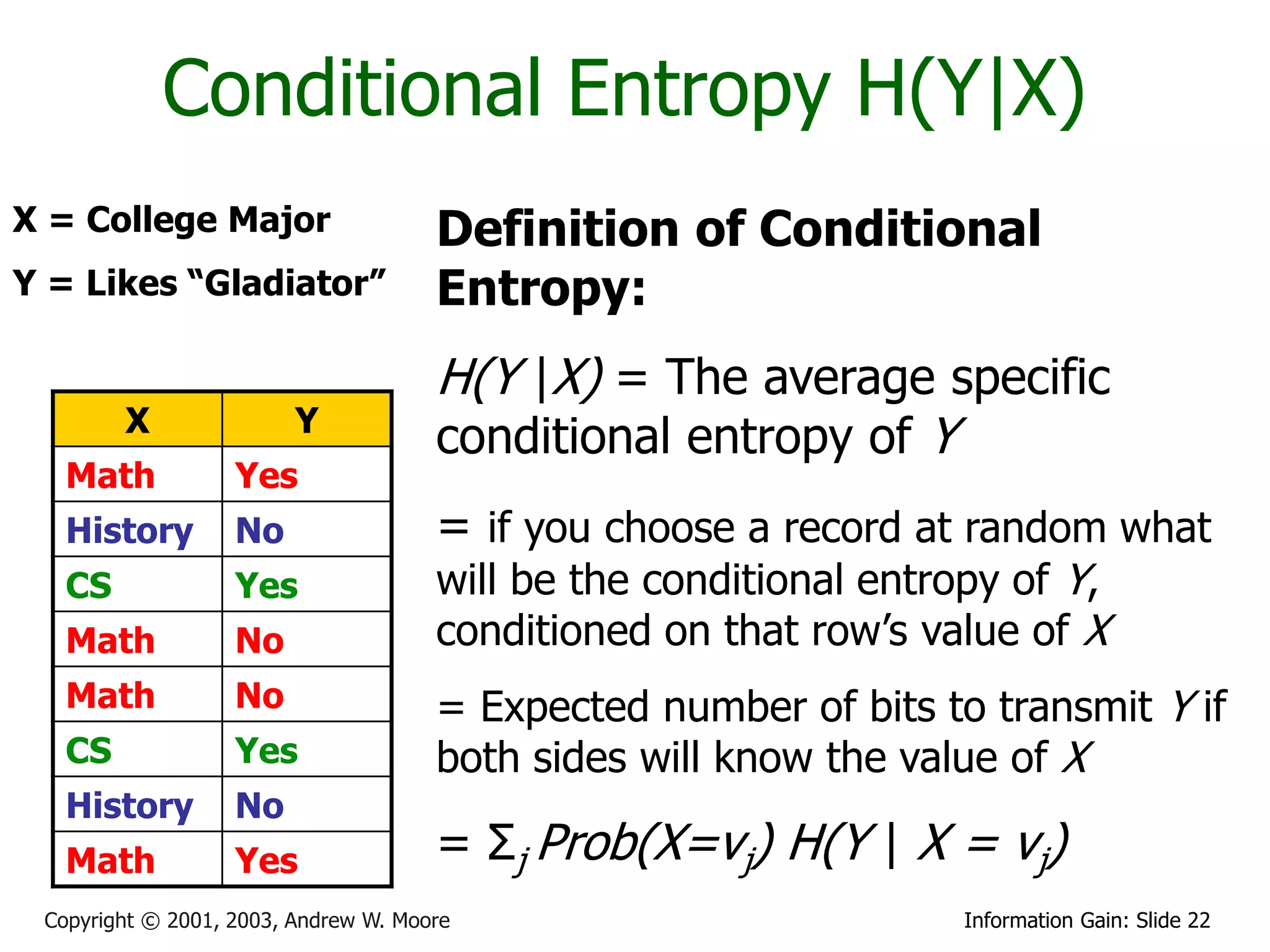
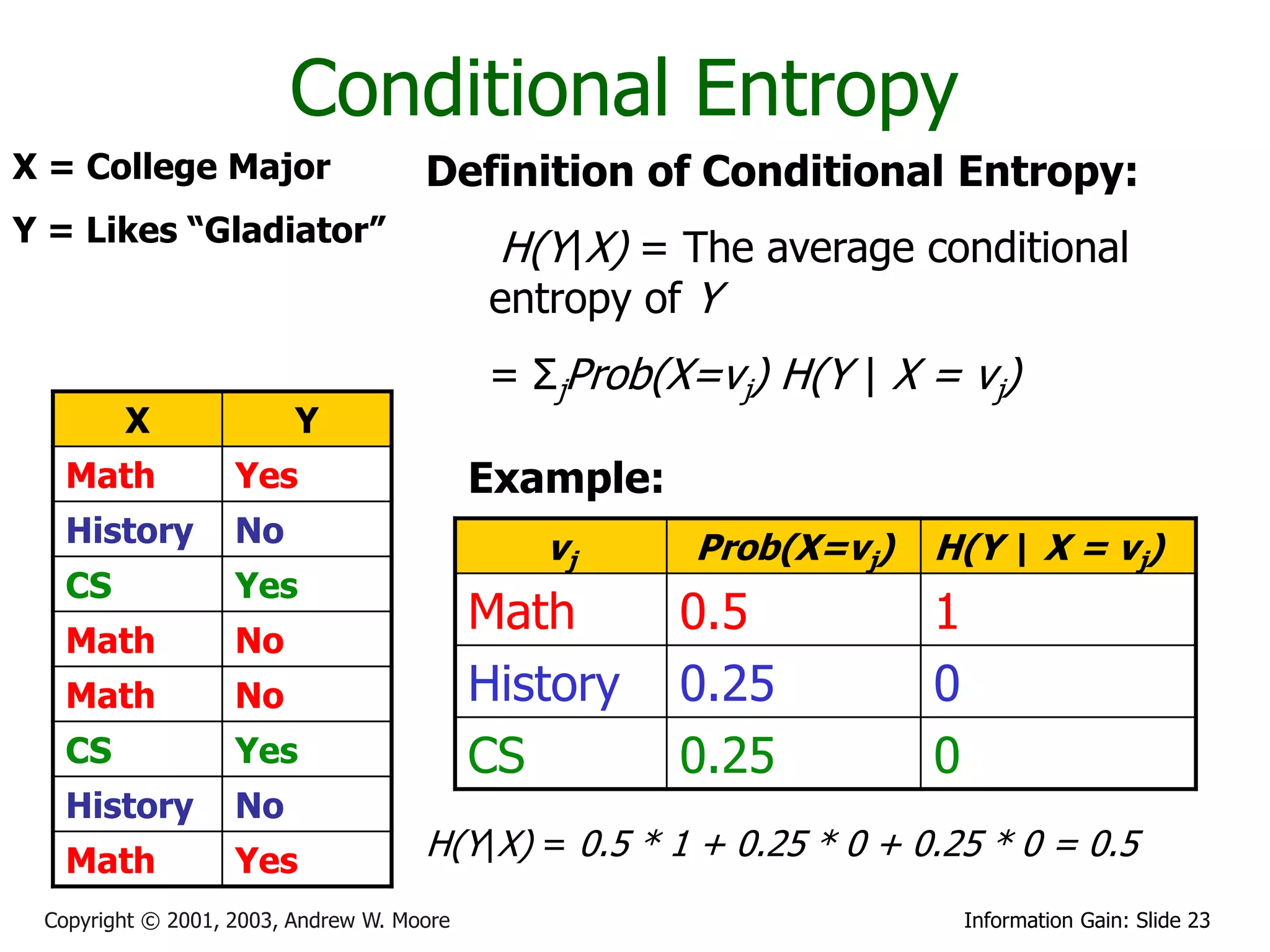
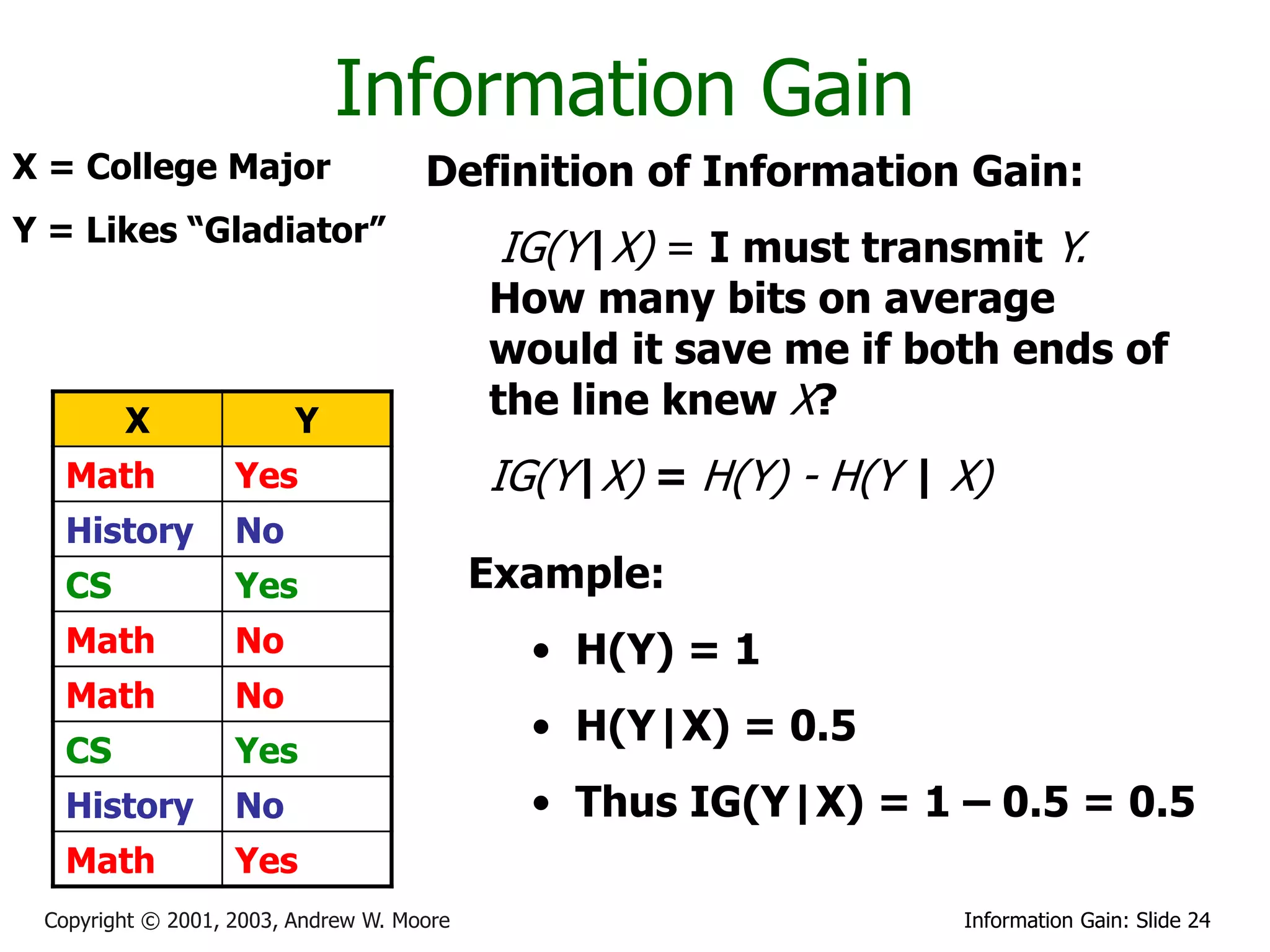
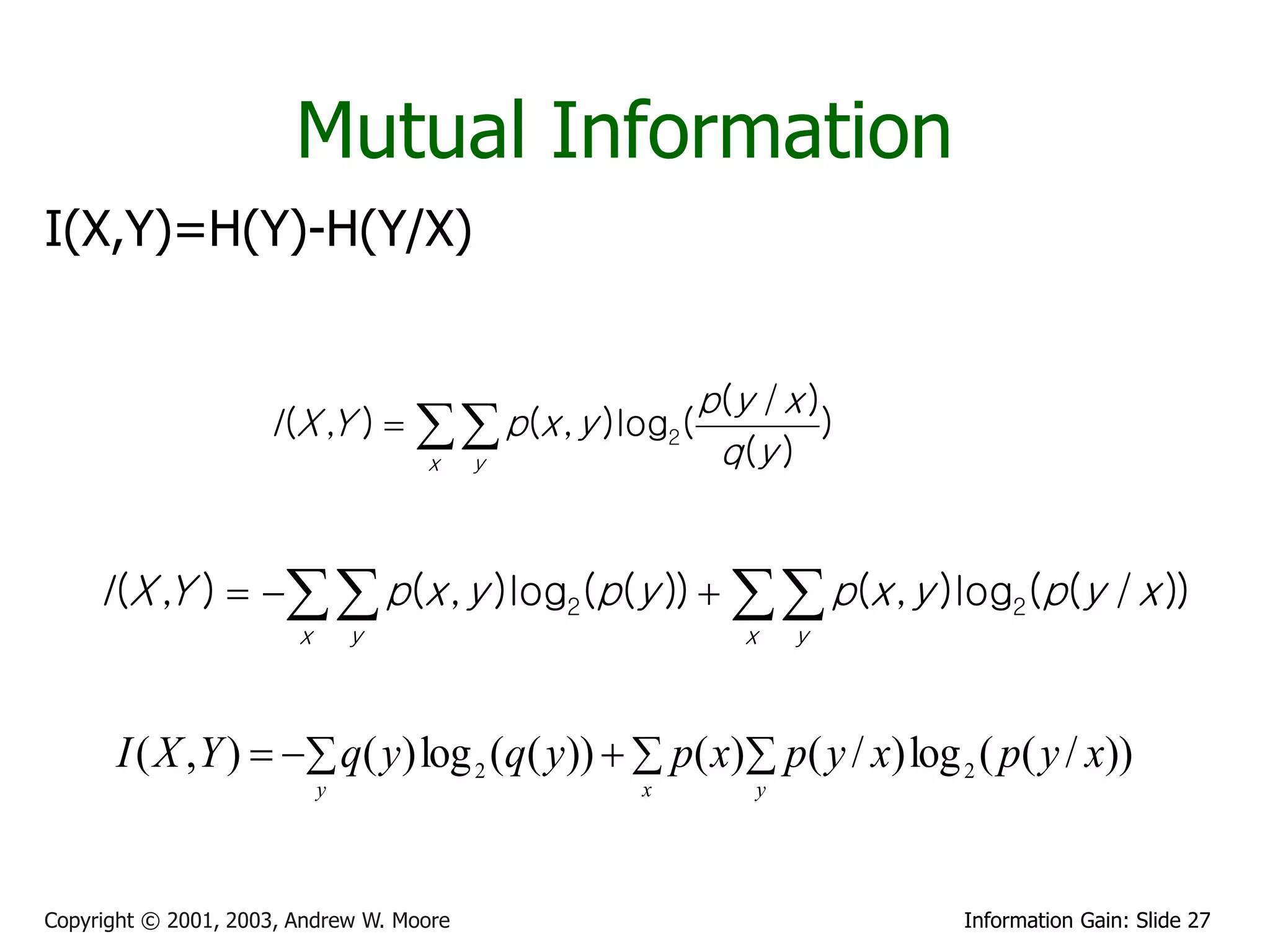
