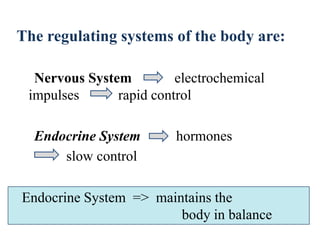
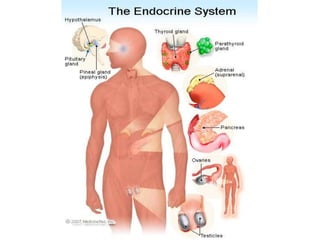
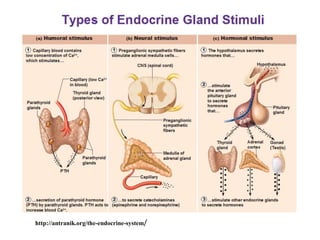
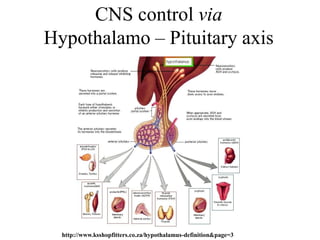
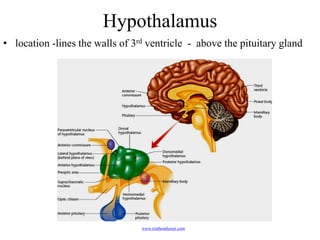
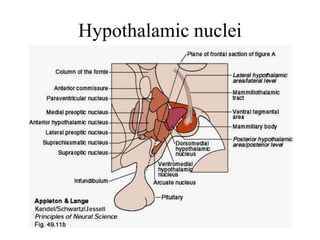
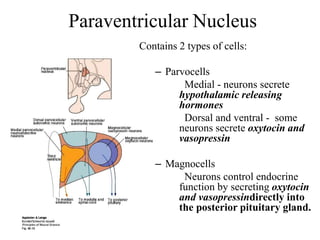
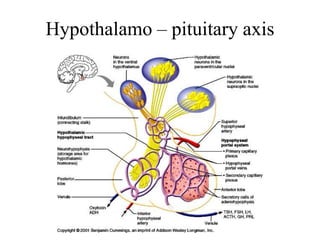
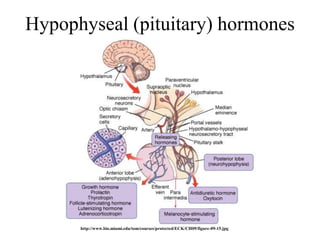
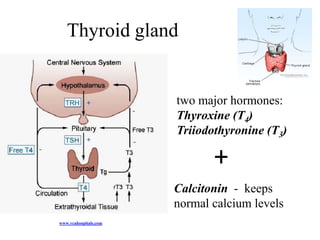
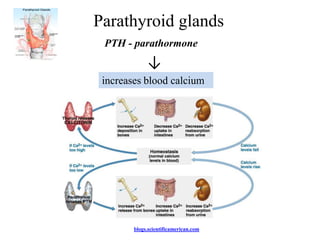
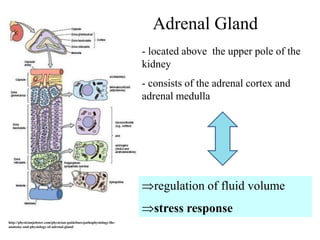
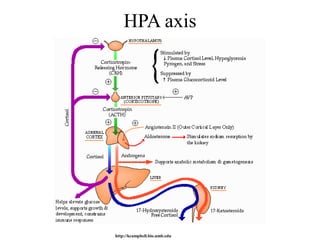
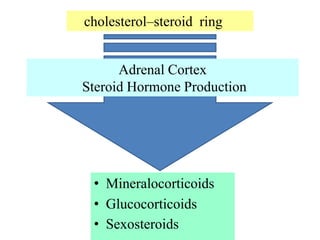
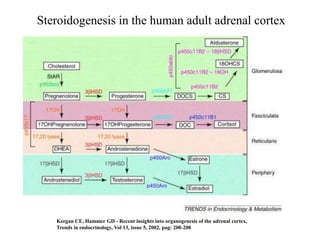
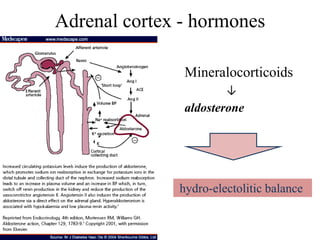
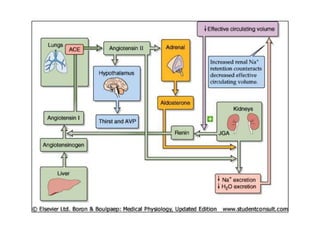
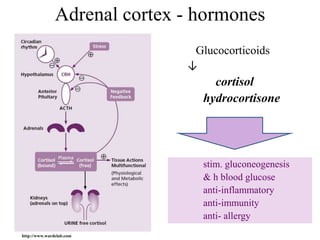
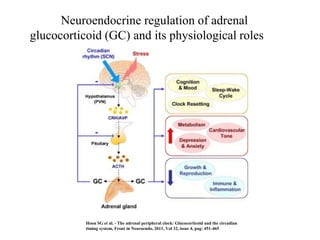
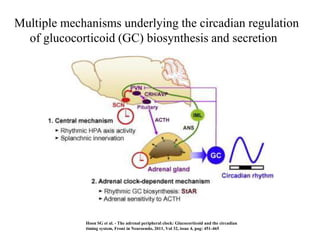
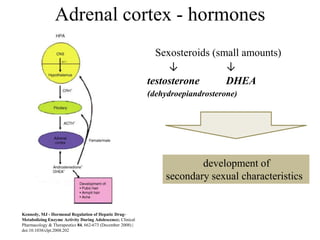
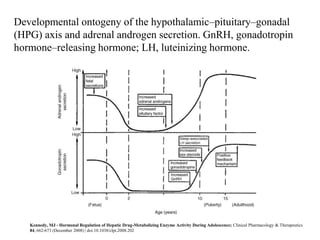
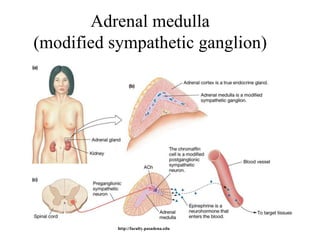
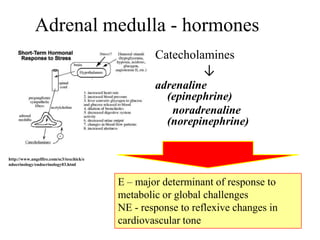
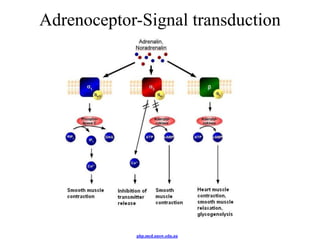
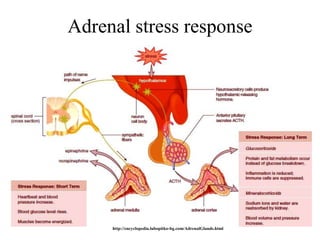
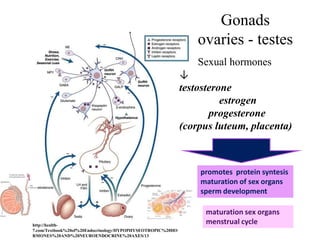
