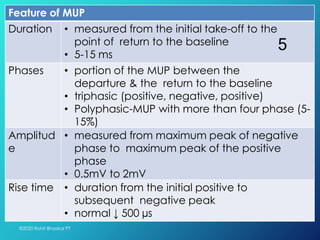
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for recording electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles using an electromyograph. It assesses muscle activation through the detection of action potentials, characterized by various features such as duration, amplitude, and number of phases. EMG analysis can be qualitative or quantitative, and factors affecting muscle unit potentials (MUP) include technical and physiological aspects.