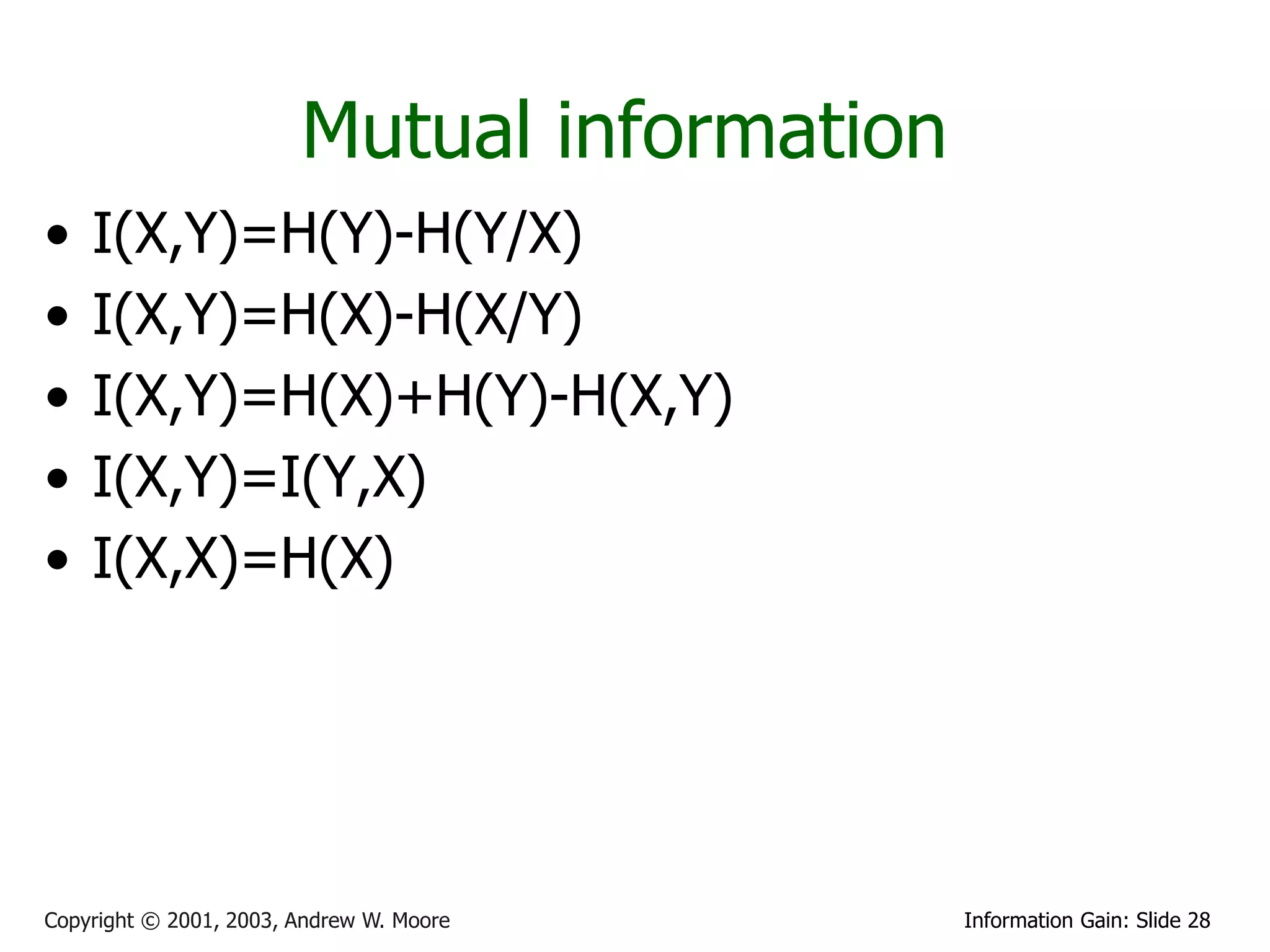
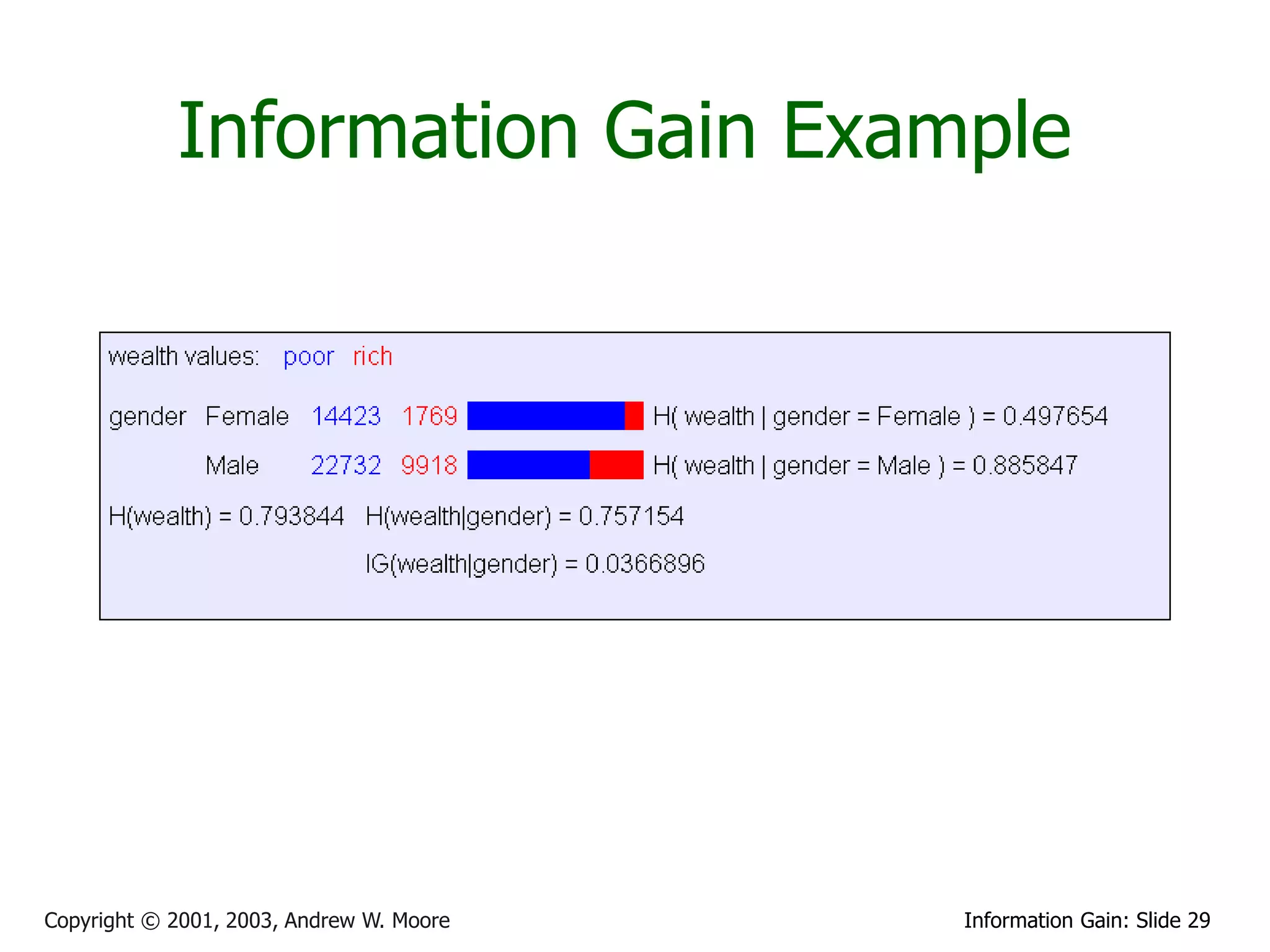
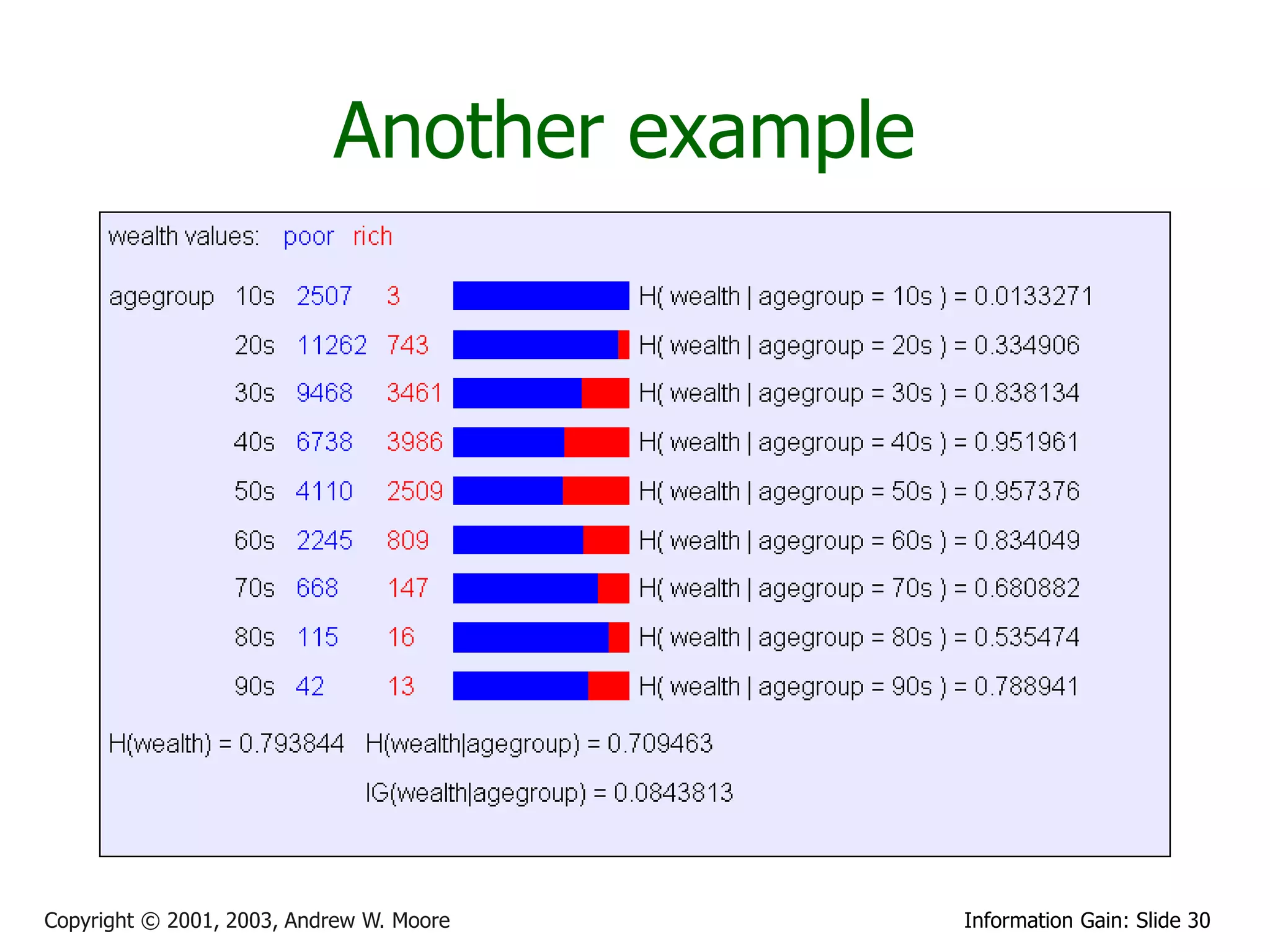
![Relative Information Gain
X = College Major Definition of Relative Information
Y = Likes “Gladiator” Gain:
RIG(Y|X) = I must transmit Y, what
fraction of the bits on average would
X Y
it save me if both ends of the line
knew X?
