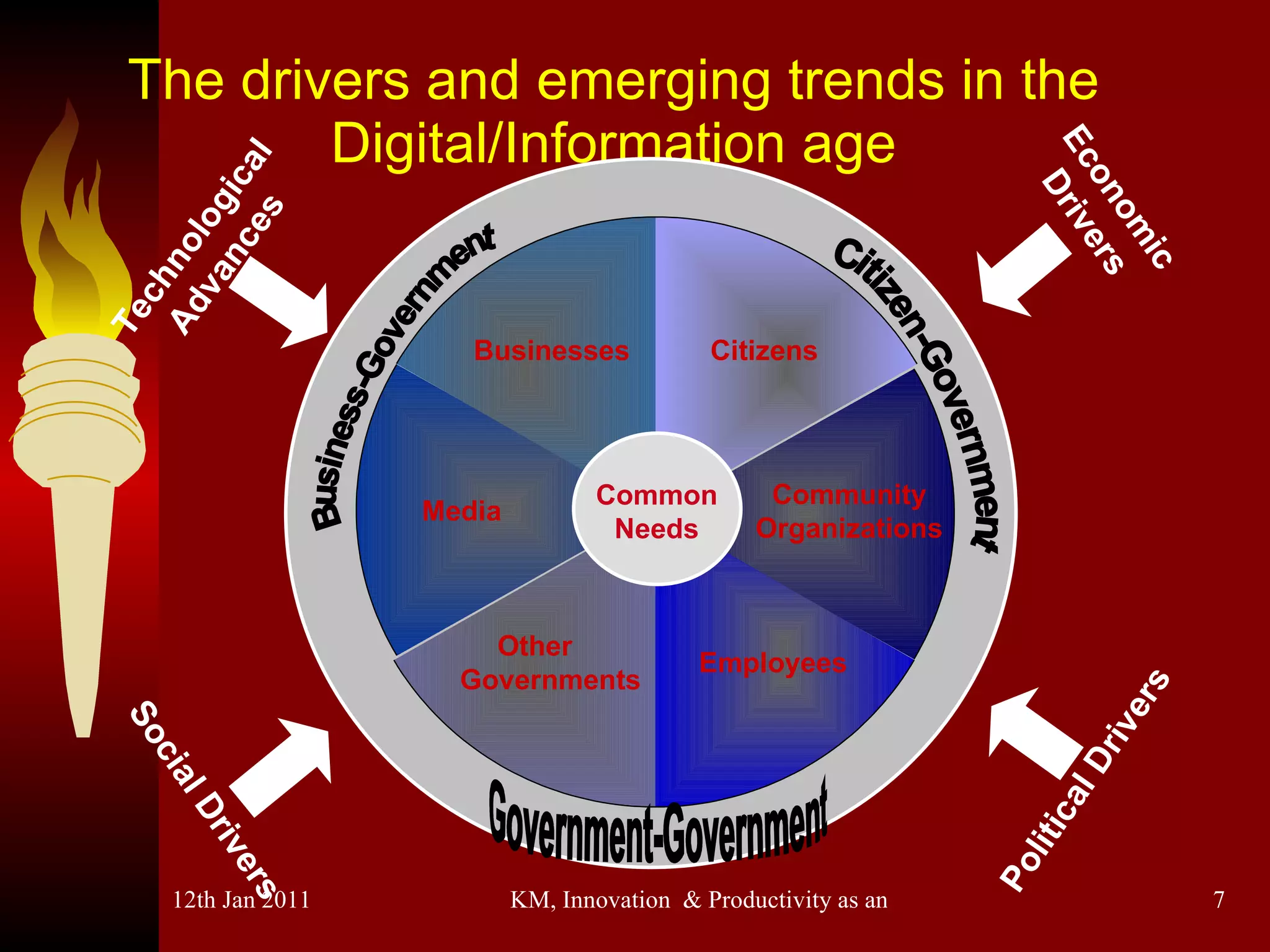
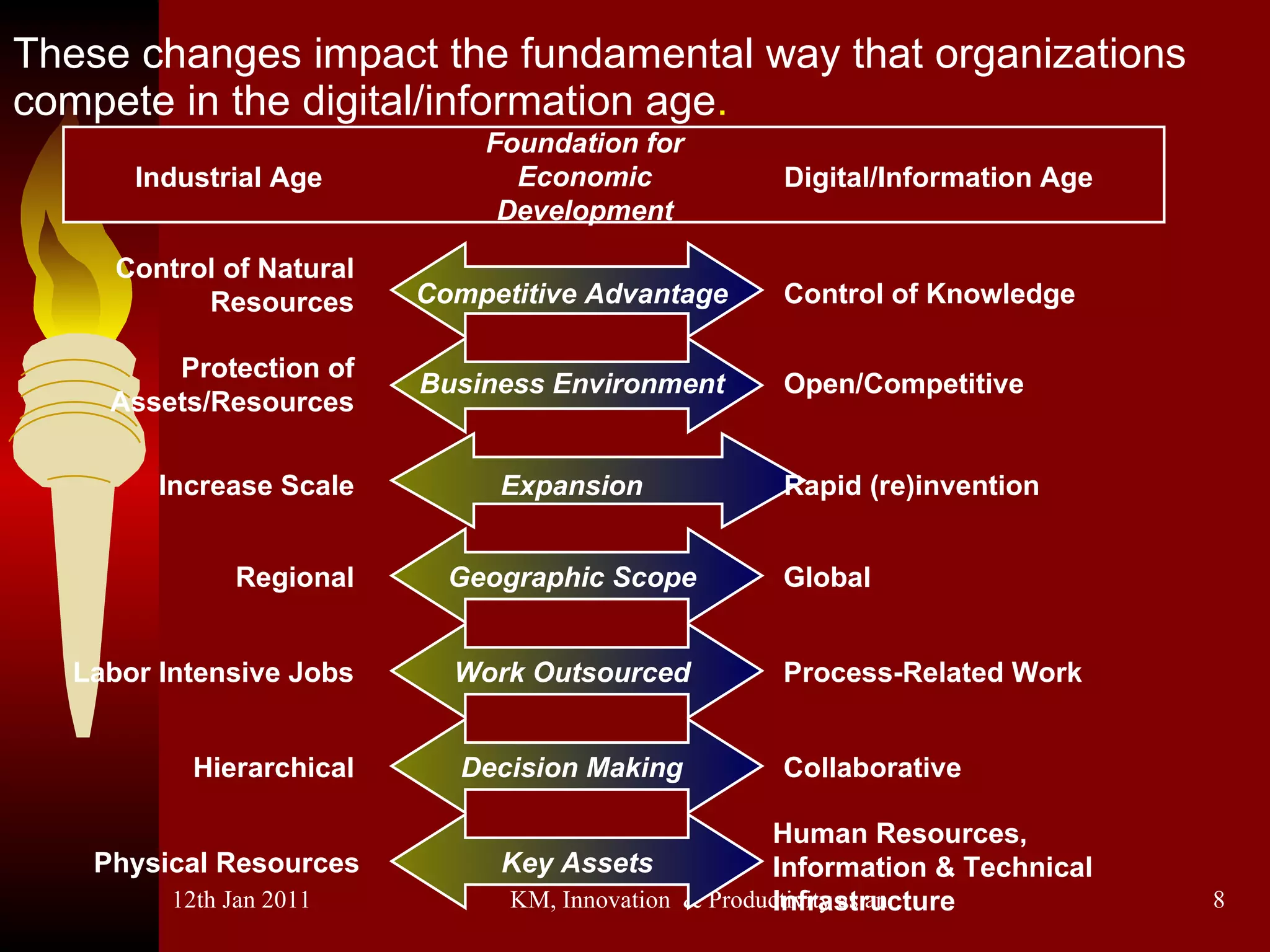
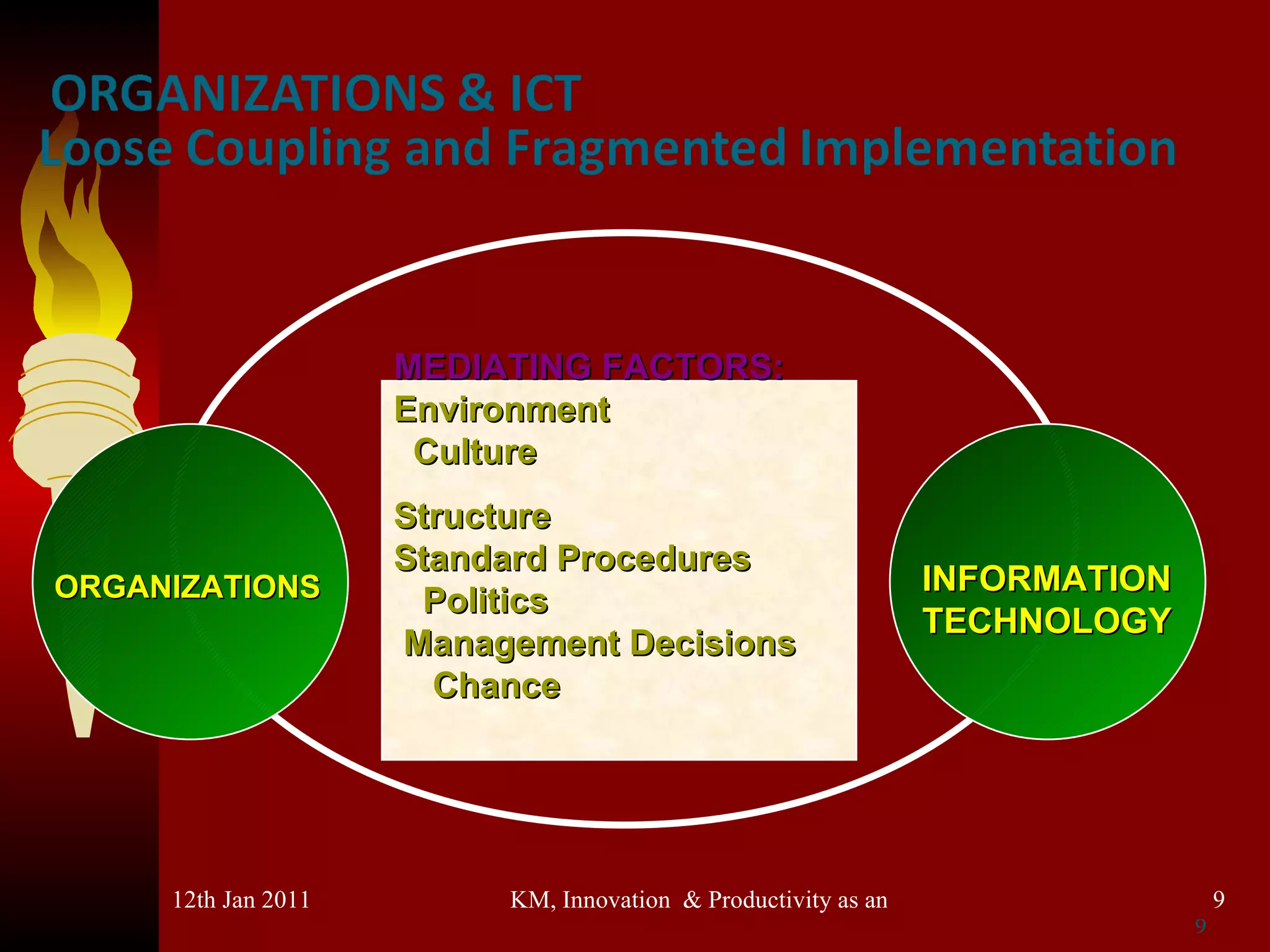
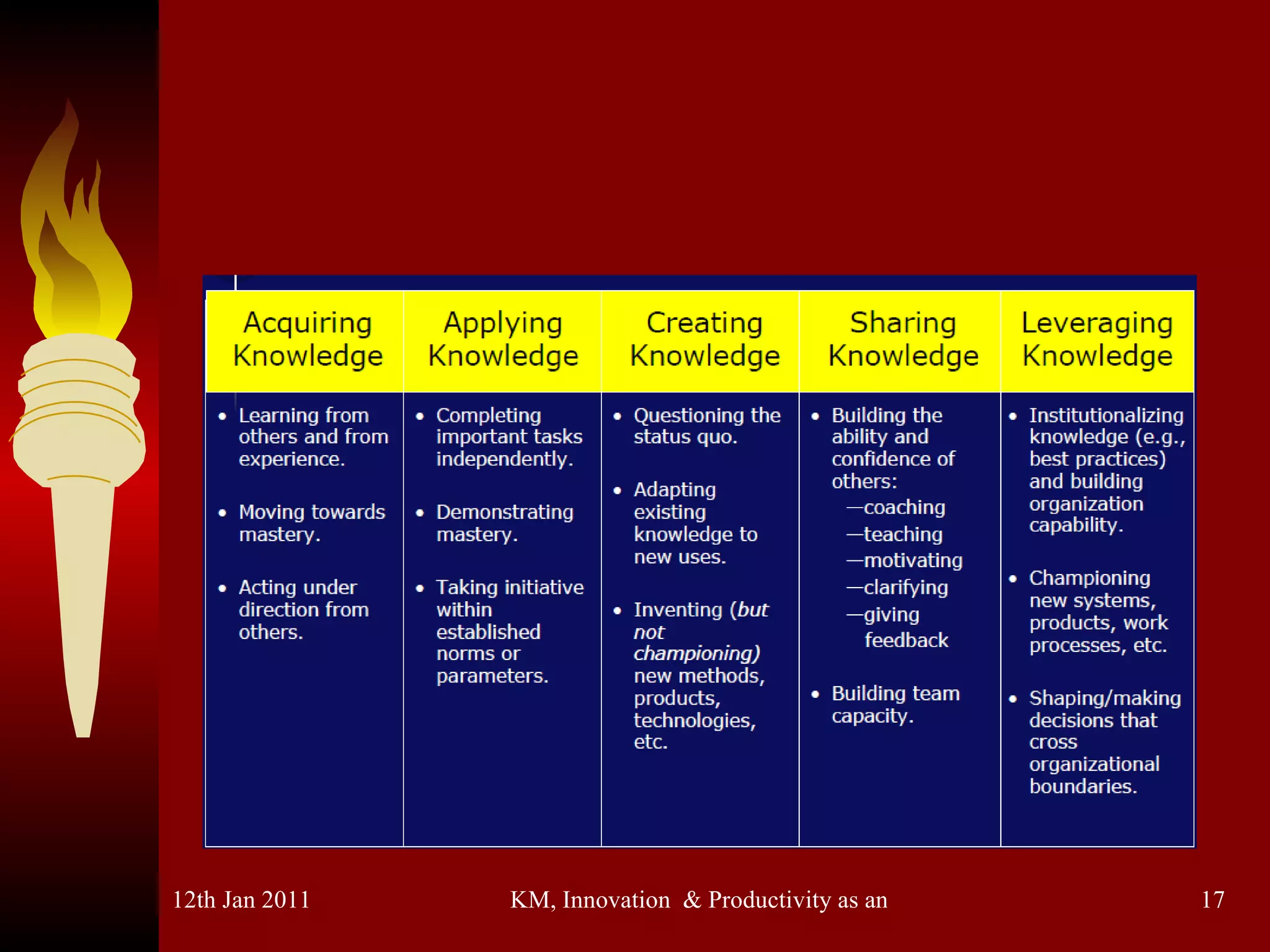
