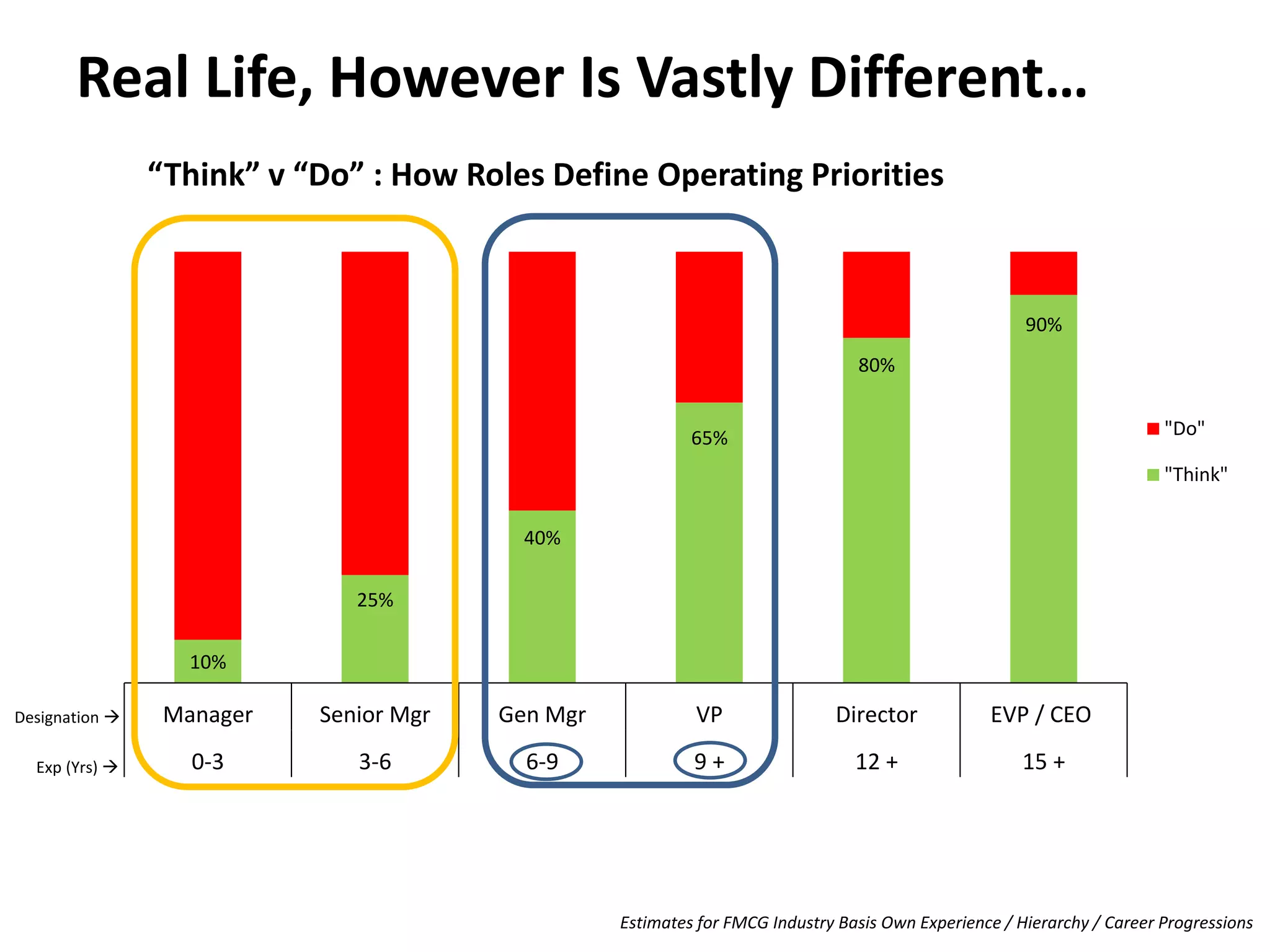
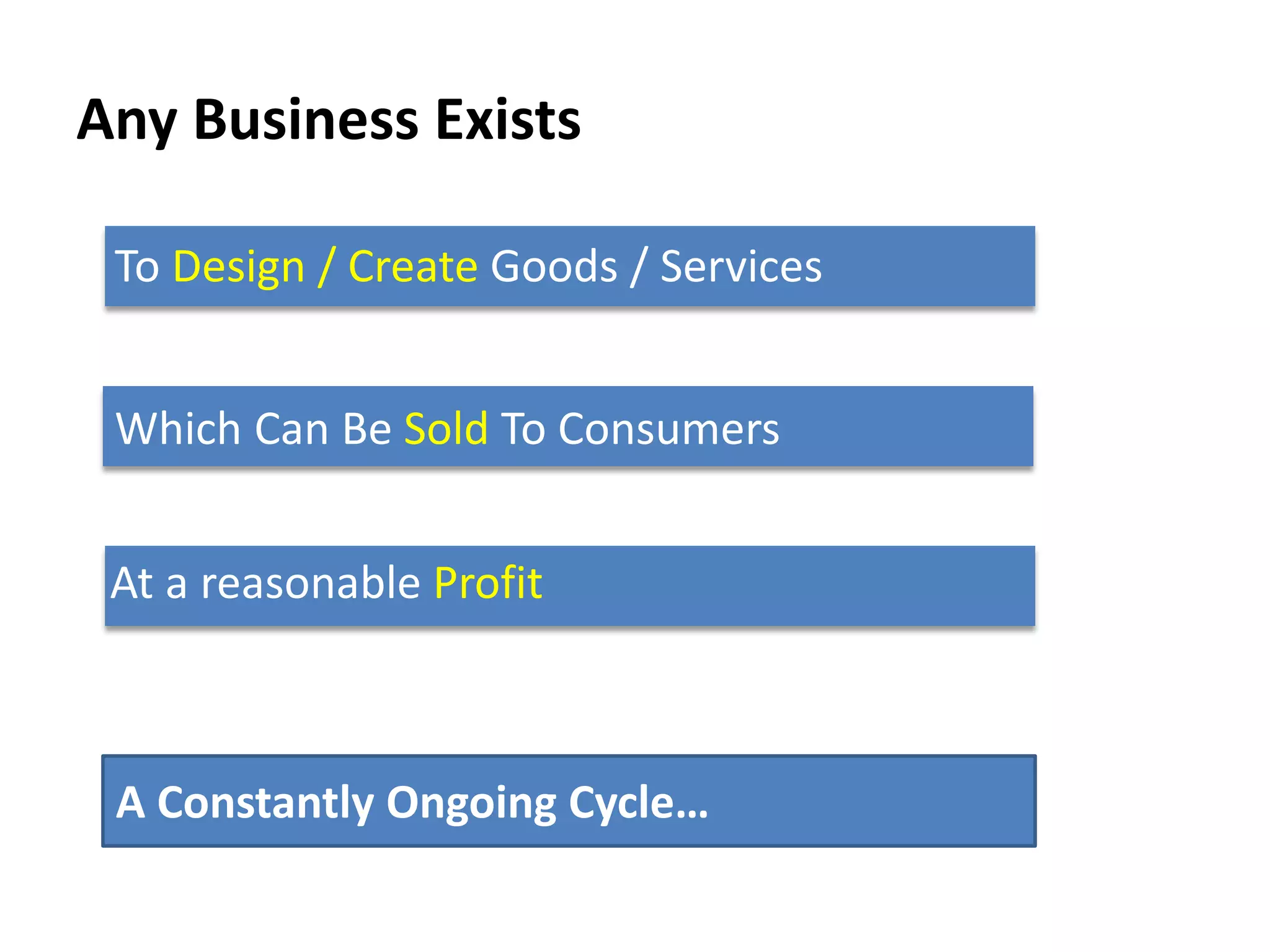
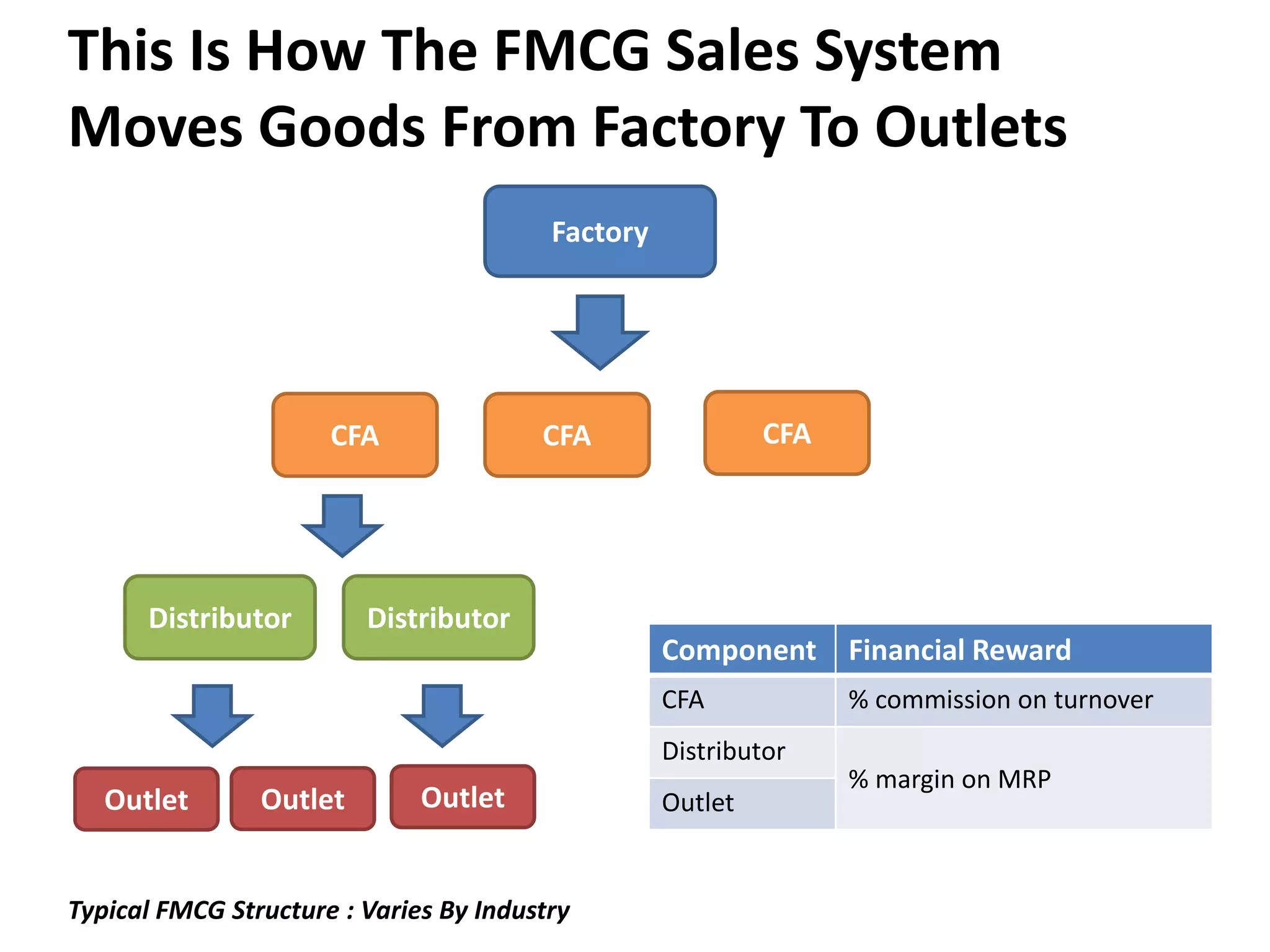