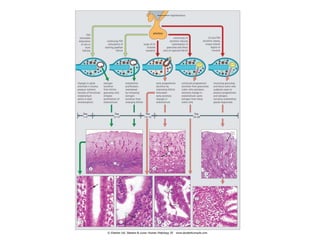
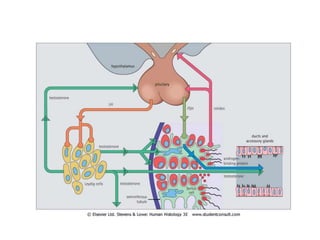
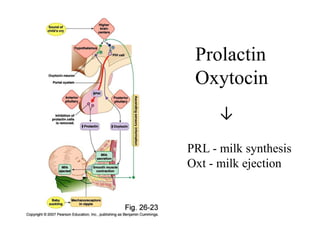
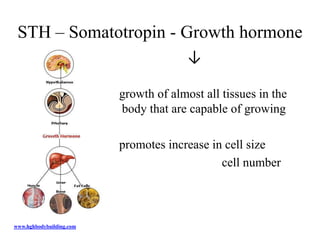
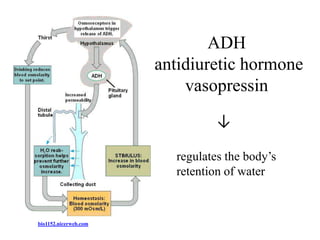
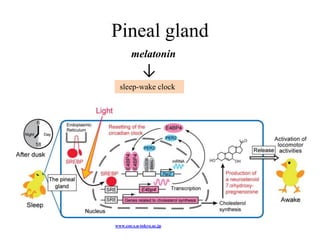
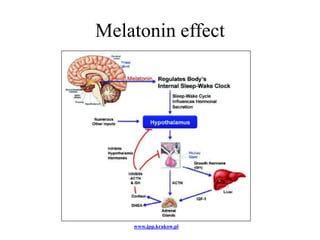
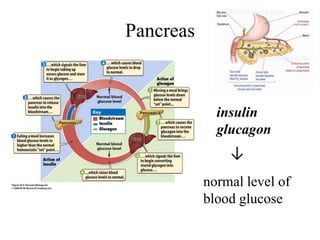
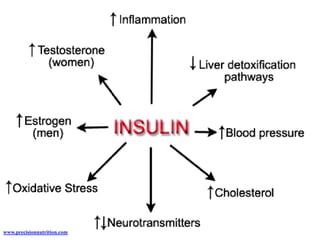
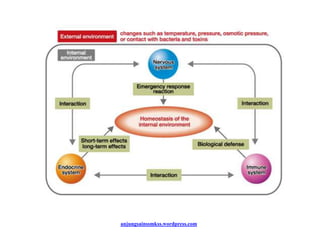
The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream. It works more slowly than the nervous system to regulate processes like metabolism, tissue function, sleep, and development. Key endocrine glands include the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain, thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck, pancreas, adrenal glands above the kidneys, ovaries/testes, pineal gland and others. Each gland secretes specific hormones that target tissues to produce responses like growth, energy use, stress response, and reproduction. The hypothalamus controls many glands through the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.