Math Yes
History No RIG(Y|X) = [H(Y) - H(Y | X) ]/ H(Y)
CS Yes
Math No Example:
Math No • H(Y|X) = 0.5
CS Yes
• H(Y) = 1
History No
Math Yes • Thus IG(Y|X) = (1 – 0.5)/1 = 0.5
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-31-2048.jpg)

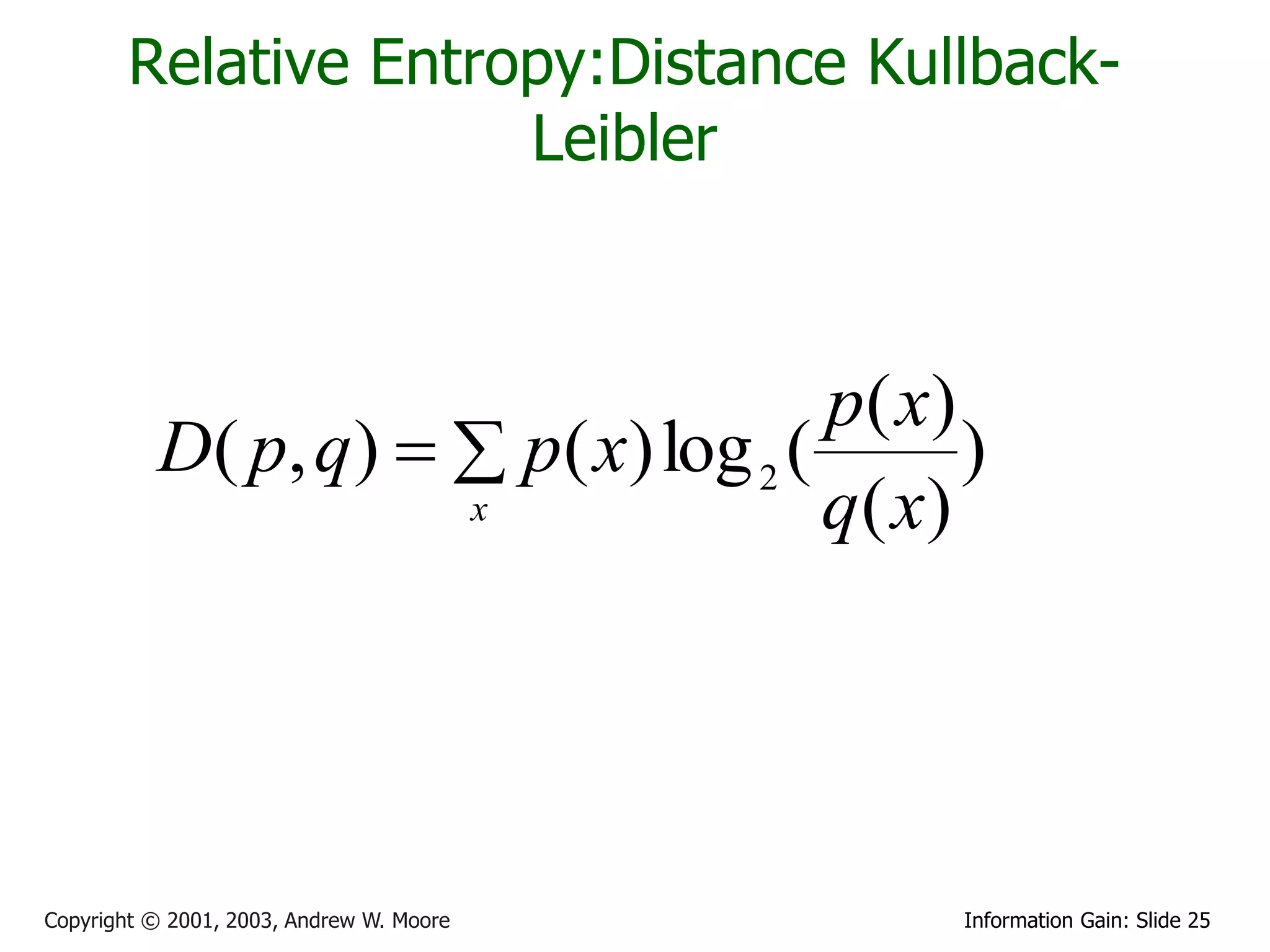
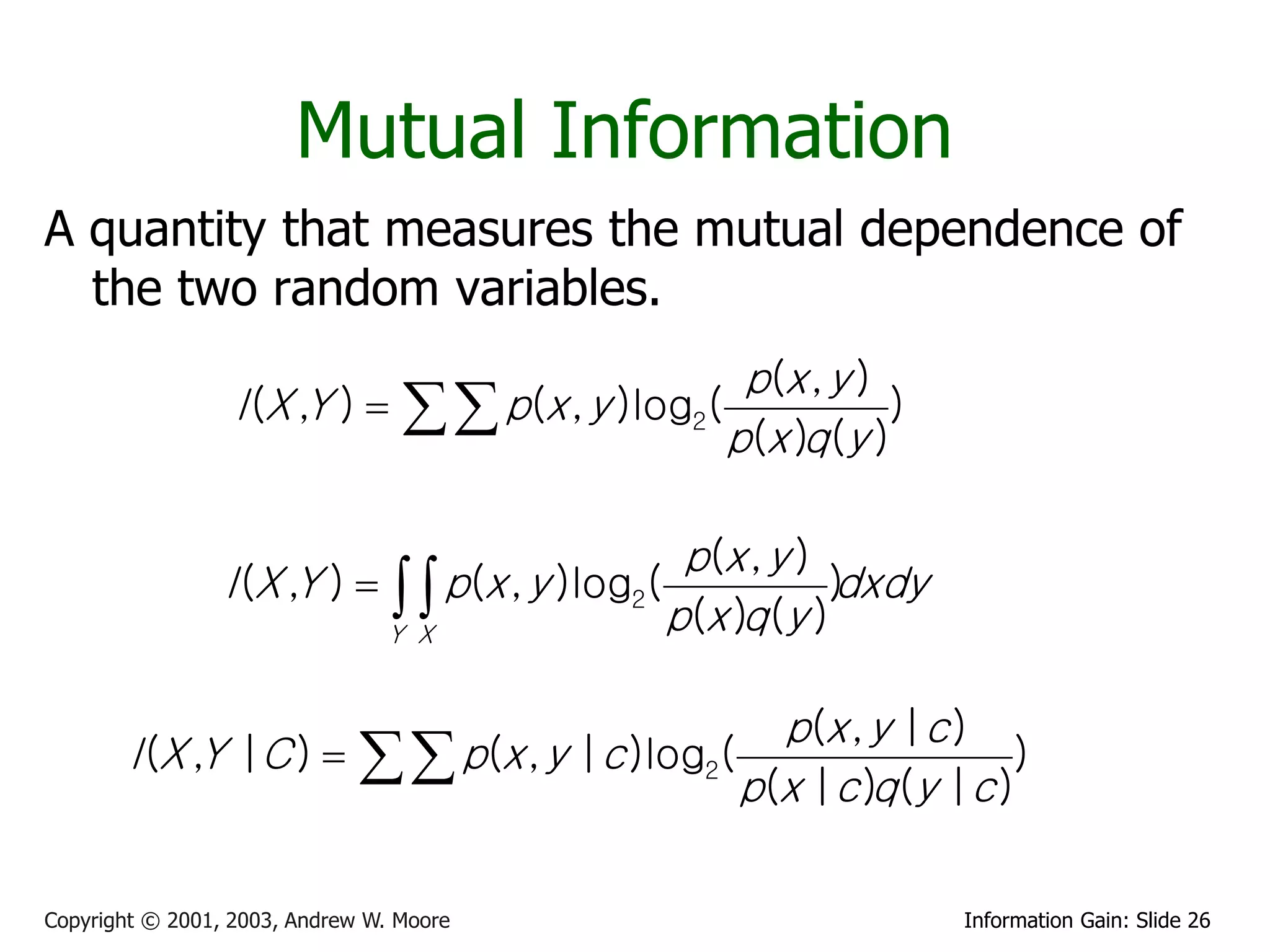
![Cross Entropy
Sea X una variable aleatoria con distribucion conocida p(x) y distribucion
estimada q(x), la “cross entropy” mide la diferencia entre las dos
distribuciones y se define por
HC ( x) E[ log( q( x)] H ( x) KL( p, q)
donde H(X) es la entropia de X con respecto a la distribucion p y KL es
la distancia Kullback-Leibler ente p y q.
