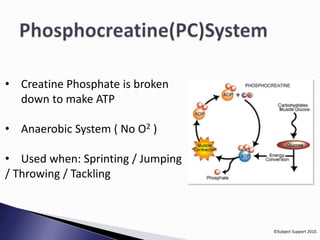
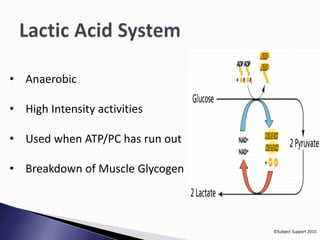
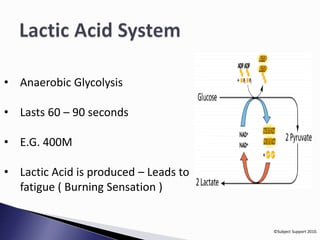
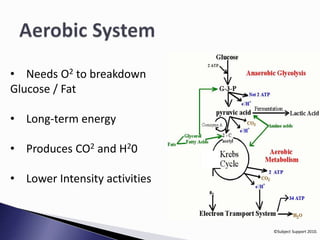
The document discusses different energy systems in the body. It asks where energy comes from and which nutrients provide energy. It then explains three main energy systems: the phosphocreatine (PC) system which provides energy for 10 seconds; the anaerobic lactic acid system which lasts 60-90 seconds; and the aerobic system which provides long-term energy through breakdown of glucose and fat but requires oxygen.