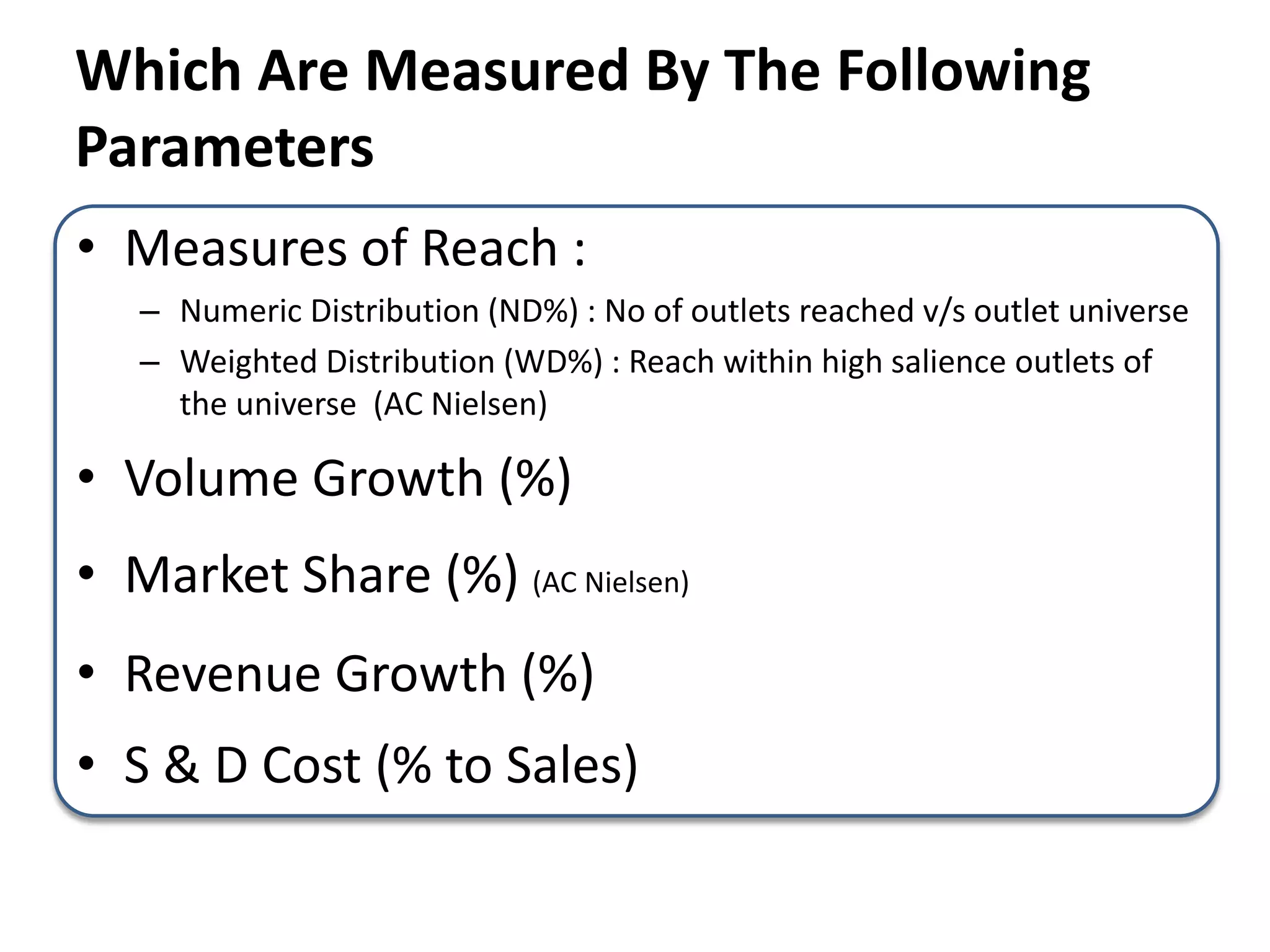
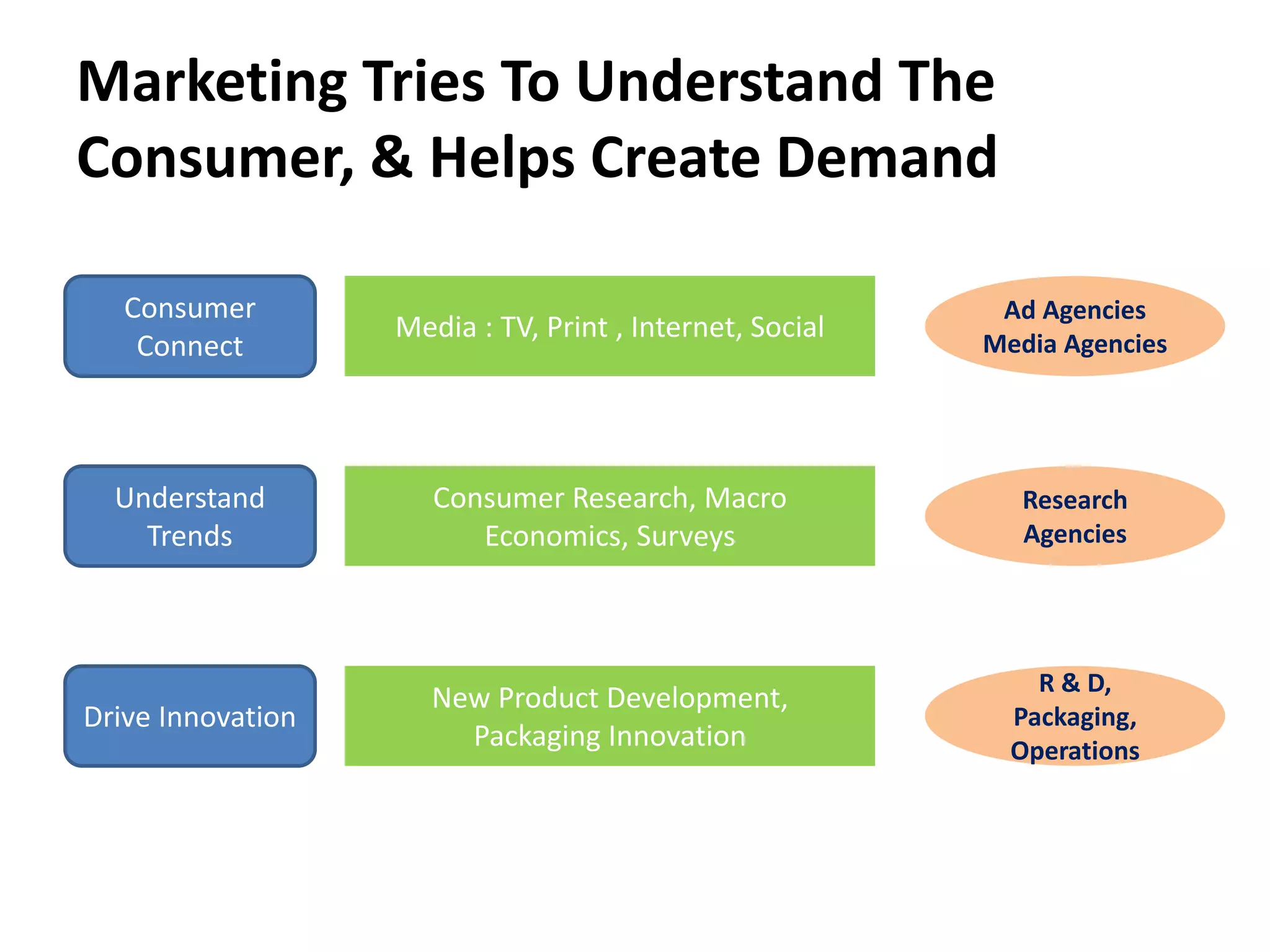
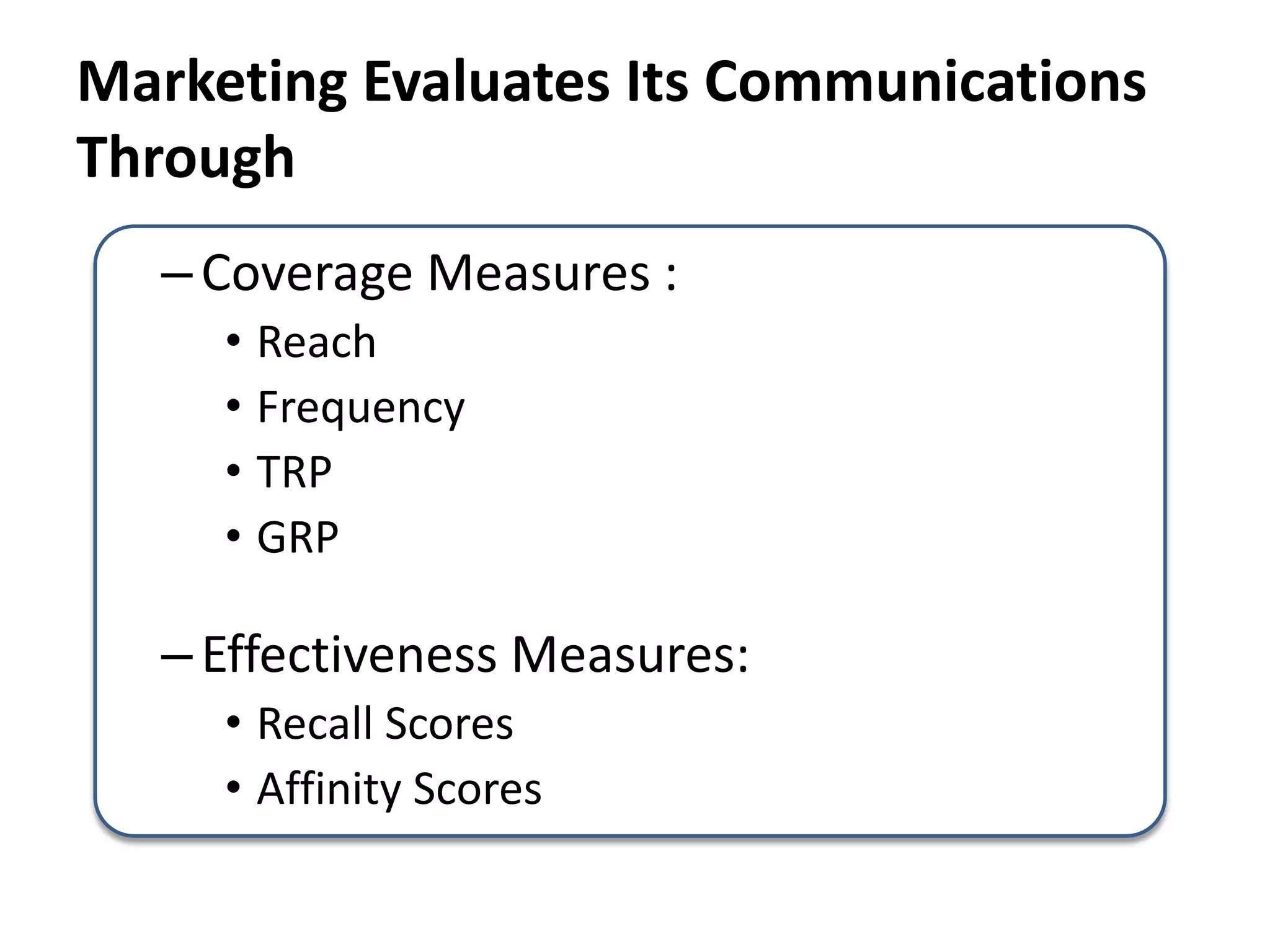