Si p y q son discretas se reduce a :
H C ( X ) p( x) log 2 (q( x))
x
y para p y q continuas se tiene
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-33-2048.jpg)
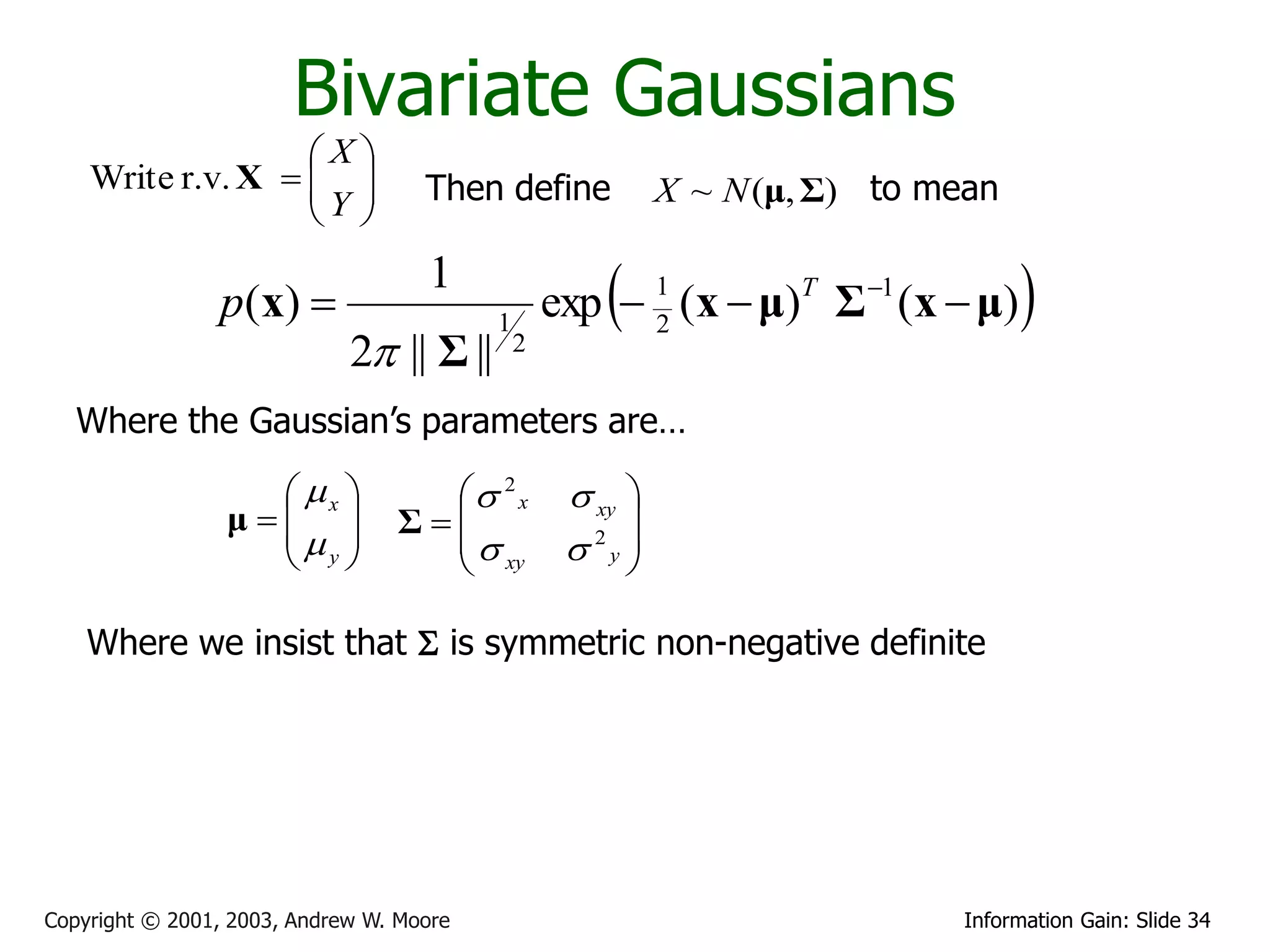
![Bivariate Gaussians
X
Write r.v. X
Y Then define X ~ N (μ, Σ) to mean
p ( x)
1
1
exp 1 (x μ)T Σ 1 (x μ)
2
2 || Σ || 2
Where the Gaussian’s parameters are…
x 2 x xy
μ
Σ
y 2
y
xy