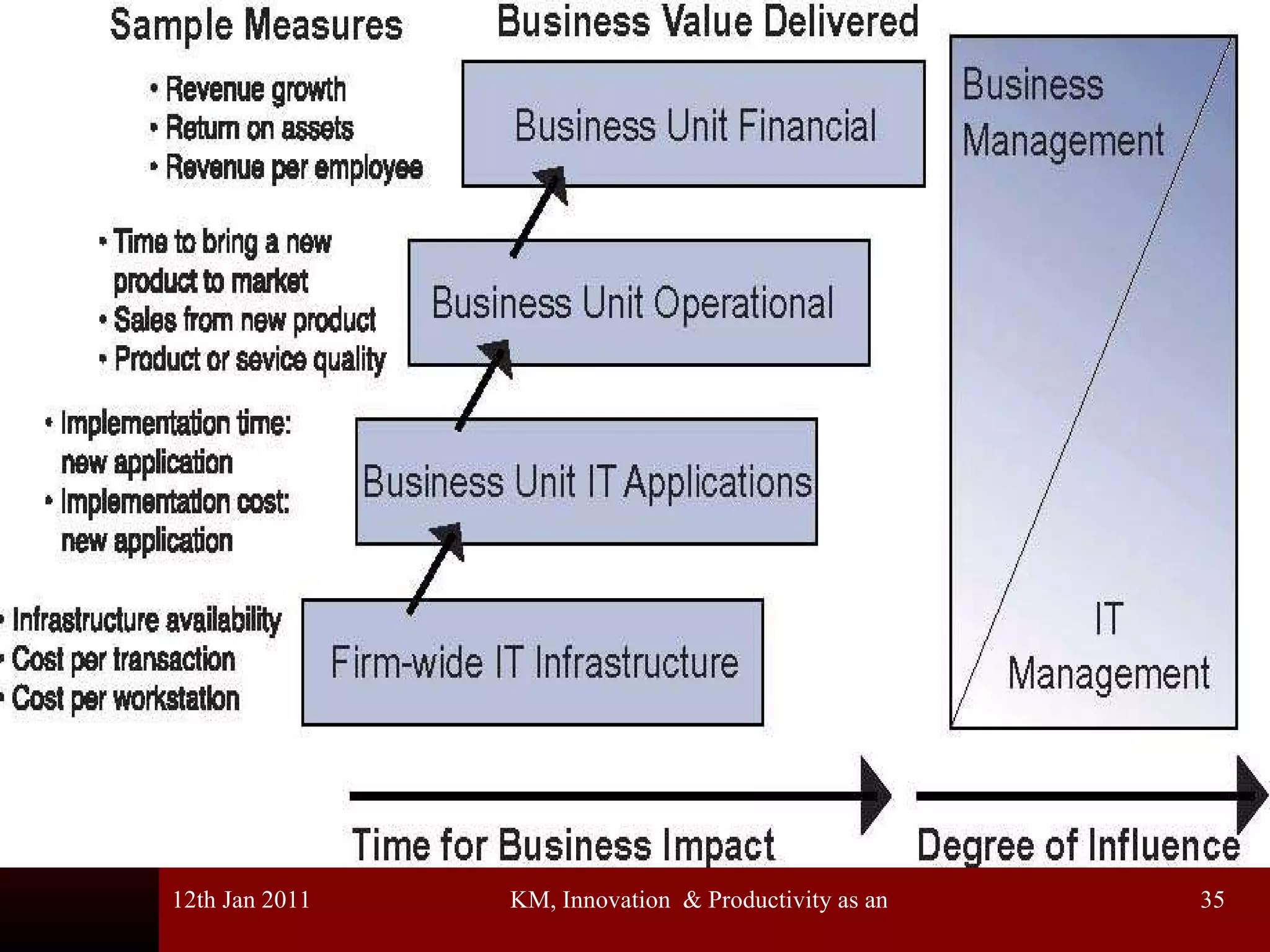
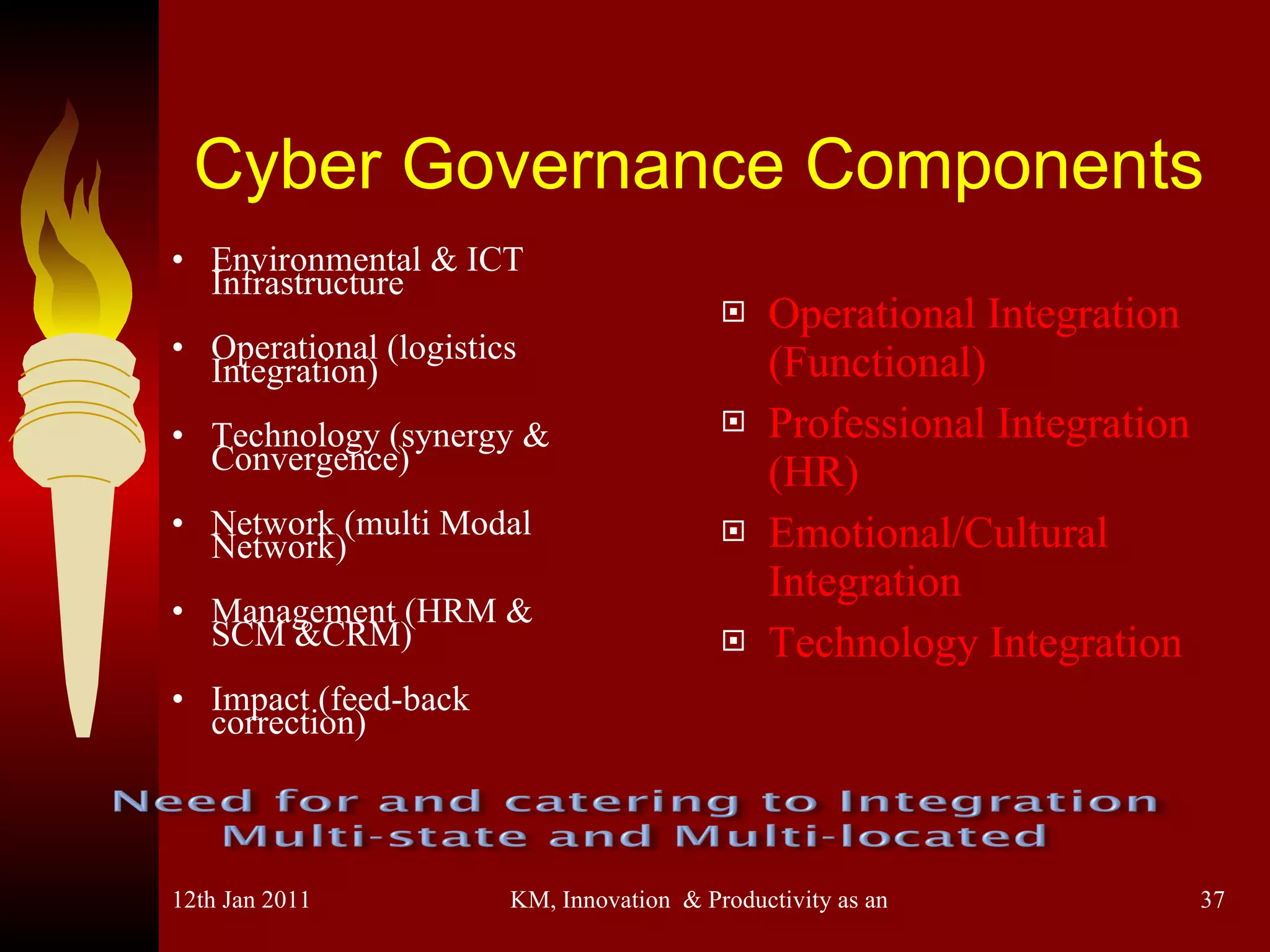
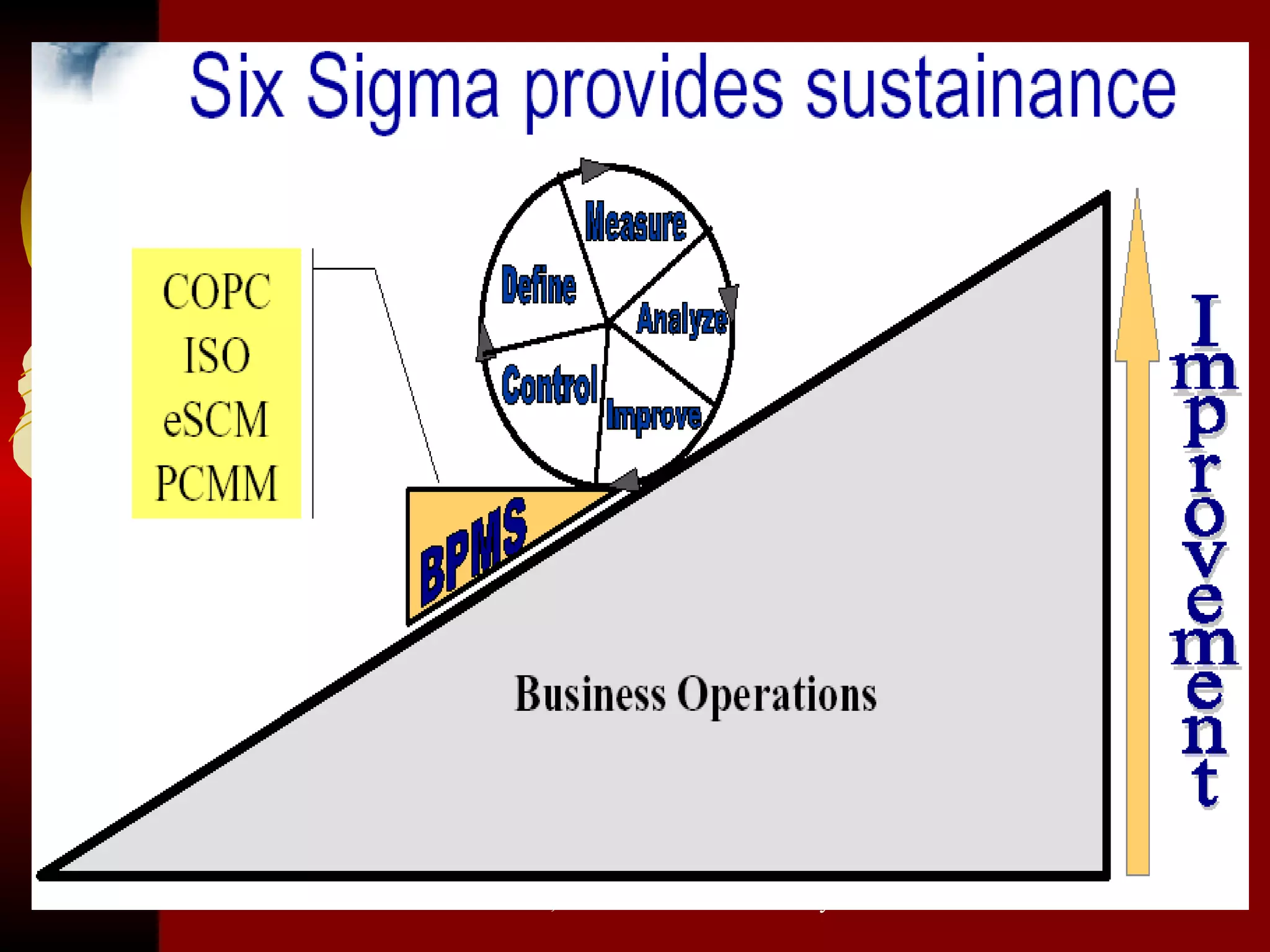
