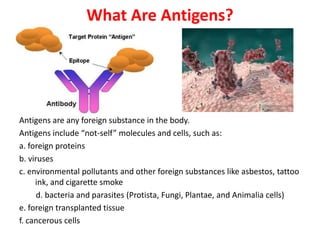
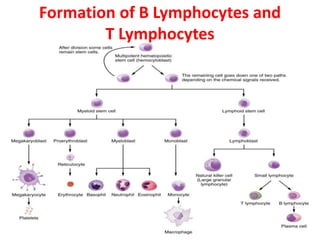
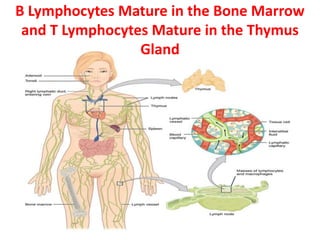
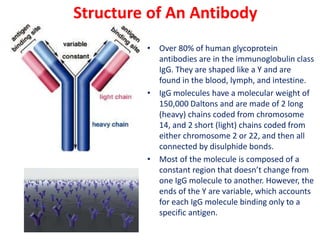
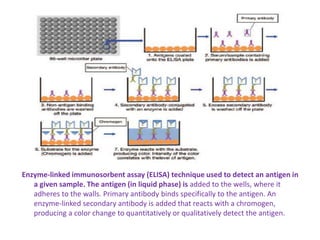
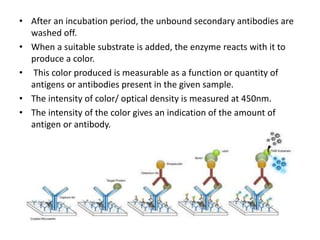
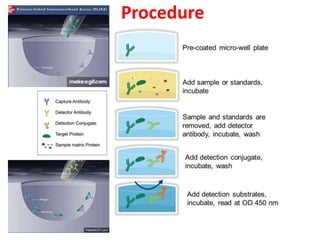
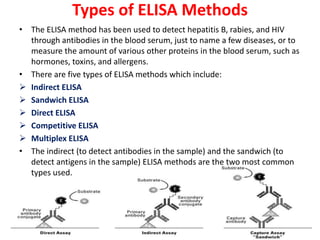
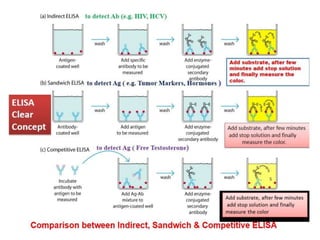
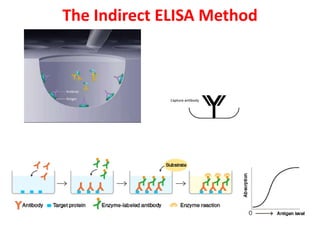
The document describes the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique. ELISA uses the coupling of antigens and antibodies and relies on their specificity and affinity. It can detect proteins, hormones, antibodies, bacteria, or viruses in a sample. The ELISA technique involves coating a microtiter plate with an antigen or antibody, adding the sample and secondary antibody linked to an enzyme, washing unbound components, and detecting the bound complex using a colorimetric or fluorescent substrate. There are different types of ELISA including indirect, sandwich, direct, competitive, and multiplex.