This document provides an introduction to electromagnetic fields. It discusses the electromagnetic model and different approaches to developing scientific theories, including the inductive and deductive approaches. Key topics covered include:
- The differences between circuit theory and field theory in electromagnetic analysis.
- An overview of the basic quantities in electromagnetic models, including electric charges, electric field intensity, magnetic flux density, and others.
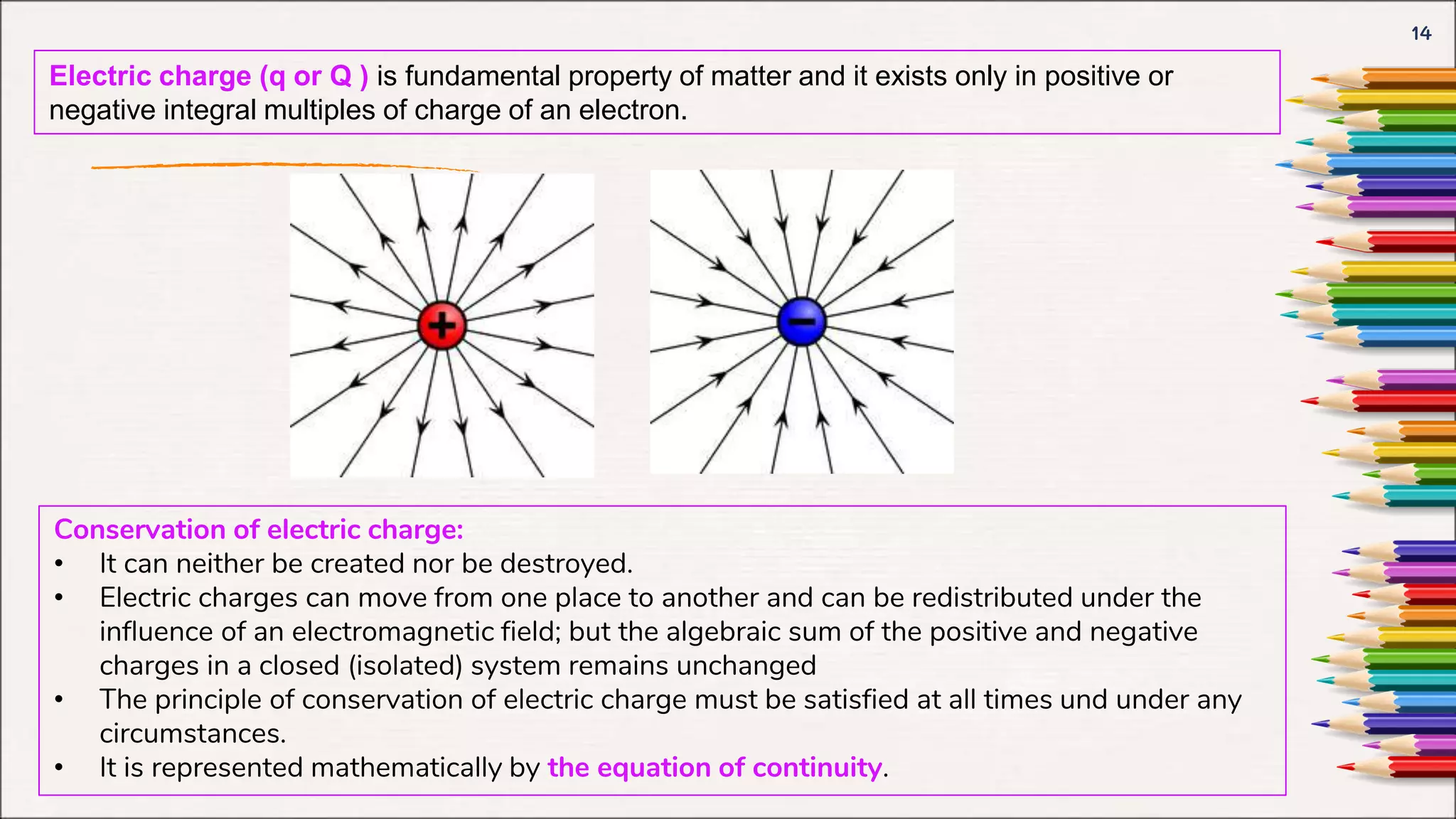
- Definitions of source quantities like electric charge, current density, and field quantities like the electric and magnetic fields.
