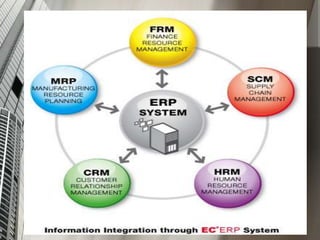
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a business management software that integrates various applications across departments, facilitating better productivity, cost efficiency, and data consistency. It offers complete visibility into processes and is characterized by a unified database that enhances security and workflow automation. The document also discusses the benefits, limitations, and the selection of ERP vendors based on organizational size.