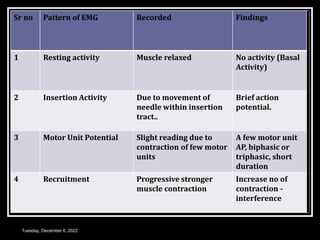
This document discusses electromyography (EMG), which is a technique for recording the electrical activity of muscles. EMG uses either surface electrodes or needle electrodes to detect motor unit potentials from muscles. It describes how EMG is performed at rest and during different levels of muscle contraction. Abnormal EMG patterns are seen in neurogenic diseases, like increased spontaneous activity and larger motor unit amplitudes, and in myopathies, like fibrillations and normal sized motor units. The document outlines the clinical applications of EMG in evaluating neuromuscular diseases and muscle function.