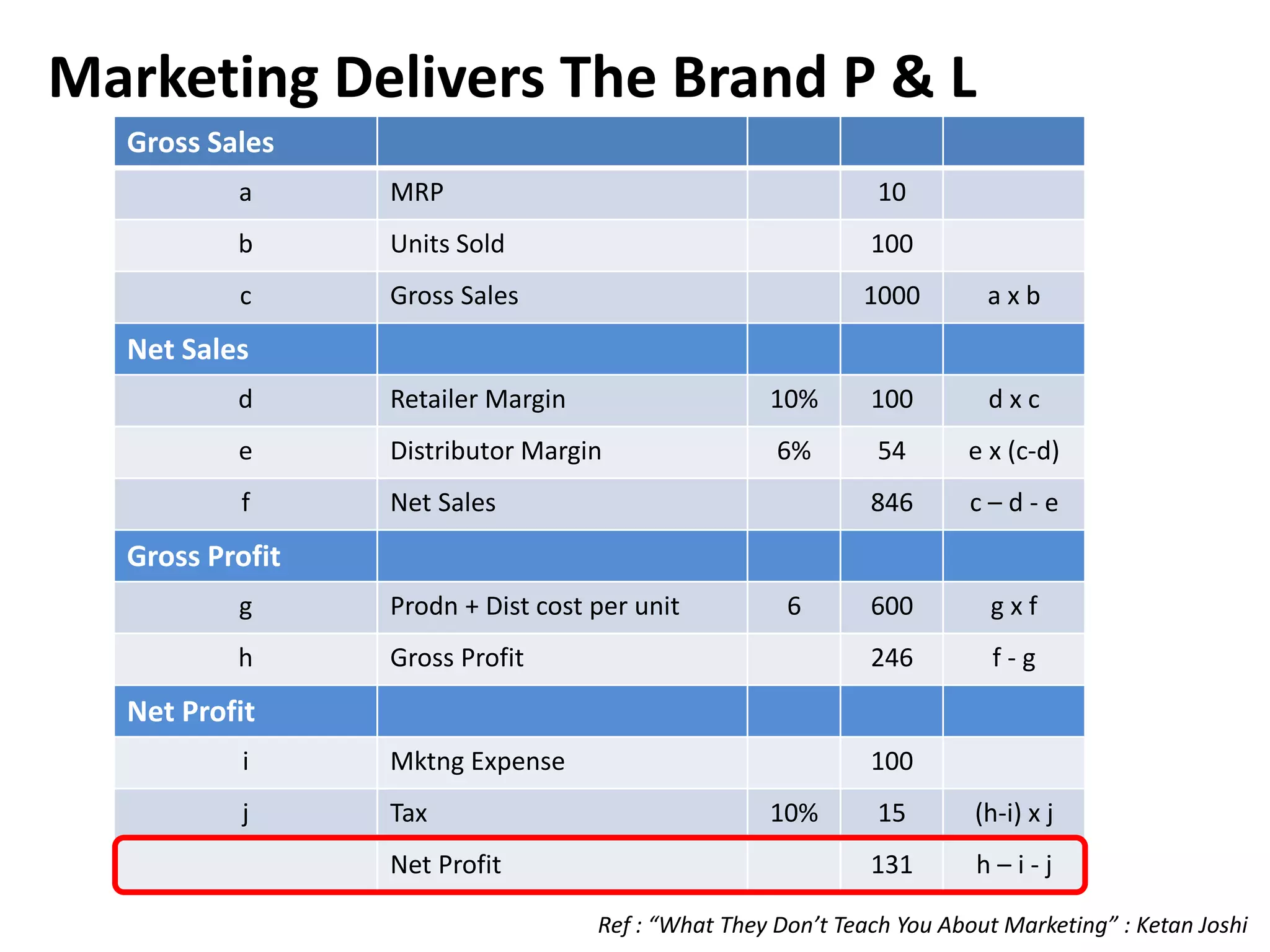
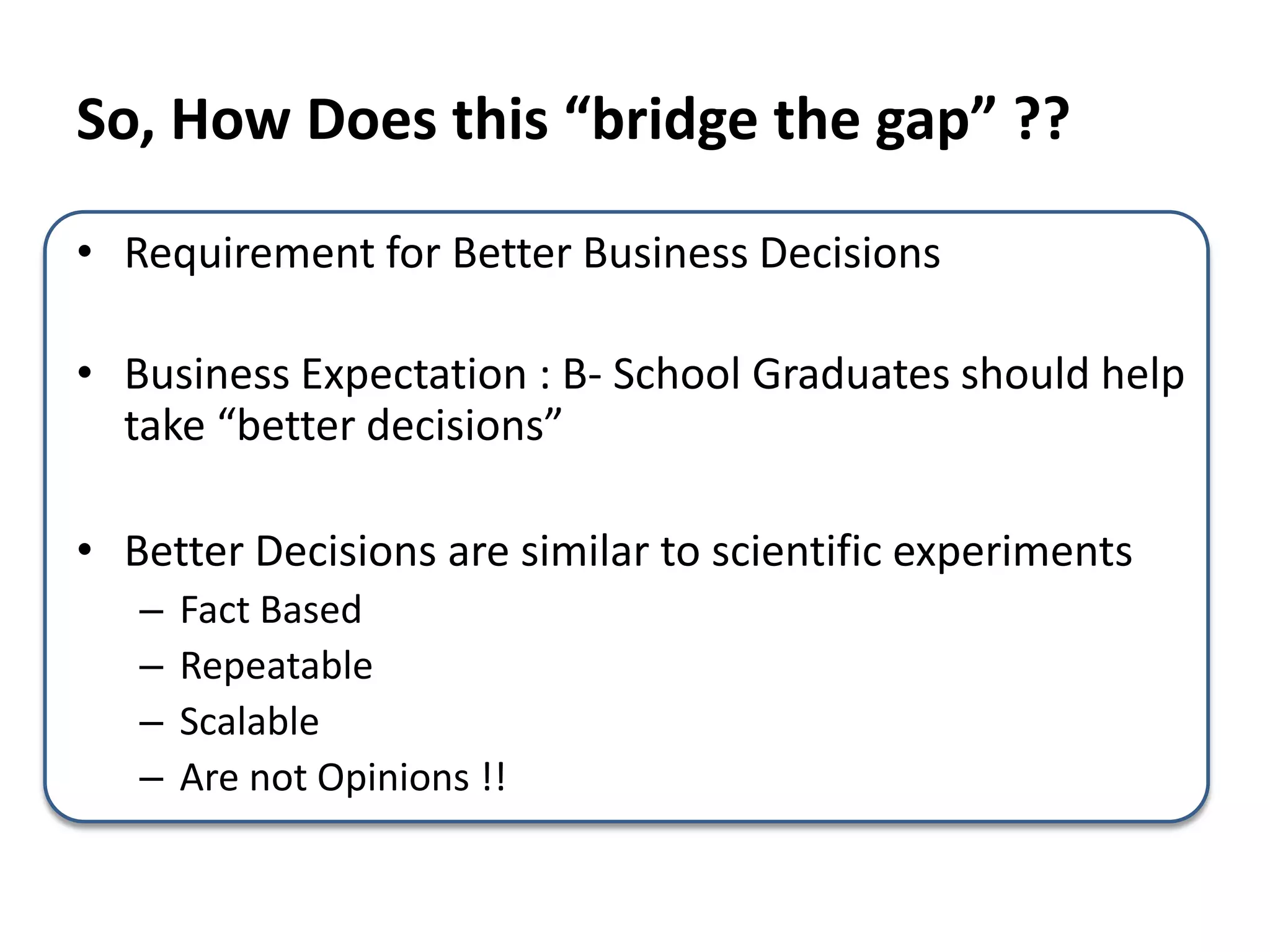
The document discusses bridging the gap between business theory taught in B-school and real-world business practices. It provides an overview of key business functions like sales, marketing, and management. For sales and marketing, it explains their goals, key activities, and metrics of success. It emphasizes the need for a "big picture" business perspective to make better, fact-based decisions. Marrying theoretical skills with an understanding of business expectations can help bridge the gap and accelerate careers. The session suggests leveraging projects and communication skills to develop operational abilities expected of managers.