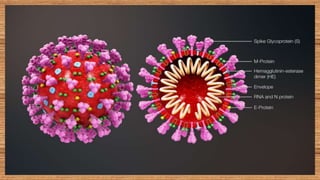
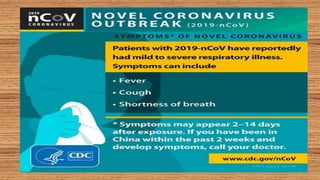
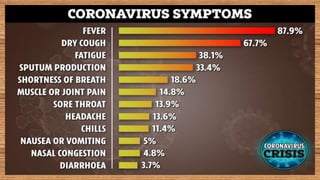
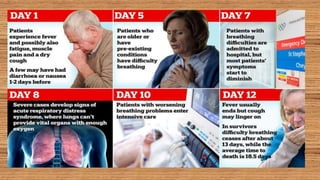
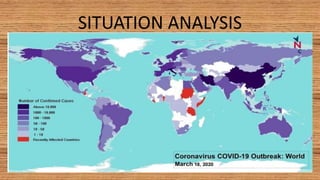
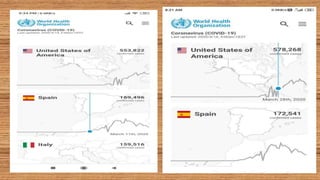
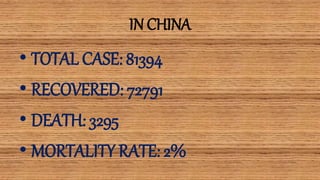
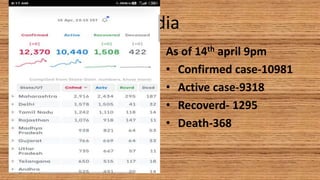
This document provides information on COVID-19 including its structural characteristics, epidemiology, case definition, diagnosis, and care of healthcare workers. It describes COVID-19 as a respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that ranges from mild to severe symptoms. Key points include modes of transmission, risk factors like age and pre-existing conditions, stages of illness, global and local case statistics, and steps healthcare workers should take like using proper PPE, hand hygiene, and isolation protocols to care for patients and protect themselves.