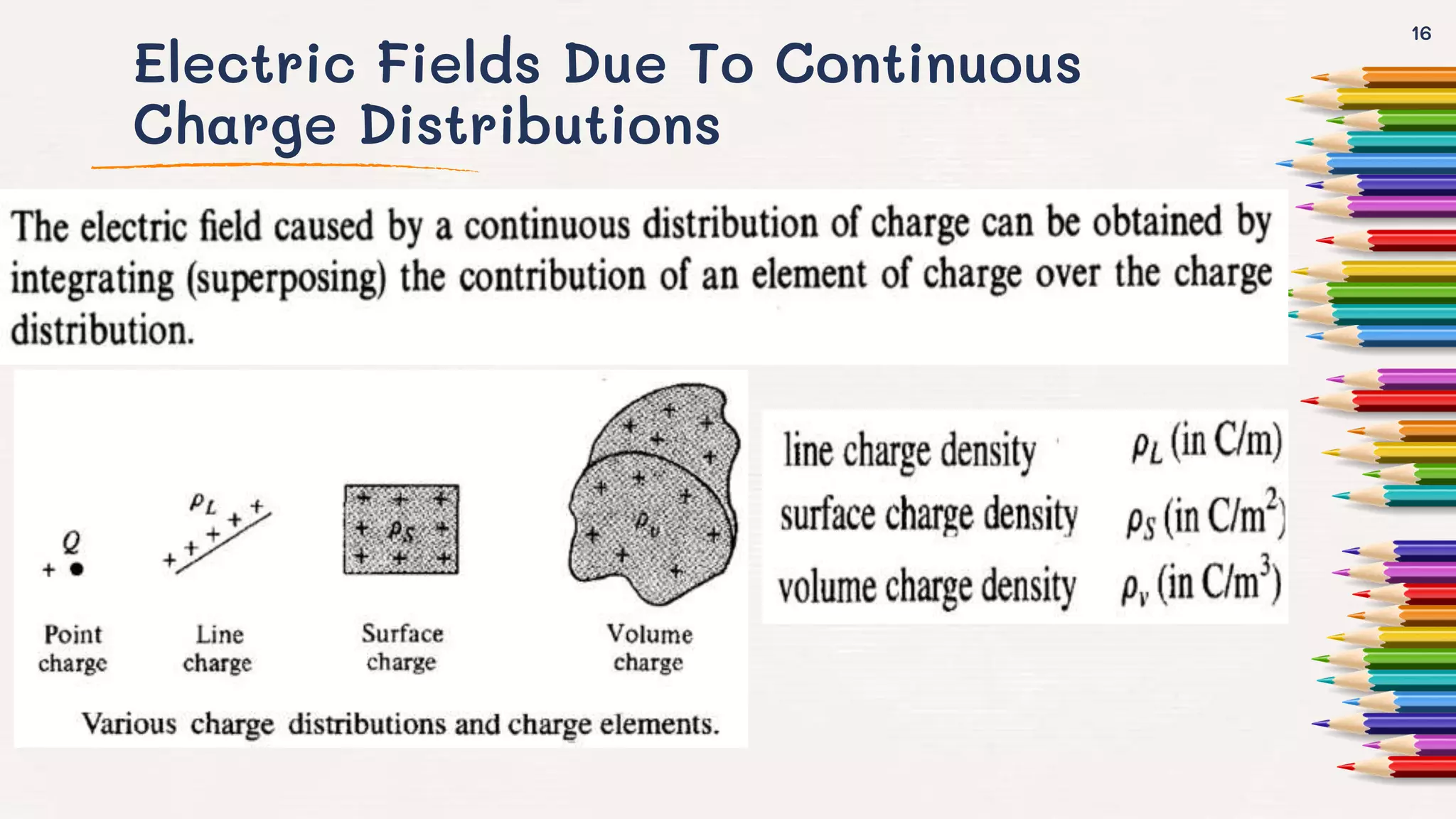
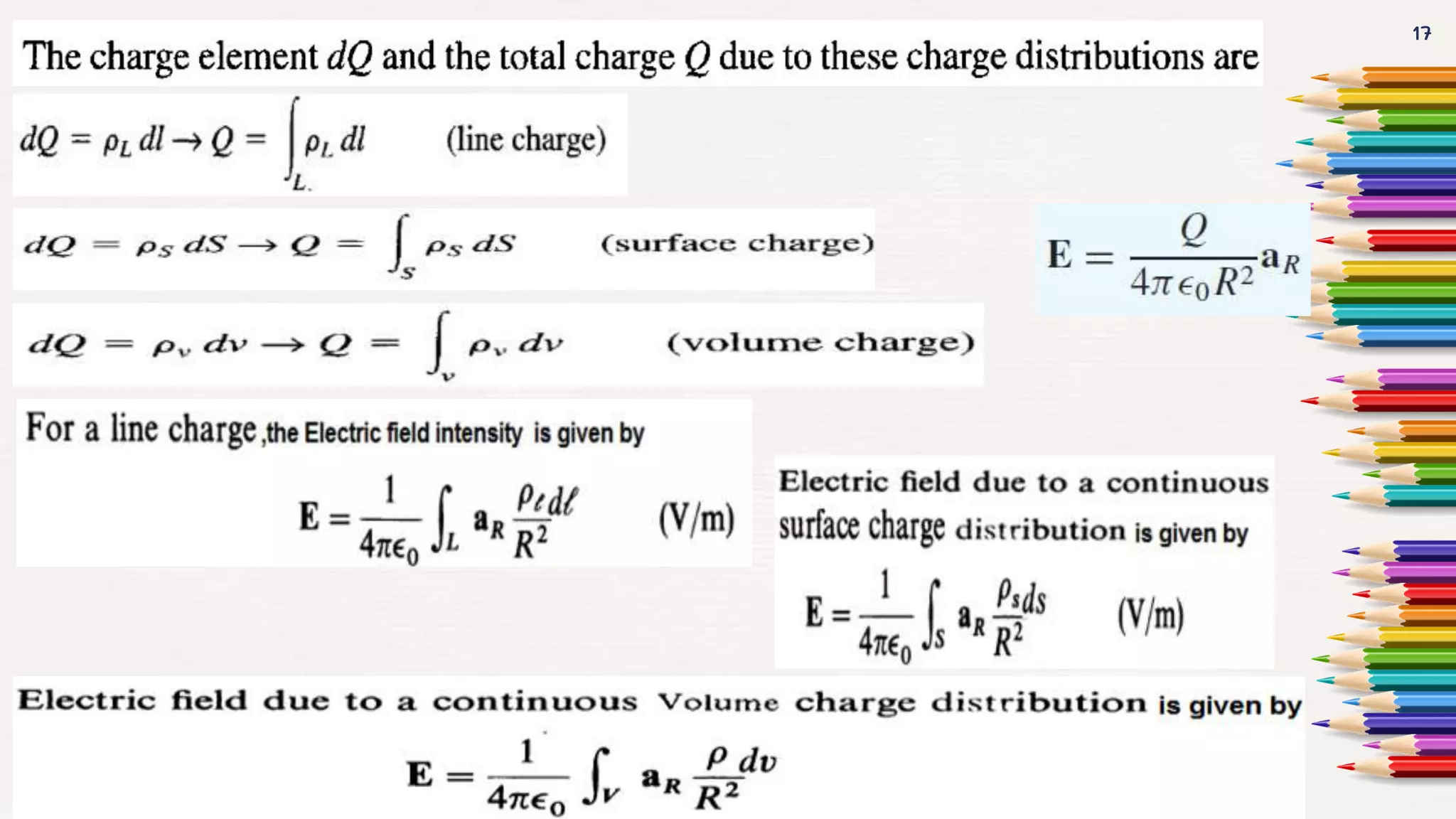
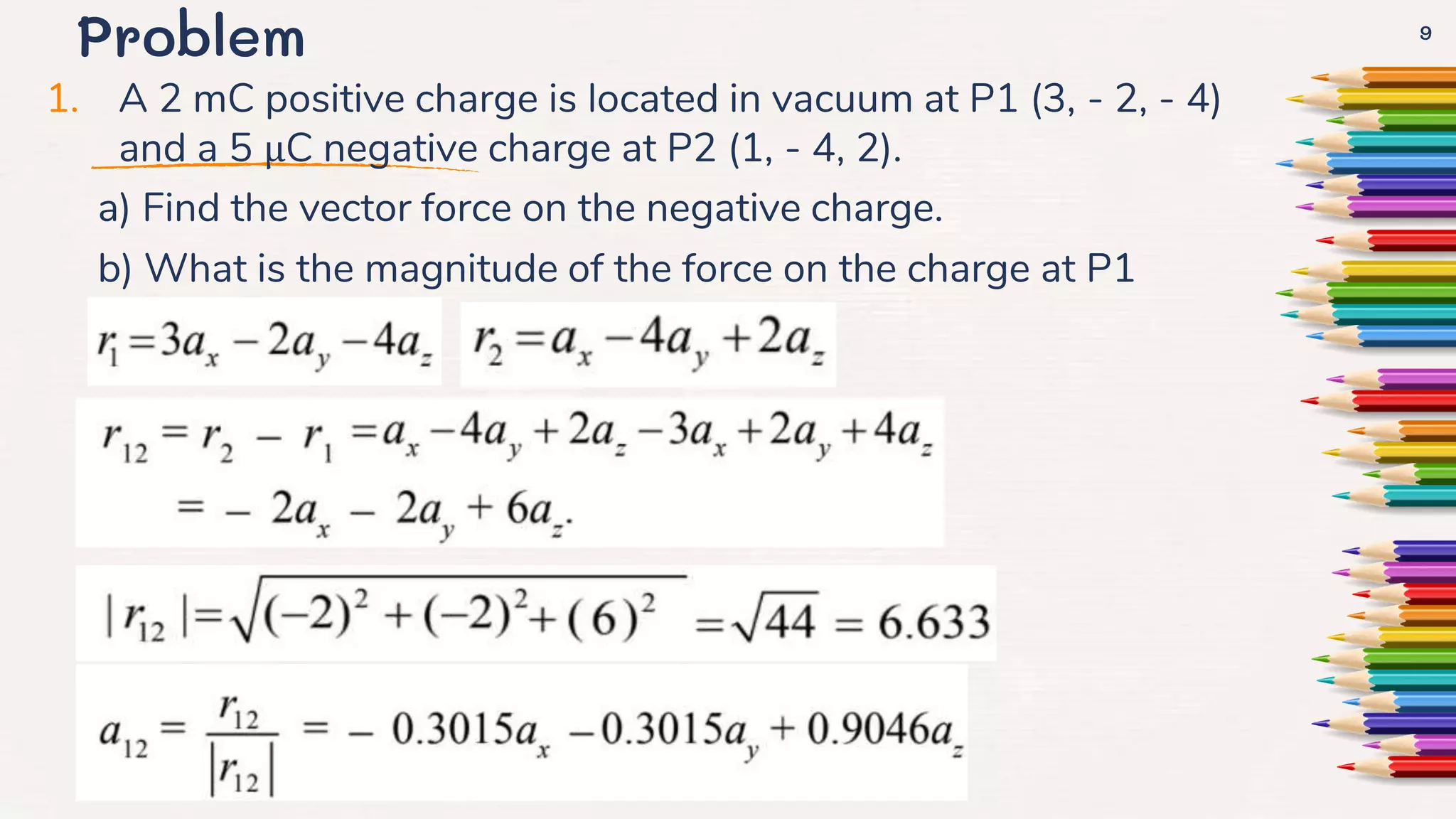