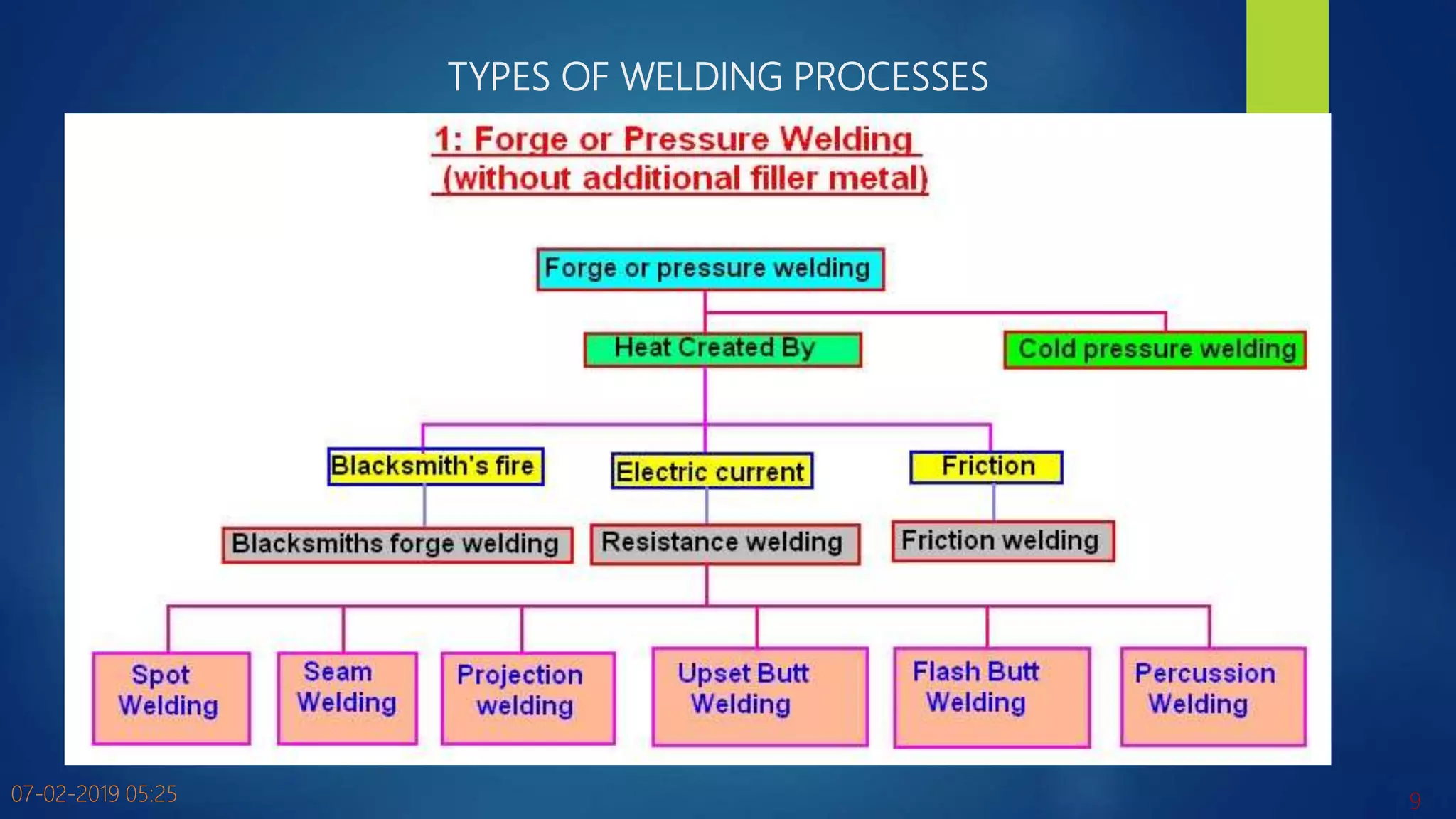
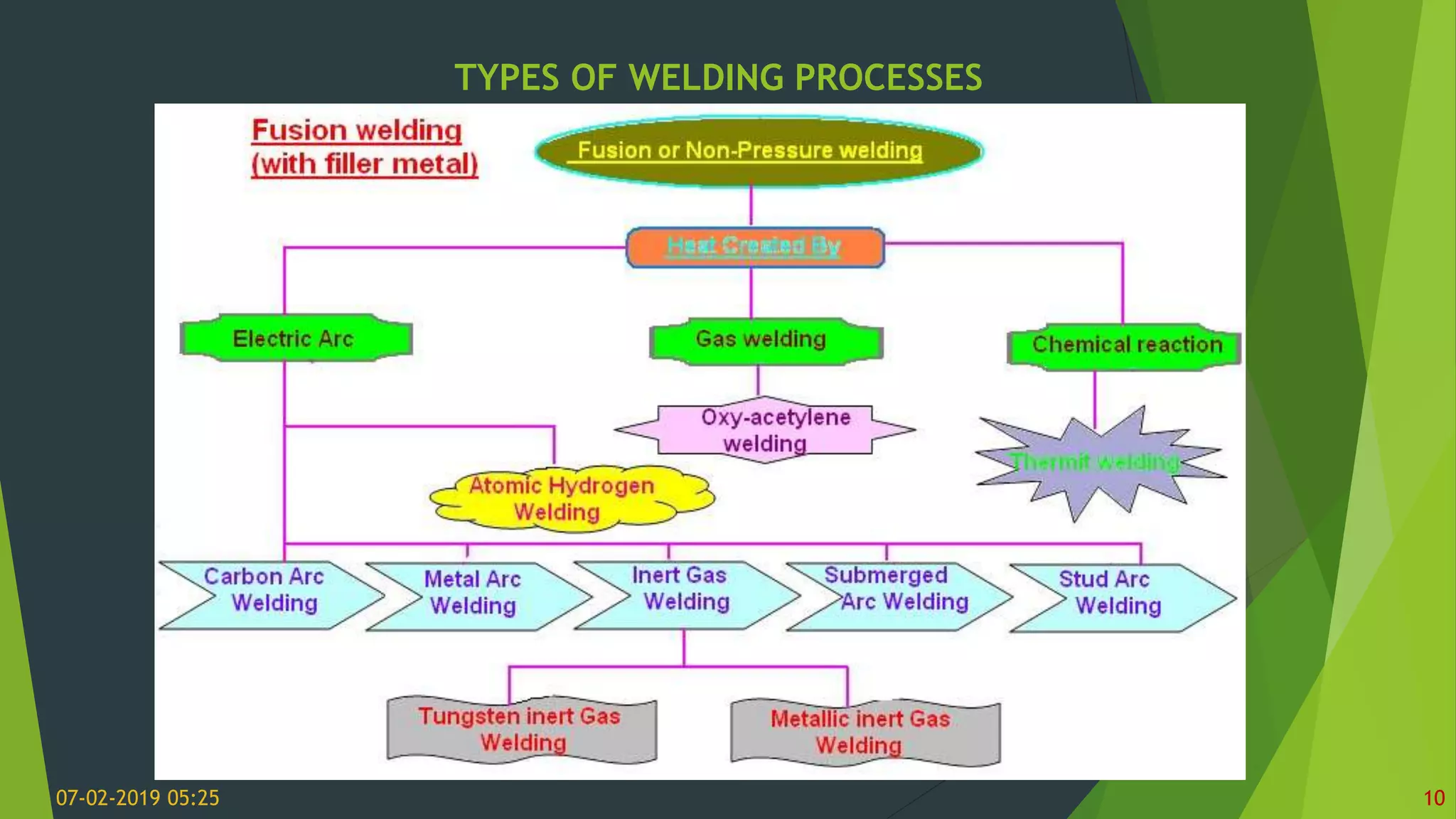
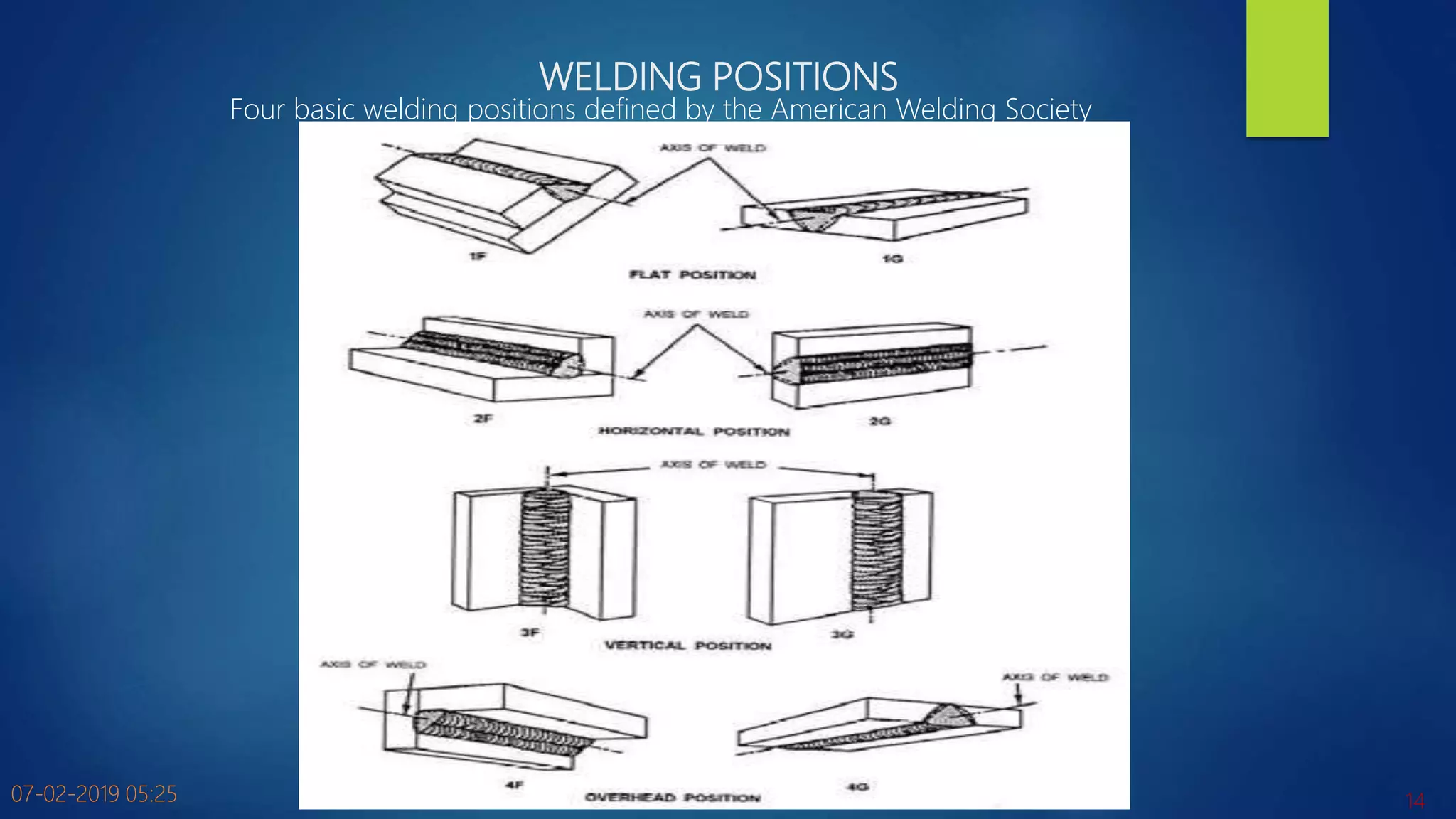
The document discusses various metal joining processes with a focus on welding. It defines welding as the process of joining two metal pieces in a permanent manner using heat, with or without pressure. Various types of welding processes are classified based on whether filler material is used, the type of filler material if used, and whether fusion, plastic deformation, or solid-state joining occurs. Key terms related to welding such as filler metals, fluxes, and welding positions are also defined. The document provides an overview of metal joining processes and fundamentals of welding.