The document discusses emulsion polymerization. Key points include:
1) Emulsion polymerization is an economically important process that is used to produce over 30% of polymers made by free radical methods.
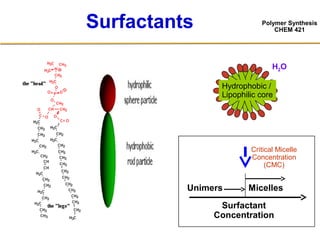
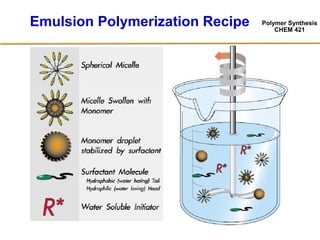
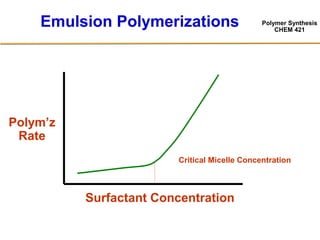
2) The recipe for emulsion polymerization involves water, water-insoluble monomer, water-soluble initiator, and surfactant.
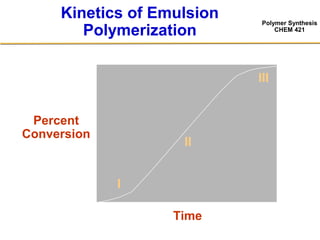
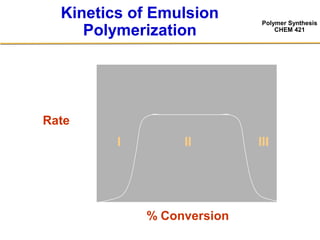
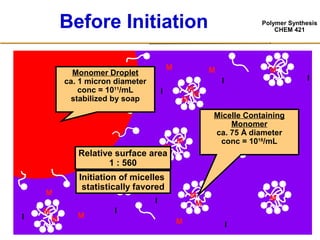
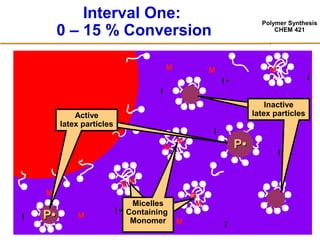
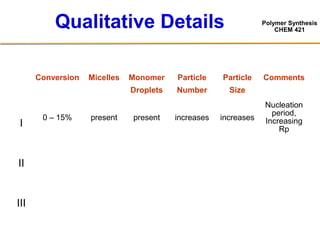
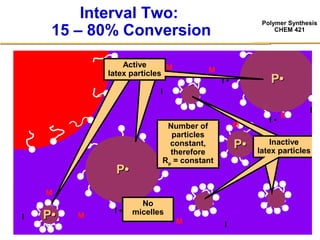
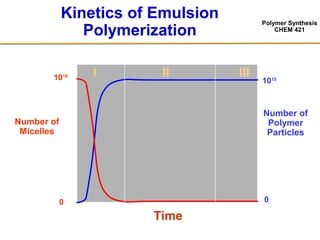
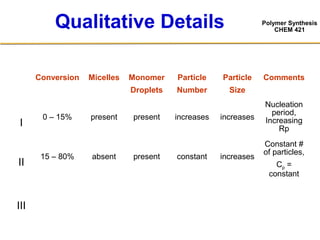
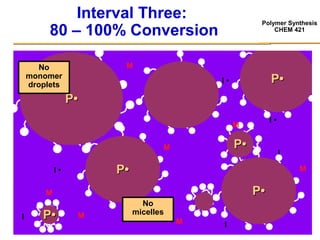
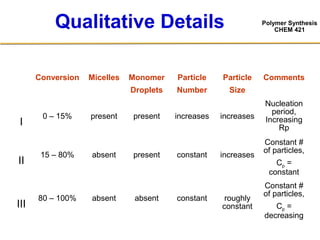
3) The kinetics of emulsion polymerization occurs in three stages: nucleation and particle growth (0-15% conversion), constant particle number (15-80% conversion), and final conversion (80-100% conversion).

![Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Emulsion Polymerization Kinetics
• Once inside a particle, radical propagates
as rp = kp[M]
• Overall rate: Rp = kp[M][P.
]
• [P.
] = N’ñ (where N’ = the sum of micelle
and particle concentrations and
ñ = average # of radicals per particle)
• Therefore,
–Increase N’ to increase rate!
][' MknNR pp =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synthesispoly-140425110303-phpapp01/85/Synthesis-poly-18-320.jpg)

![Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Emulsion Polymerization Kinetics
• How to increase Rp?
–Increase N’ to increase rate
»Increase surfactant concentration to increase N’
][' MknNR pp =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synthesispoly-140425110303-phpapp01/85/Synthesis-poly-20-320.jpg)
![Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Molecular Weight in Emulsion
Polymerizations
• Molecular weight determined by rate of growth
of a chain divided by rate of radical entry (ri)
–How to increase molecular weight?
DP
rp
= ——ri
Ri
= ——
N
ri = kp[M]rp
N kp [M]
Ri
= ———DP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synthesispoly-140425110303-phpapp01/85/Synthesis-poly-21-320.jpg)
![Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Free Radical Solution
Polymerizations
• Recall
– To increase molecular weight…
» Increase monomer concentration
» Decrease initiator concentration
– To increase Rate of Polymerization
» Increase monomer concentration
» Increase initiator concentration
٧ =
kp [M]
2 (kt kd f [I])1/2
= —————
Can’t do
both!
Rp = kp [M] (kd f [I] / kt)1/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synthesispoly-140425110303-phpapp01/85/Synthesis-poly-22-320.jpg)