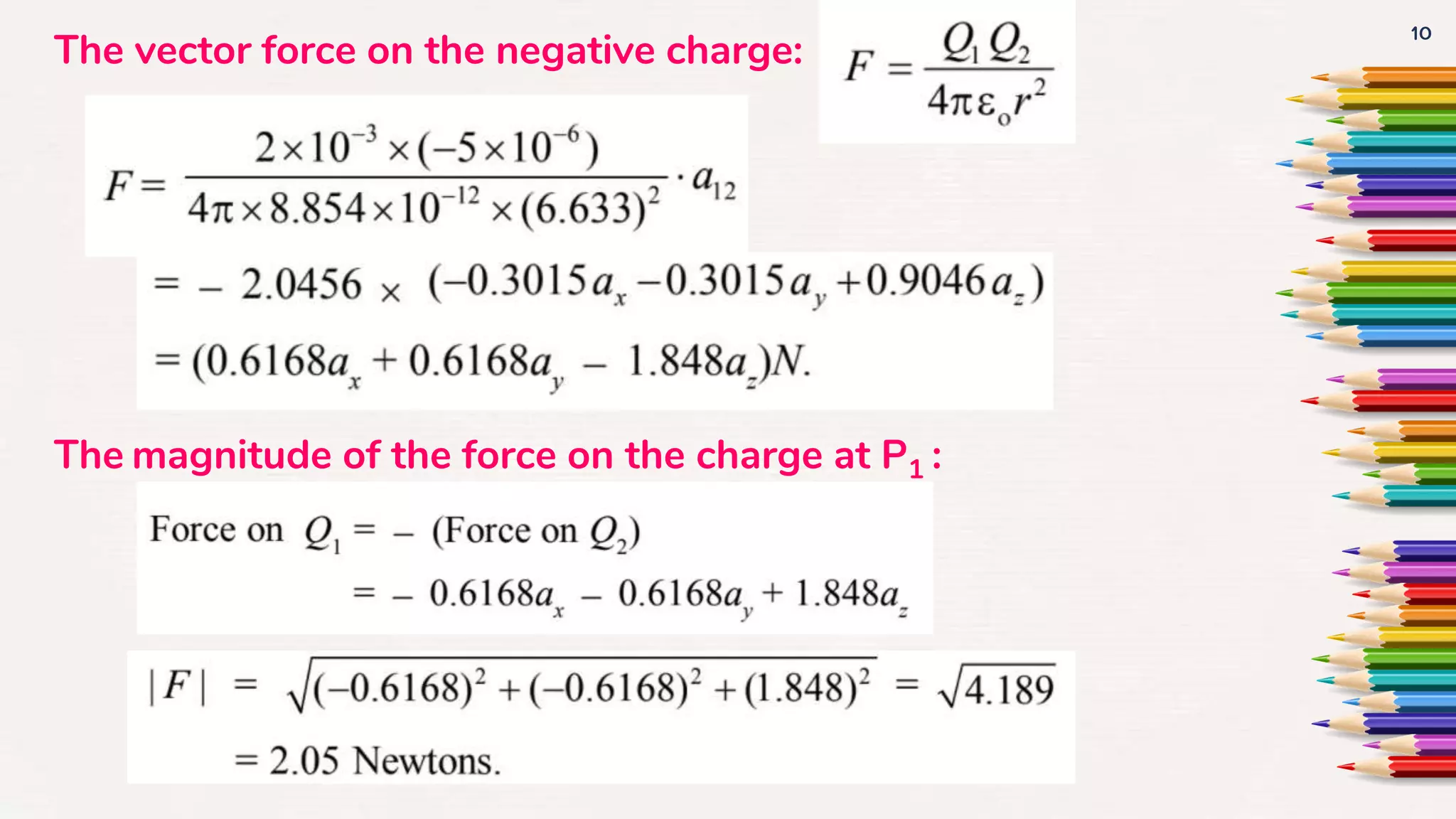This document provides an overview of the topics covered in the unit on electrostatics, including:
- Coulomb's law, electric fields, Gauss's law and applications.
- Electric potential, conductors and dielectrics in static electric fields.
- Boundary conditions and capacitance of parallel, cylindrical, and spherical capacitors.
- Electrostatic energy and Poisson's and Laplace's equations.
