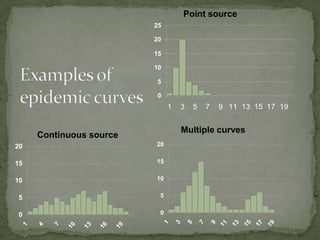
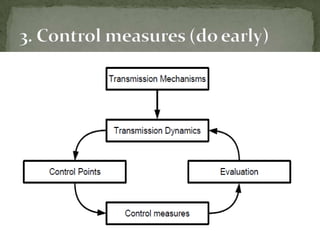
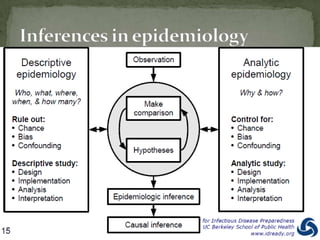
This document discusses hospital outbreak investigations. It defines endemic and epidemic infections in hospitals. Common source and propagated epidemics are described. Steps in investigating outbreaks in hospitals and communities are provided, including forming an investigation team, developing a case definition, conducting epidemiological and laboratory analyses. The goals of outbreak investigations are outlined. Methods for confirming and controlling outbreaks are discussed.