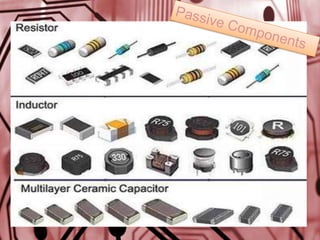
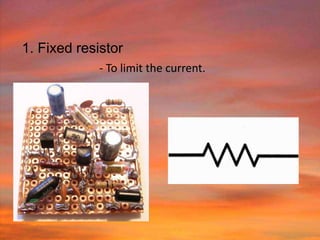
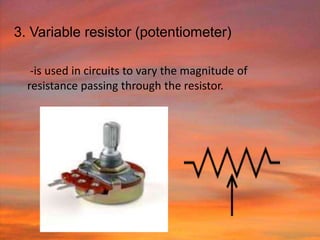
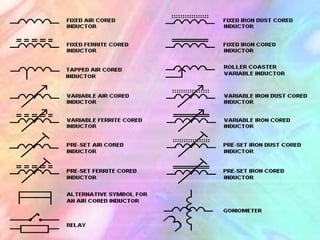
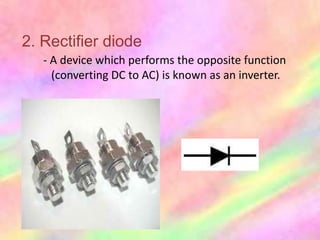
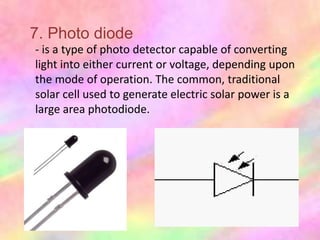
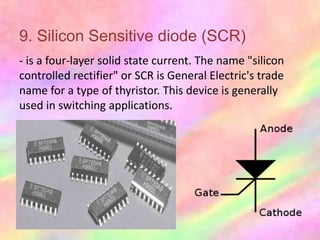
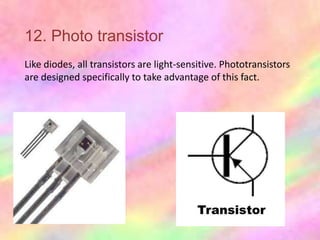
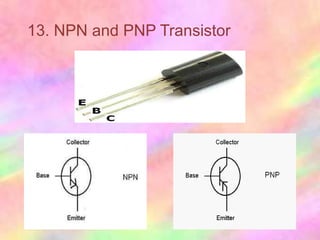
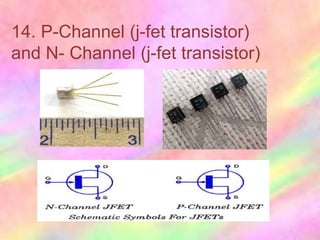
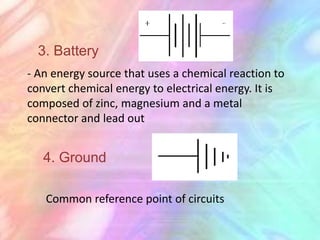
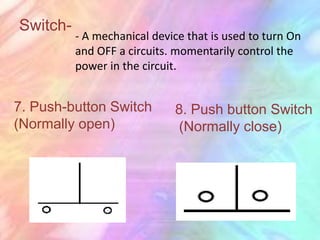
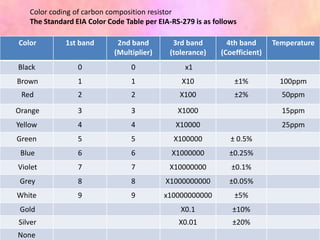
This document discusses the fundamentals of electronics and electronic circuit components. It is composed of passive and active components. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors do not generate voltage but control current, while active components like diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits can generate, amplify, and control current. It then describes various types of resistors, capacitors, inductors, semiconductors, and other common electronic components along with their functions and applications in circuits. Color coding schemes for identifying resistor values and tolerances are also explained.