Where we insist that S is symmetric non-negative definite
It turns out that E[X] = and Cov[X] = S. (Note that this is a
resulting property of Gaussians, not a definition)
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-35-2048.jpg)
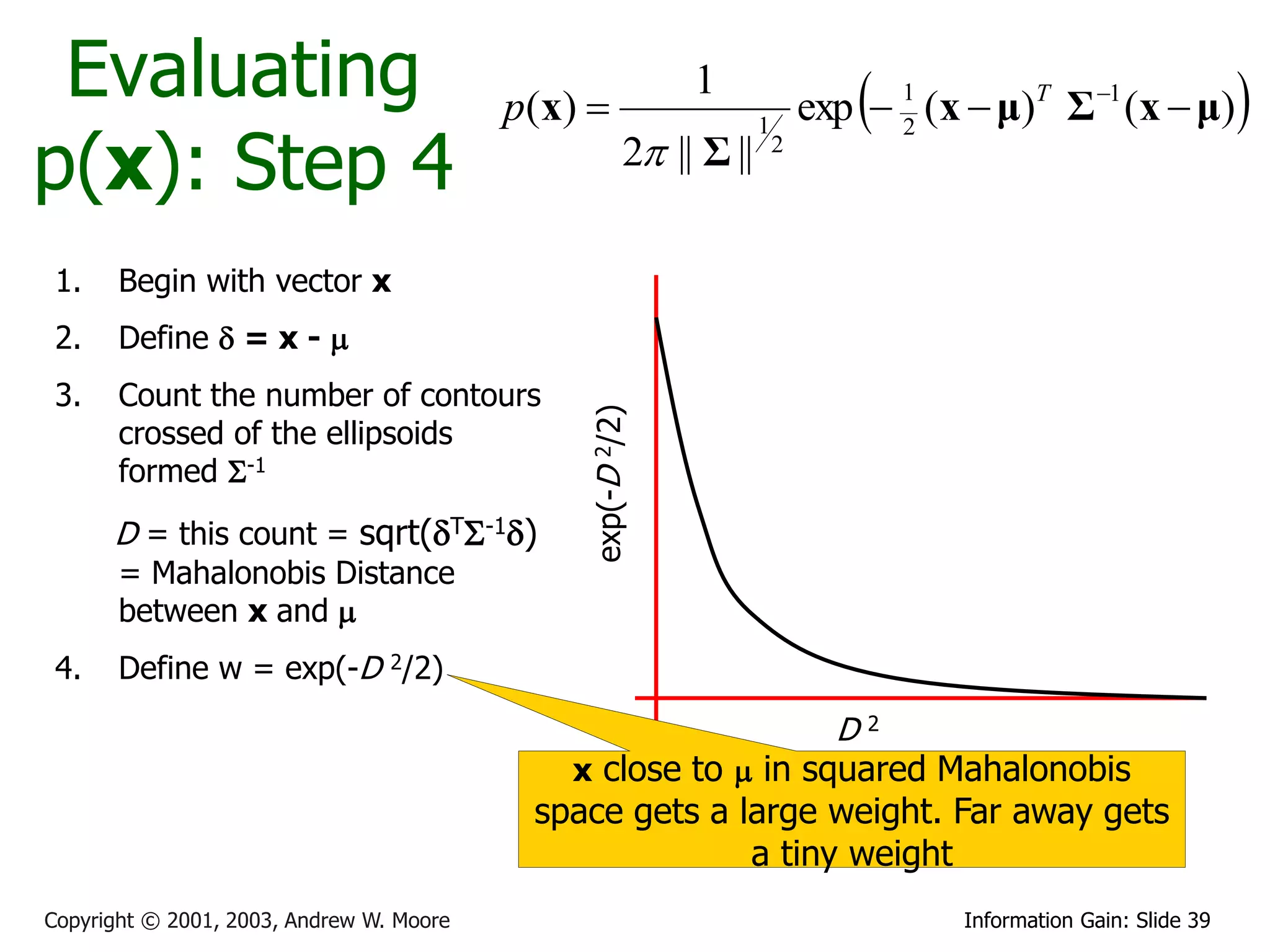
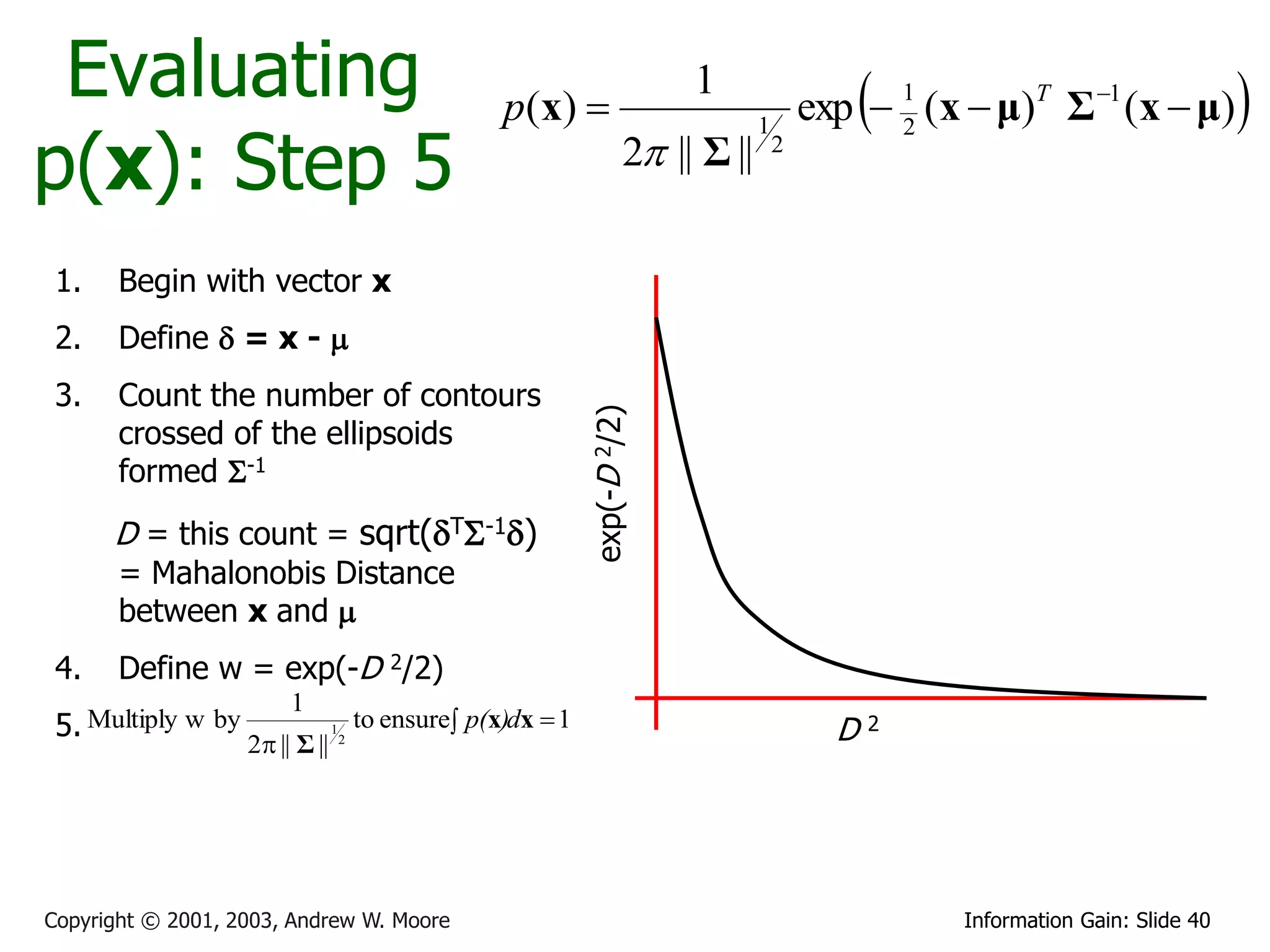
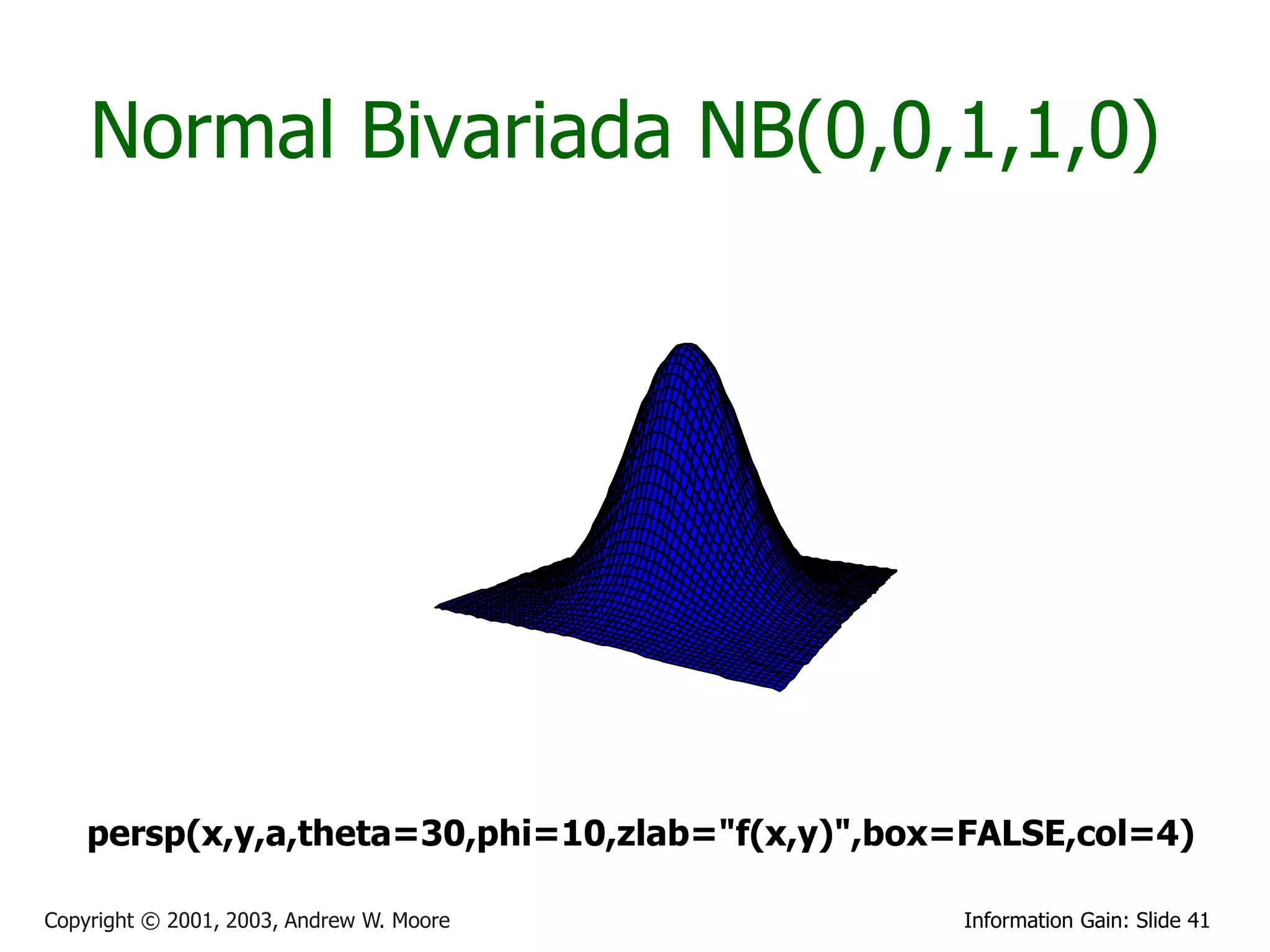
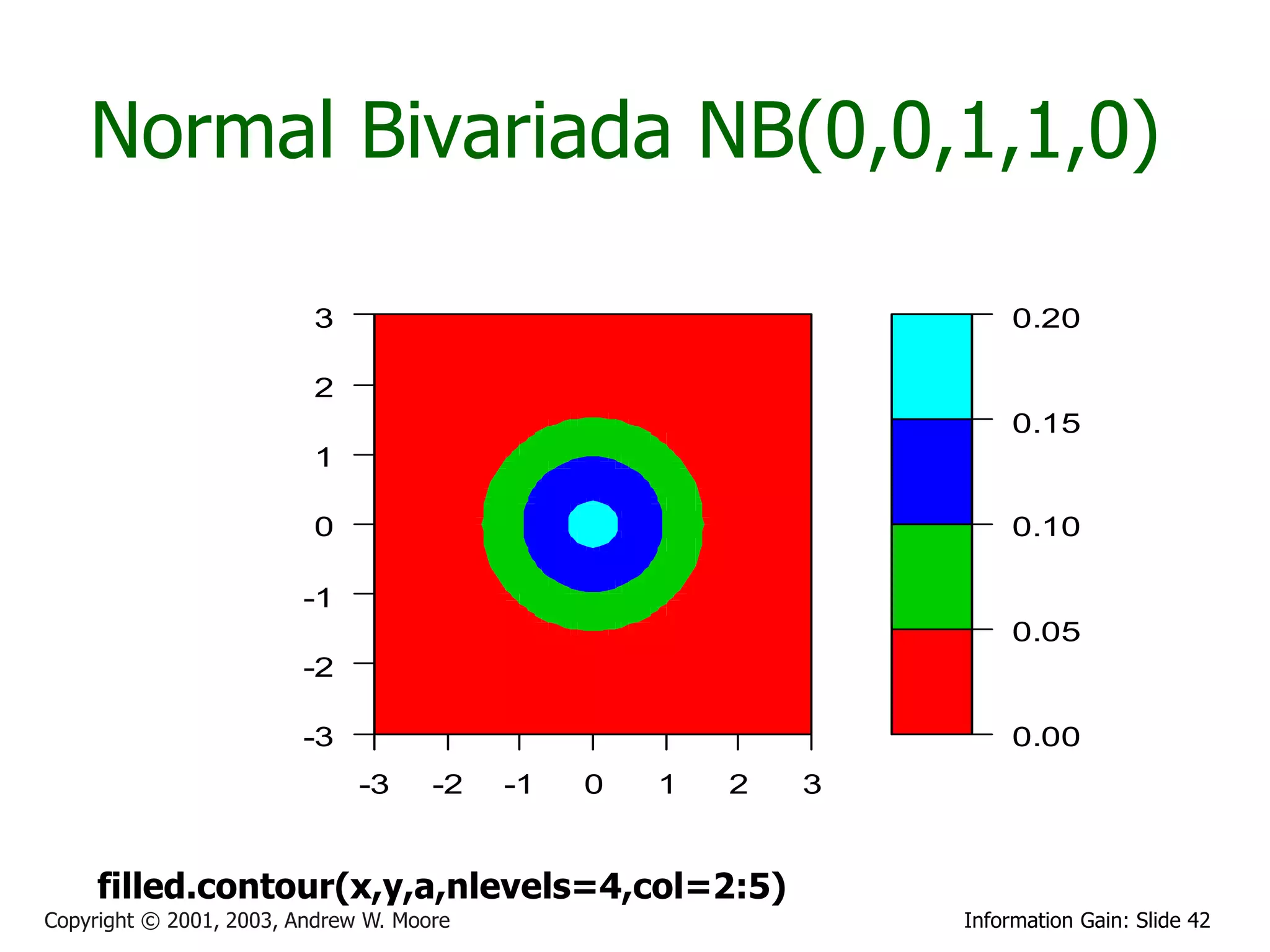
