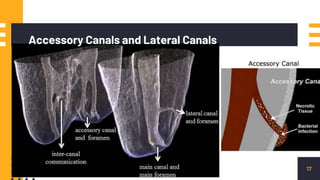
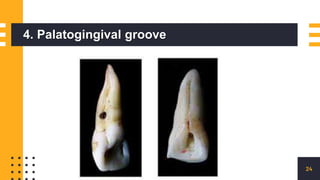
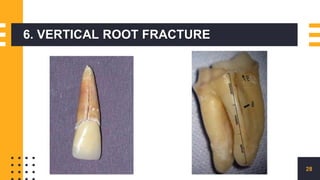
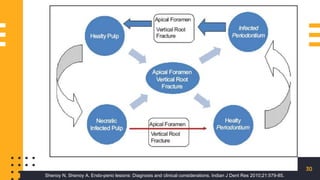
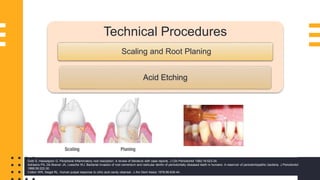
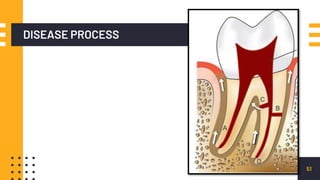
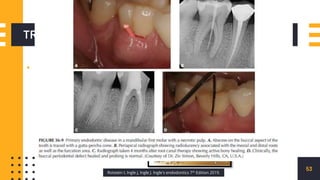
The document discusses endo-perio lesions, exploring their terminologies, etiological factors, and the pulp-periodontal relationship. It provides a historical perspective, classification systems, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options for these lesions. The document emphasizes the complex interplay between endodontic and periodontal conditions and their clinical implications.