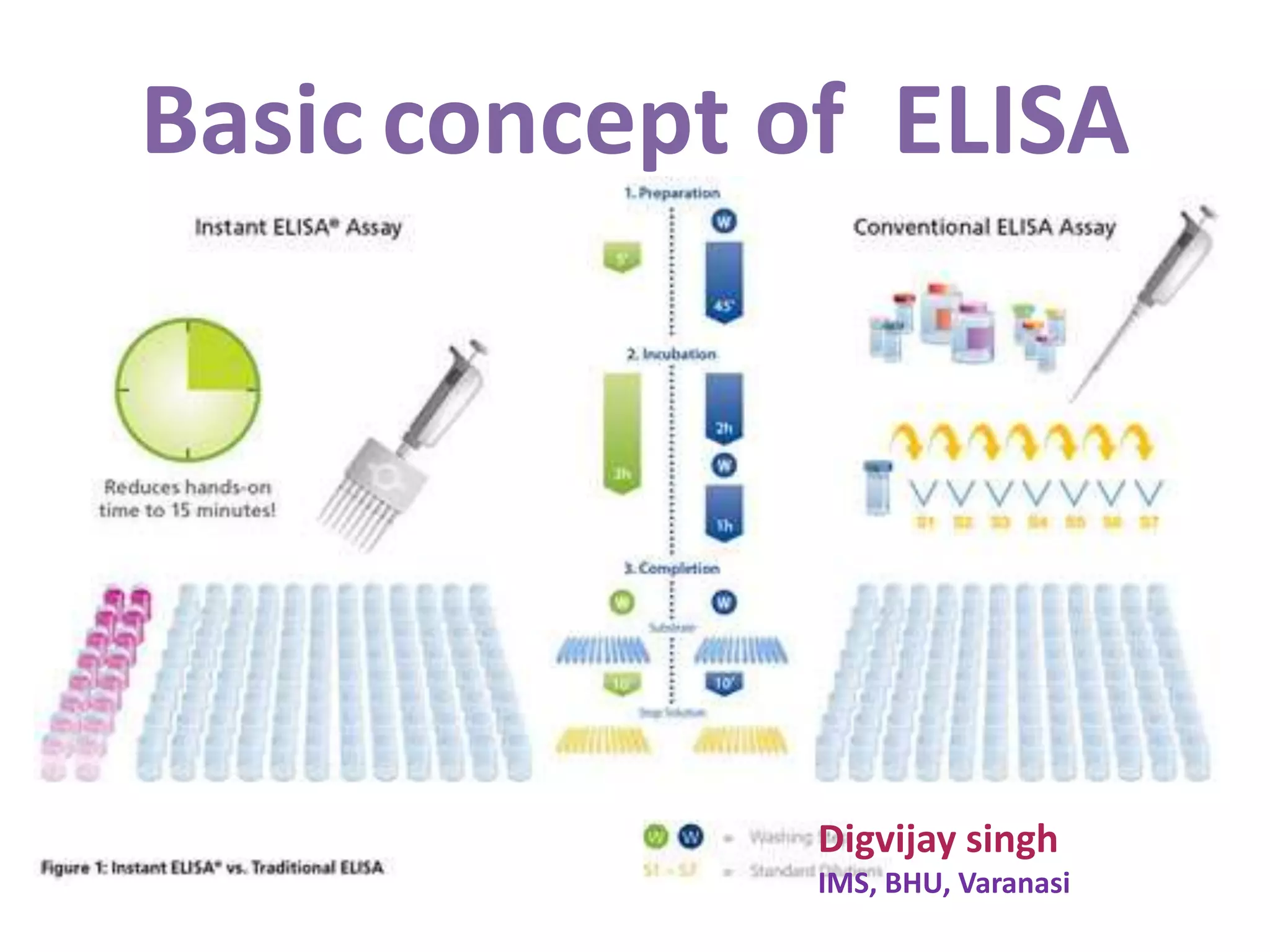
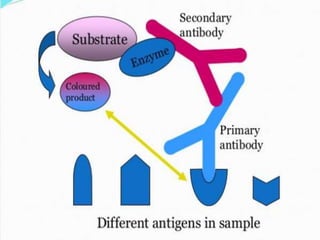
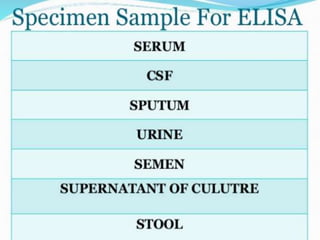
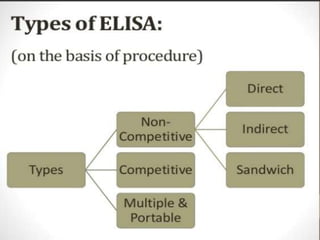
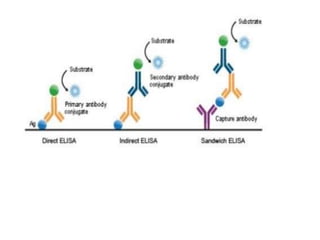
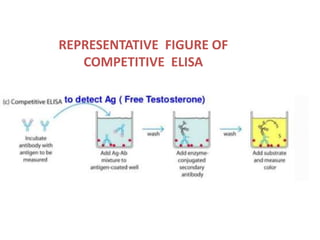
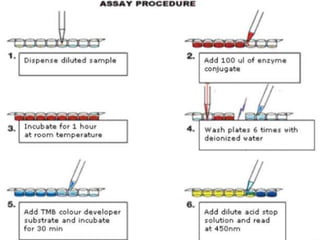
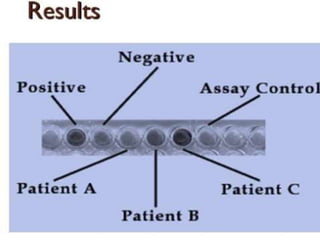
ELISA is an immunological technique used to detect the presence of antigens or antibodies in samples. It works by immobilizing an antigen or antibody on a plate and detecting it using an enzyme-linked antibody or antigen. This allows quantification of the analyte being tested for. ELISA has advantages like being sensitive, specific, easy to perform, and having a long shelf life for reagents. It is commonly used to detect proteins, hormones, drugs, tumor markers, antibodies, and antigens in clinical and research applications.