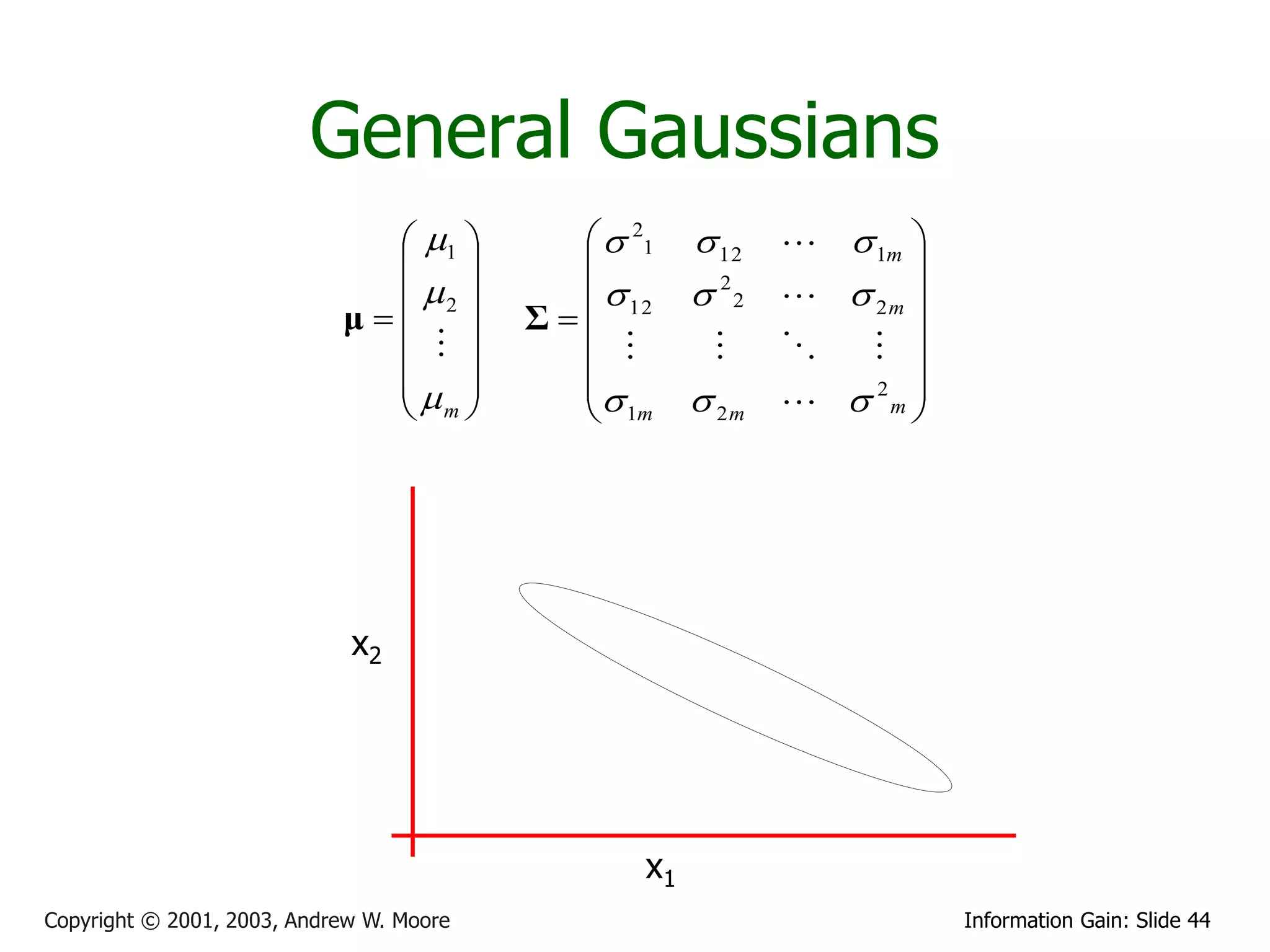
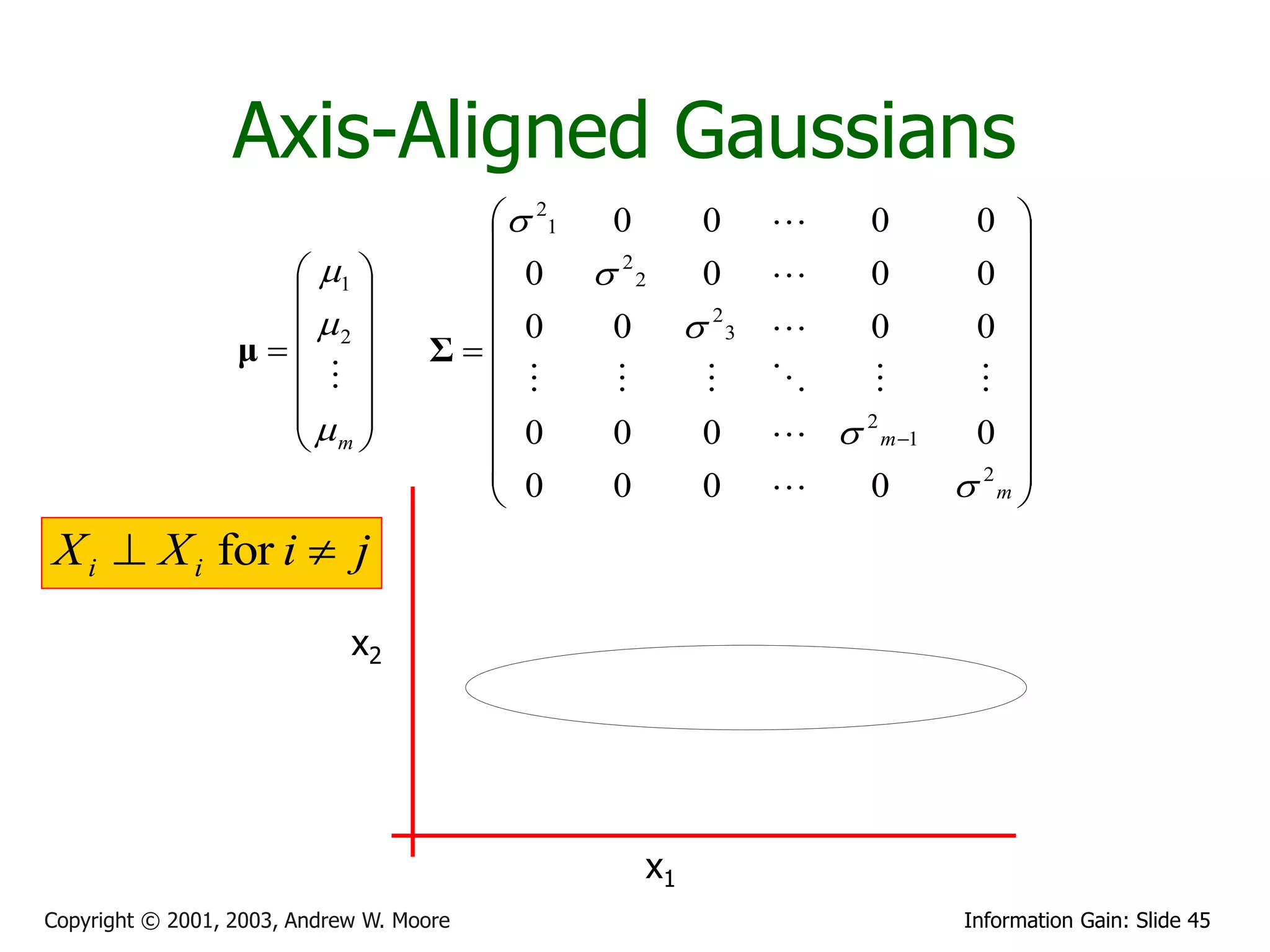
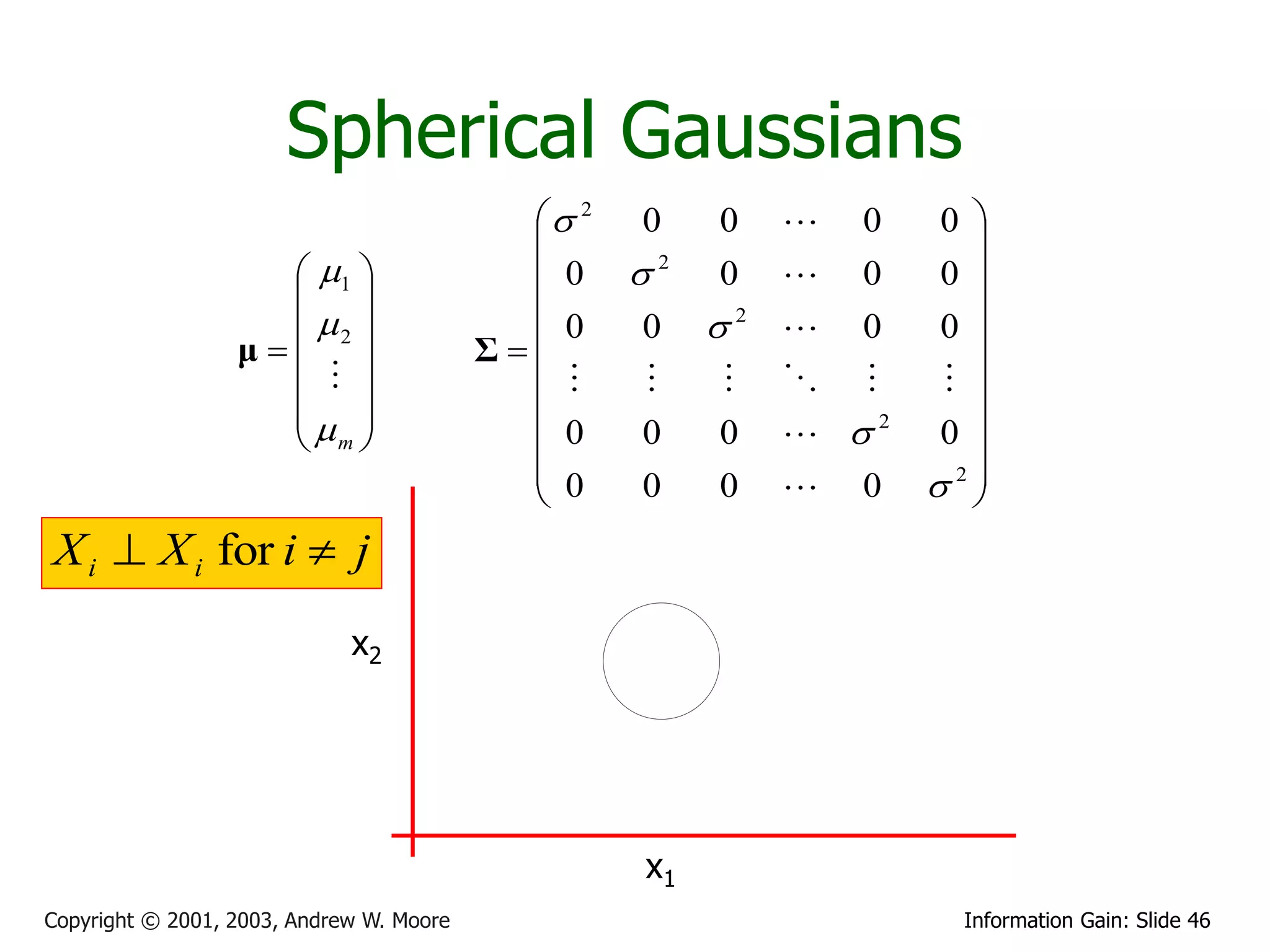
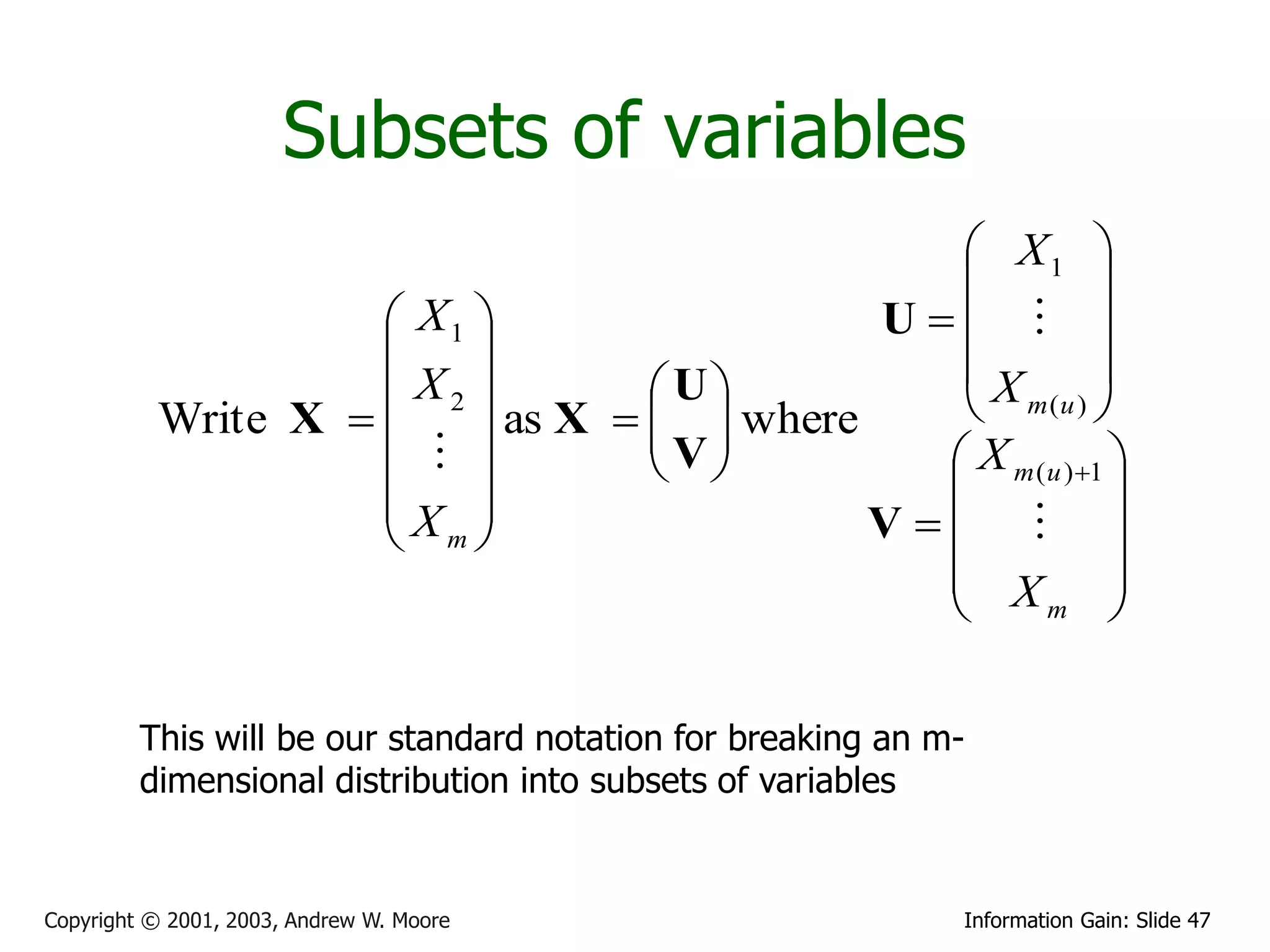
![Multivariate Gaussians
X1
X2
Write r.v. X Then define X ~ N (μ, Σ) to mean
X
m
p ( x) m
1
1
exp 1 (x μ)T Σ 1 (x μ)
2
(2 ) 2
|| Σ || 2
1 21 12 1m
Where the Gaussian’s
parameters have… 2 12 2 2 2m
μ Σ
2
m 1m 2 m m
Where we insist that S is symmetric non-negative definite
Again, E[X] = and Cov[X] = S. (Note that this is a resulting property of Gaussians, not a definition)
Copyright © 2001, 2003, Andrew W. Moore Information Gain: Slide 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmooreentropy-130326014925-phpapp01/75/2013-1-Machine-Learning-Lecture-02-Andrew-Moore-Entropy-43-2048.jpg)