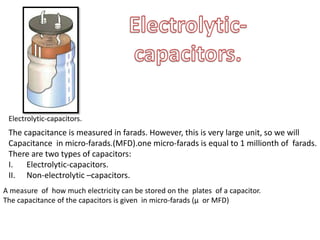
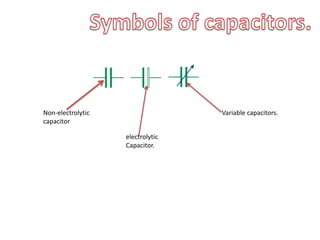
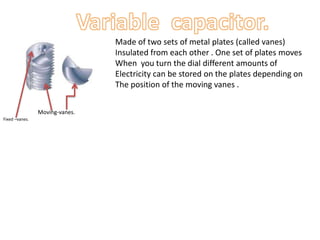
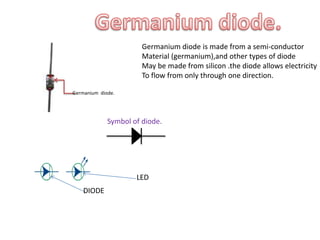
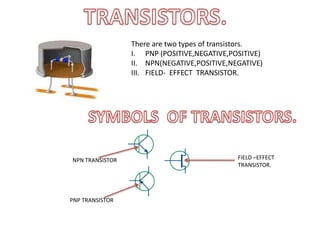
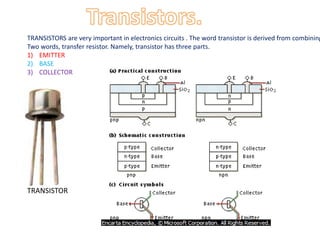
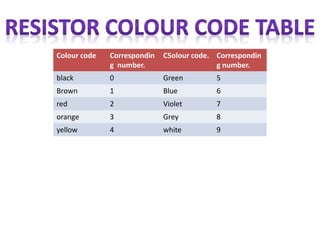
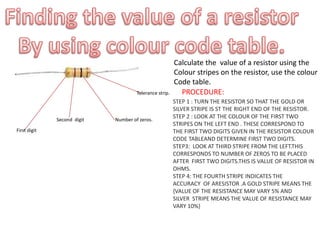
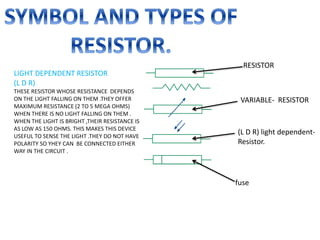
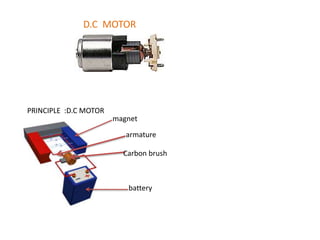
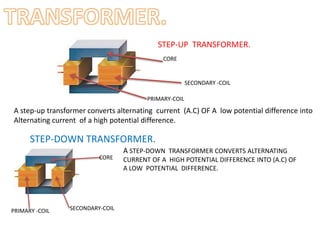
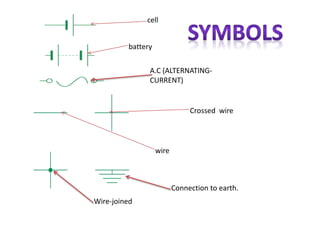
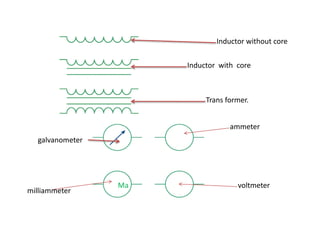
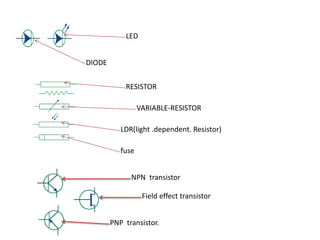
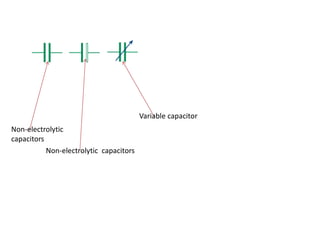
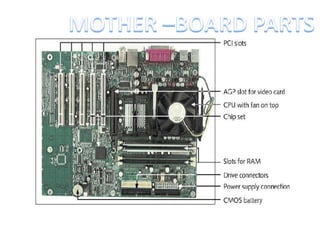
This document provides an index and overview of common electronic components including capacitors, diodes, transistors, resistors, LEDs, DC motors, transformers, and their symbols. It describes the basic functions and properties of electrolytic and non-electrolytic capacitors, diodes, NPN and PNP transistors, resistors including color codes, light dependent resistors, LEDs, DC motors, and transformers. The document also includes illustrations of electronic component symbols.