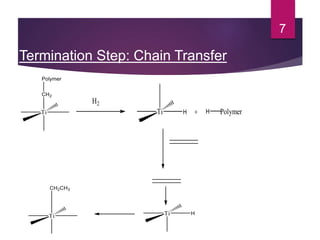
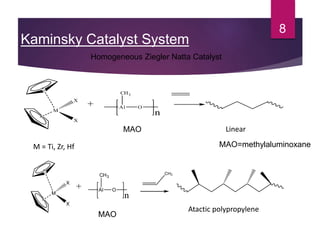
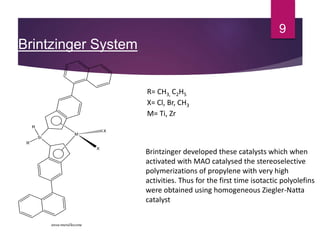
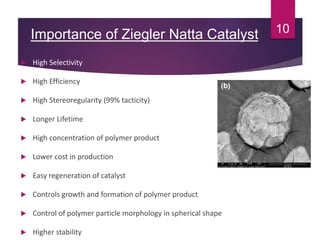
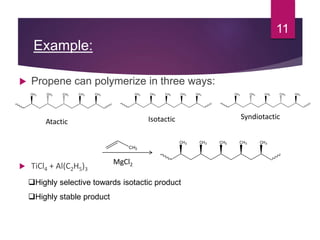
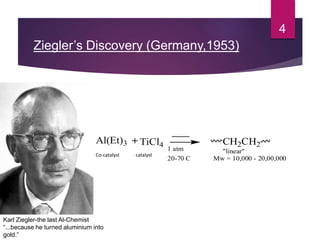
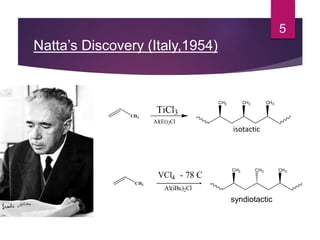
Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta discovered Ziegler-Natta catalysts in the 1950s, for which they received the Nobel Prize. Ziegler-Natta catalysts are highly selective and efficient in producing polyolefins like polyethylene and polypropylene. They work via a Cossee mechanism of migratory insertion and chain transfer. Various generations of Ziegler-Natta catalysts have been developed with improved activities. These catalysts find widespread applications in producing commodities like HDPE, LDPE, PP, and other polyolefins.



![Mechanism of Ziegler-Natta
Polymerization: The Cossee Mechanism
6
Ti
CH2
Polymer
Catalyst accepts
ethylene as a
ligand
1,2- Migratory
insertion [Ethyl
migration]
Ti CH2CH3
H2C CH2
ligand
association
Ti CH2CH2
CH2H2C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ziegler-nattacatalystnew-151123135651-lva1-app6892/85/Ziegler-natta-catalyst-6-320.jpg)