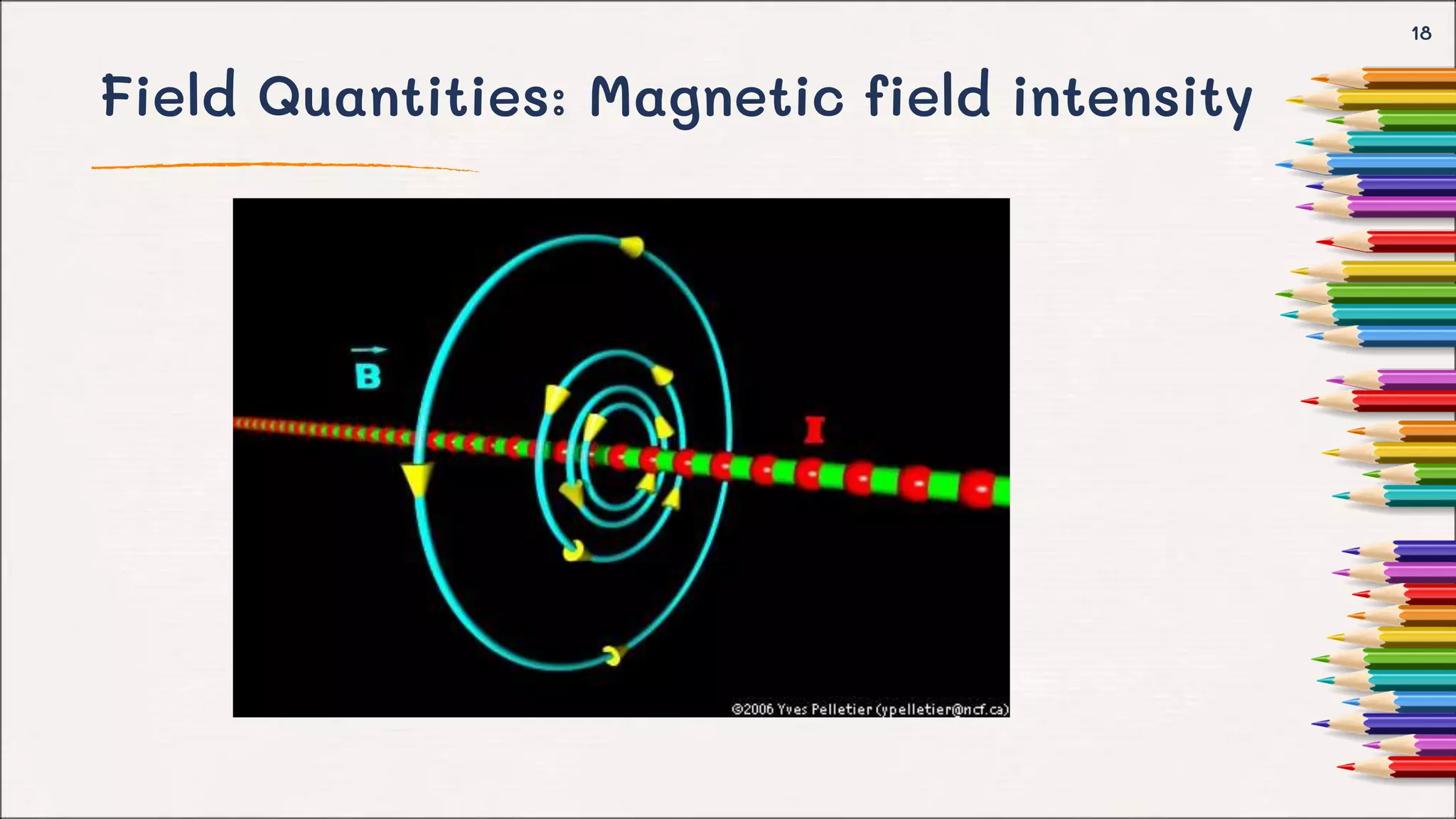
- Explanations of important field quantities like the electric field intensity vector E and magnetic field intensity vector H.