- Current density, Ohm's law, electromotive force, and Kirchhoff's laws.
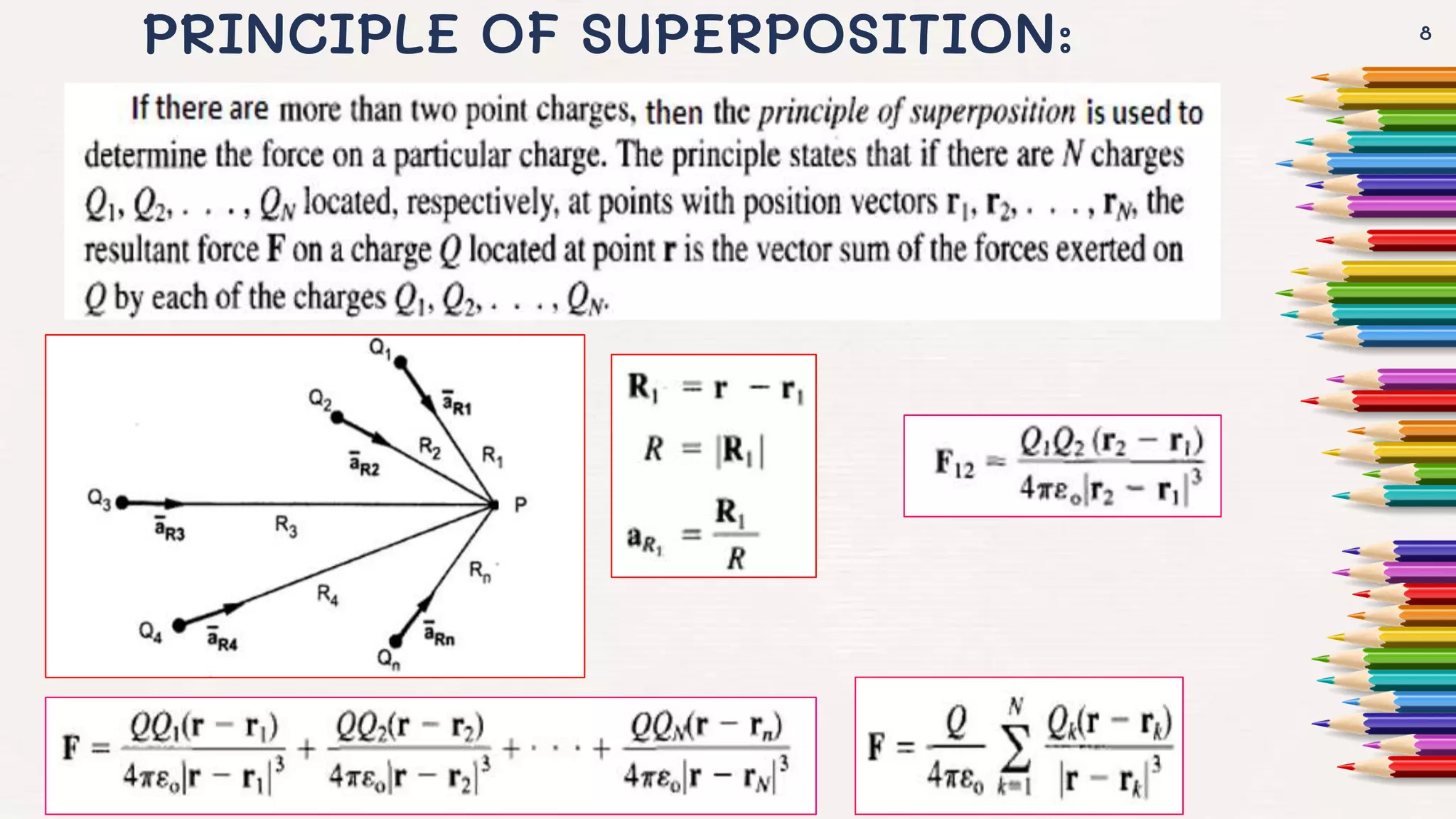
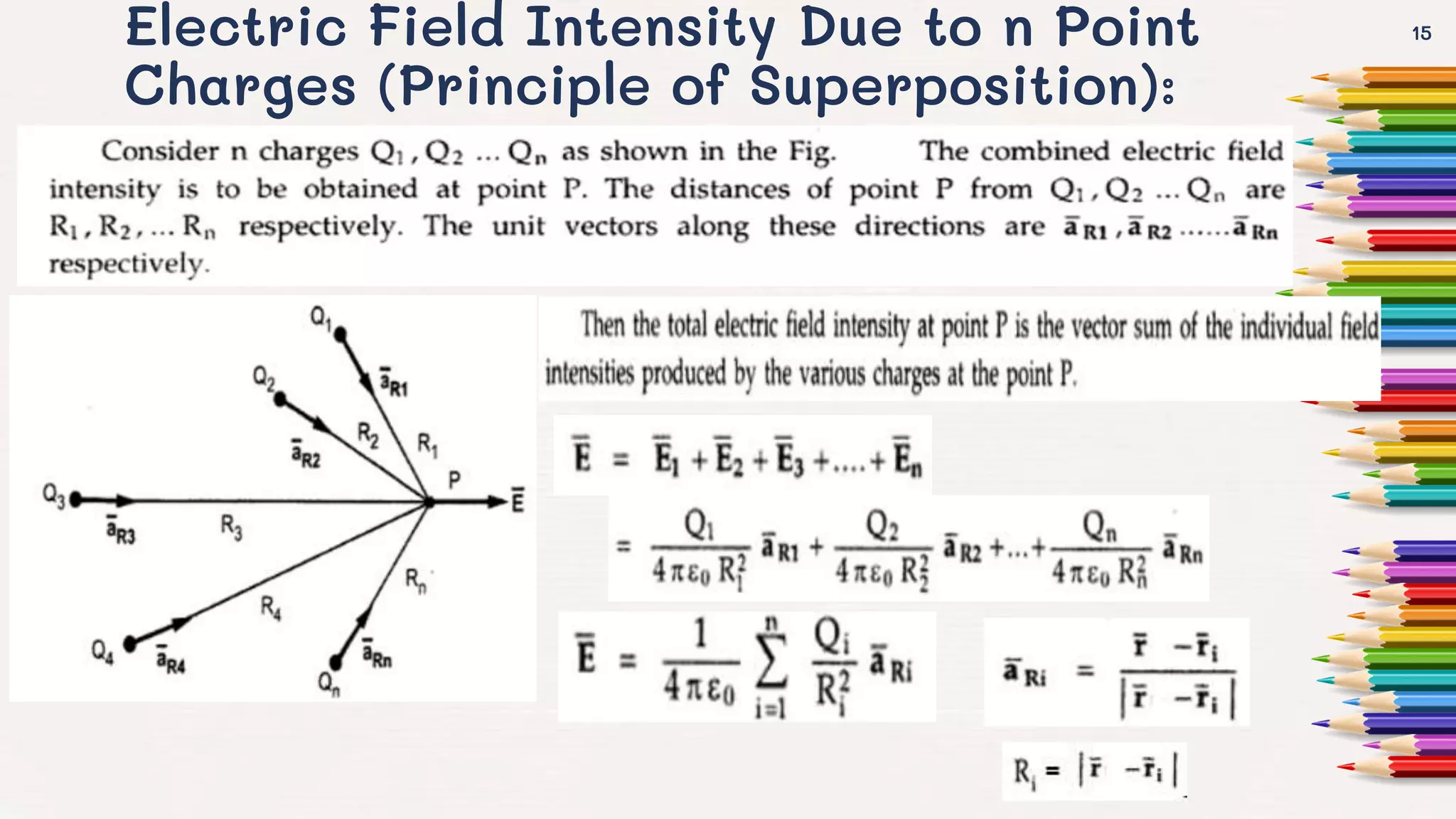
It then goes on to define Coulomb's law, the electric field intensity, and the principle of superposition. Examples of calculating electric force and field due to point charges are also provided