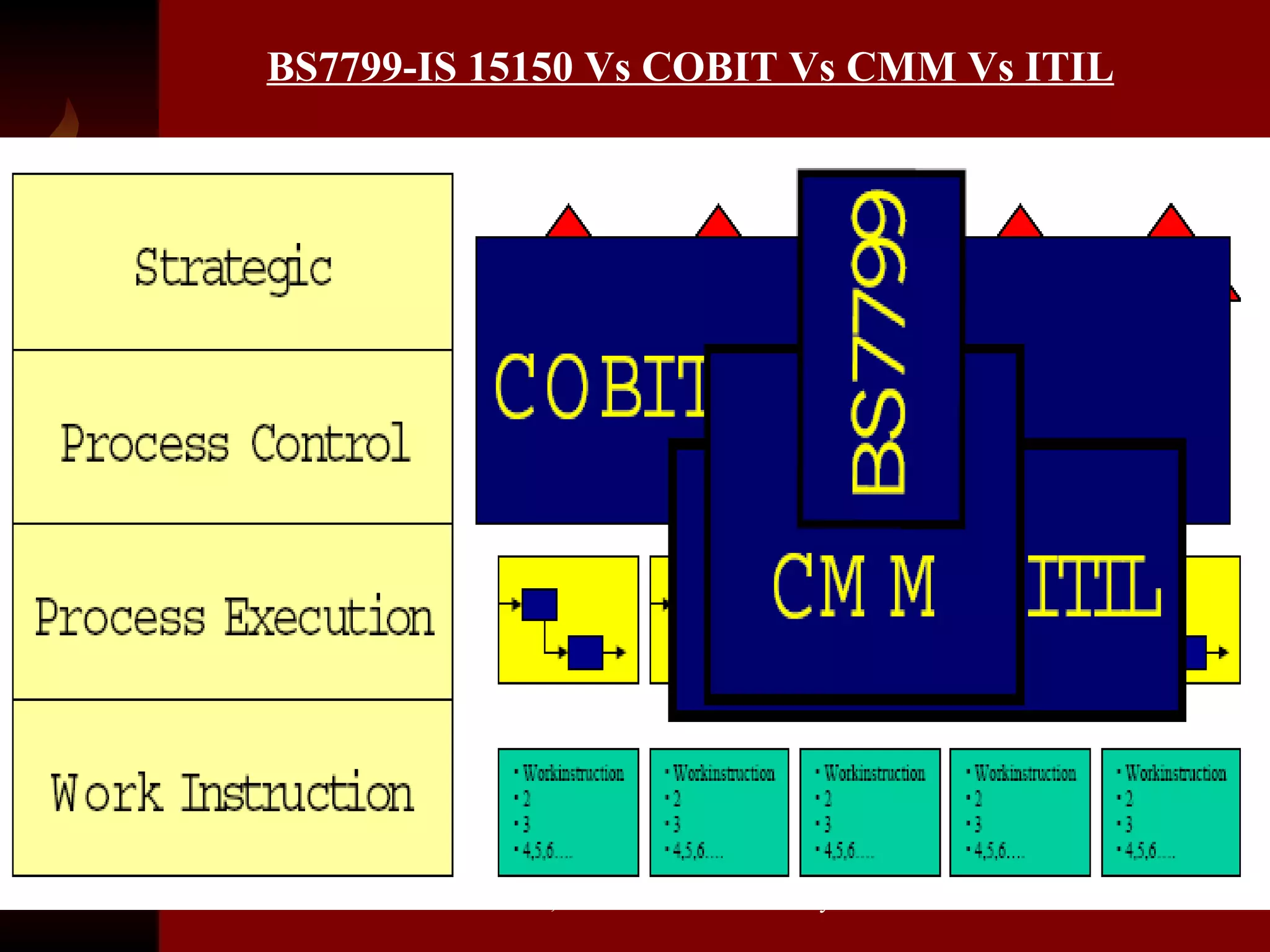
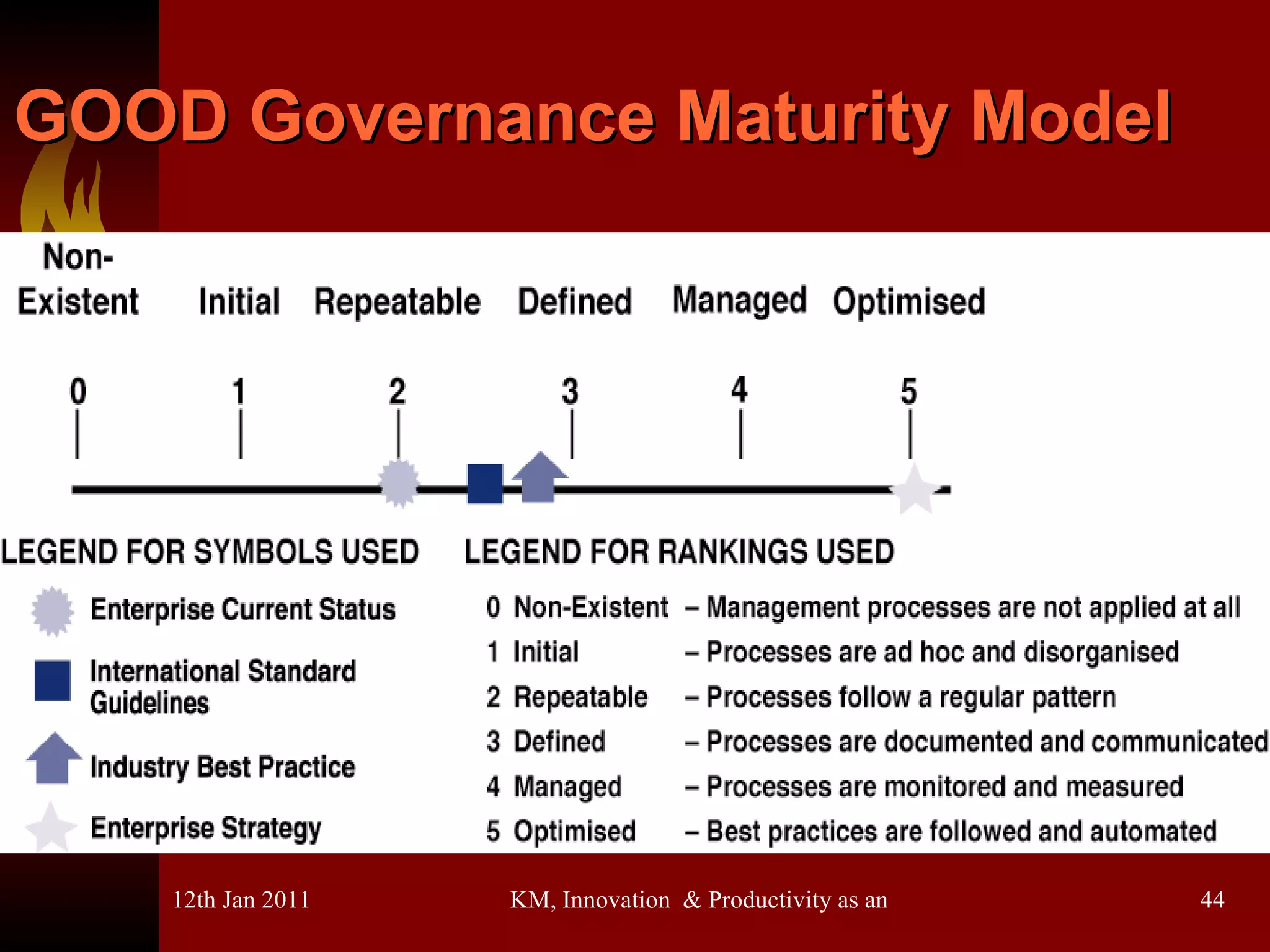
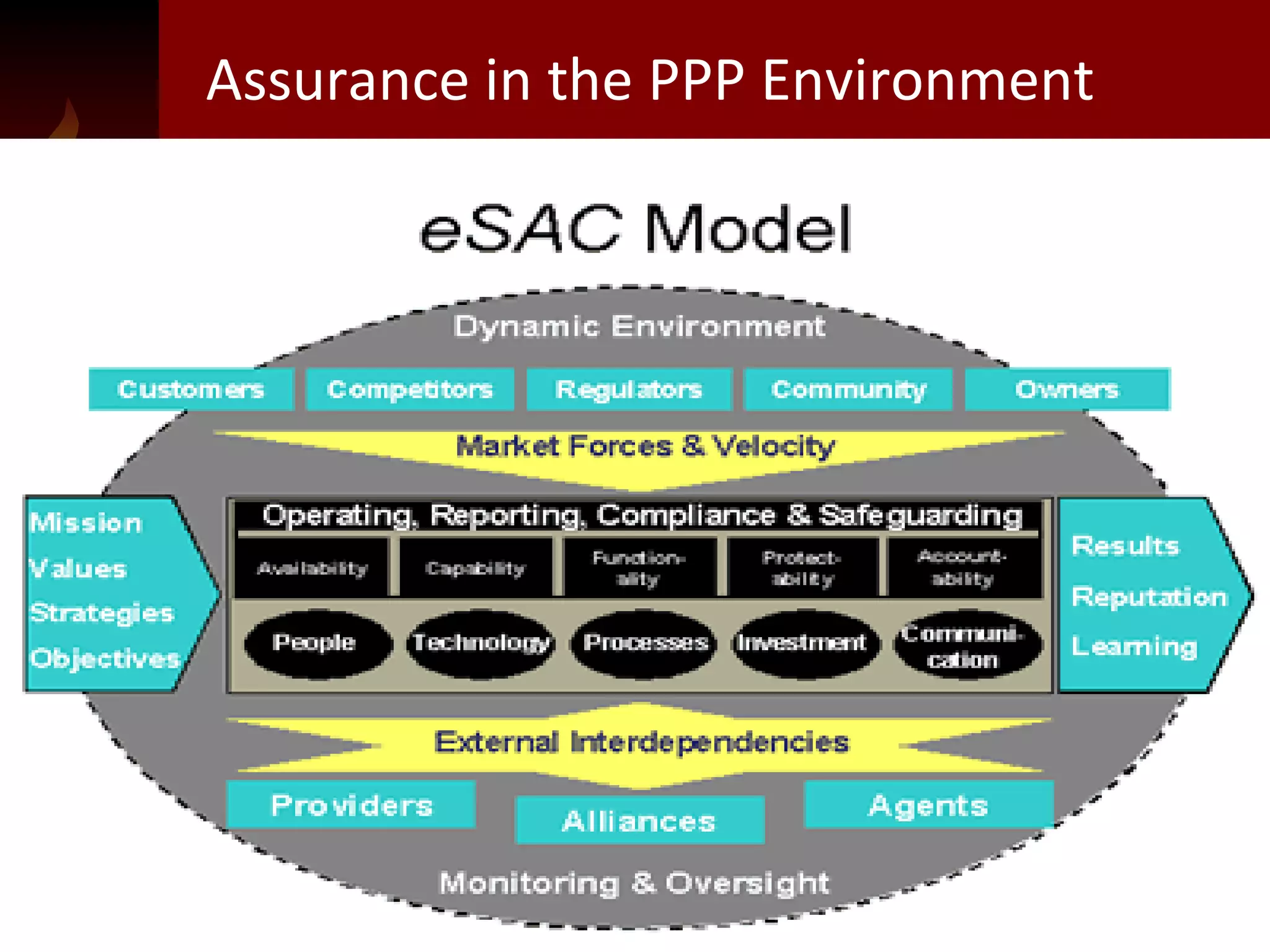
The document discusses knowledge management, innovation, and productivity as integral parts of good governance. It covers recent developments in these areas, myths about knowledge management, and how innovation and productivity can be improved through standards and governance frameworks. Maturity models are presented as a way to evaluate knowledge management strategies and ensure good governance of cybersecurity and information technology.






































![THANK YOU For Interaction: Prof. K. Subramanian [email_address] [email_address] [email_address] [email_address] Tele: 29533068](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iipalecturekmgoodgovernancejan122011-110408181446-phpapp01/75/Iipa-lecture-km-good-governance-jan-12-2011-49-2048.jpg)