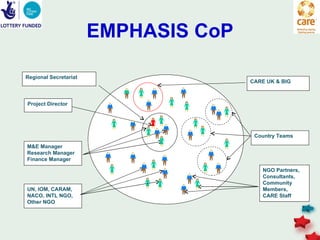
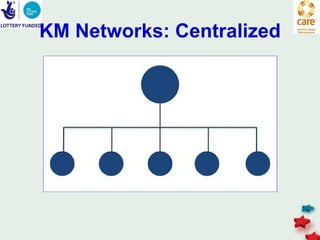
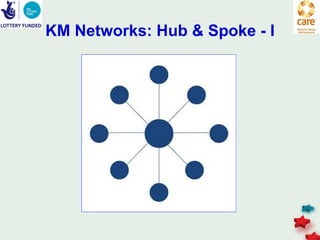
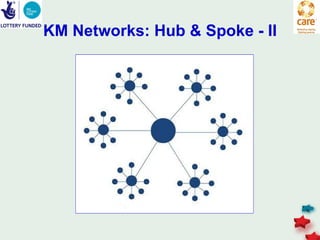
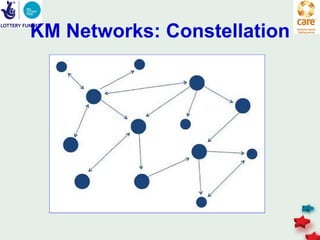
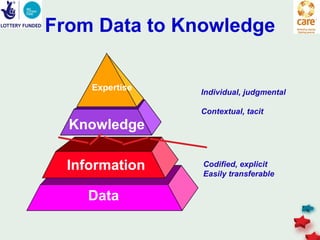
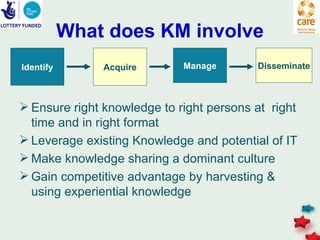
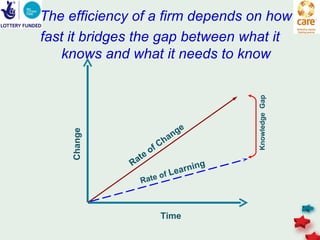
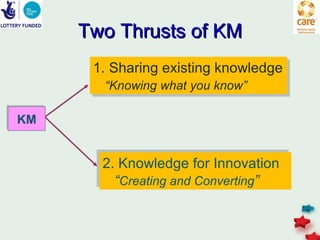
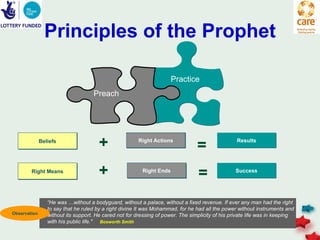
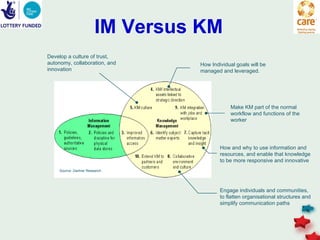
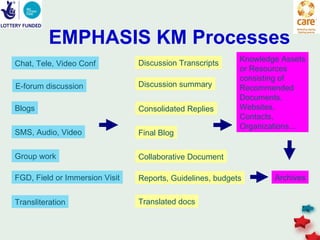
The document discusses knowledge management in the context of an EMPHASIS project. It describes the environment as complex with regional and matrix structures. Communities of practice are discussed as informal networks for sharing ideas. Different knowledge management network structures are presented, and challenges around costs, quality, and innovation are noted. Sustaining change through knowledge is emphasized, with knowledge seen as the most important resource.


![Community of Practice (CoP)
An affinity group. An informal network or forum
where tips are exchanged and ideas generated
[Thomas A. Stewart].
A group of professionals, informally bound to one
another through exposure to a common class of
problems, common pursuit of solutions, and
thereby themselves embodying a store of
knowledge [McKinsey & Co.].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emphasisintroductiontokm-120330084947-phpapp01/85/Emphasis-introduction-to-km-3-320.jpg)